Quiz Maker - Geneva 304
... 104. Which is greater in distance, a parsec or a light year? 105. What is proper motion? 106. The actual motion of a star, or it's space velocity, involves motion in three dimensions; two of the dimensions being related to the tangential velocity or proper motion. What is the third dimension of spac ...
... 104. Which is greater in distance, a parsec or a light year? 105. What is proper motion? 106. The actual motion of a star, or it's space velocity, involves motion in three dimensions; two of the dimensions being related to the tangential velocity or proper motion. What is the third dimension of spac ...
Space Science Unit
... So now what? • The stars are plotted on the diagram according to their surface temperature and absolute magnitude. • Once the stars are placed on the diagram, astronomers have noticed clustering of the plotted stars. • These clusters are grouped together into the various stages of a stars life cycl ...
... So now what? • The stars are plotted on the diagram according to their surface temperature and absolute magnitude. • Once the stars are placed on the diagram, astronomers have noticed clustering of the plotted stars. • These clusters are grouped together into the various stages of a stars life cycl ...
2.1d-f-g Planets in the zodiac, inclined to the ecliptic
... motion, like the wobble of a spinning top toy. The precession occurs over about a 26,000 year cycle, meaning that the North Star changes during this time. In about 11,000 years time, the Pole Star will become Vega, as opposed to Polaris as at present. (Synodic Periods) When viewing a planet from Ear ...
... motion, like the wobble of a spinning top toy. The precession occurs over about a 26,000 year cycle, meaning that the North Star changes during this time. In about 11,000 years time, the Pole Star will become Vega, as opposed to Polaris as at present. (Synodic Periods) When viewing a planet from Ear ...
H-R Diagram Notes
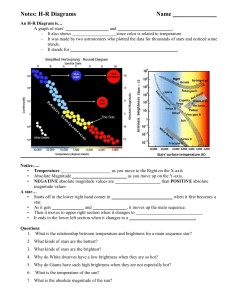
... An H-R Diagram is… A graph of stars’ ___________________ and ________________________. – It also shows ___________________ since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. – It stands for _____________________ ...
... An H-R Diagram is… A graph of stars’ ___________________ and ________________________. – It also shows ___________________ since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. – It stands for _____________________ ...
How long does it take light to travel from the Moon to the Earth, a L
... The reason we experience different seasons is: ____ The Earth’s orbit around the Sun is an ellipse so some"mes we are closer to the Sun (summer in Santa Cruz) and some"mes further from the Sun ( ...
... The reason we experience different seasons is: ____ The Earth’s orbit around the Sun is an ellipse so some"mes we are closer to the Sun (summer in Santa Cruz) and some"mes further from the Sun ( ...
Day Starters
... The Earth “wobbles” like a top and moves through a cycle of “North Stars” every 25,000 years. b. The Earth’s axis is “tilted” c. The Earth’s orbit gets larger and smaller d. The “tilt” of the Earth moves between 22.1º and 24.5º 4. An Astronomical Unit is a. The distance around Earth’s orbit b. One l ...
... The Earth “wobbles” like a top and moves through a cycle of “North Stars” every 25,000 years. b. The Earth’s axis is “tilted” c. The Earth’s orbit gets larger and smaller d. The “tilt” of the Earth moves between 22.1º and 24.5º 4. An Astronomical Unit is a. The distance around Earth’s orbit b. One l ...
Day 1 - Ch 1
... What can we see in the visible sky? • Humans can see about 6000 stars in the night sky (with good vision and a very dark clear night). • Some of these form patterns called asterisms. • These have been grouped into constellations (88 in the current system). Most have old names from mythology; thos ...
... What can we see in the visible sky? • Humans can see about 6000 stars in the night sky (with good vision and a very dark clear night). • Some of these form patterns called asterisms. • These have been grouped into constellations (88 in the current system). Most have old names from mythology; thos ...
Introduction to the sky
... equator. It is a projection of the Earth's equator out to the celestial sphere. The number of degrees that a celestial object is north or south of the celestial equator is called the declination (DEC) It is the analogue of latitude on the sky. The analogue of longitude is called right ascension (RA) ...
... equator. It is a projection of the Earth's equator out to the celestial sphere. The number of degrees that a celestial object is north or south of the celestial equator is called the declination (DEC) It is the analogue of latitude on the sky. The analogue of longitude is called right ascension (RA) ...
Stars_Galaxies_Introduction - Etiwanda E
... – How is energy produced by the sun? – How are sunspots, prominences, and solar flares related? – Why is our sun considered to be an average star? – How does our sun differ from stars in binary systems? ...
... – How is energy produced by the sun? – How are sunspots, prominences, and solar flares related? – Why is our sun considered to be an average star? – How does our sun differ from stars in binary systems? ...
Ancient Egyptian Astronomy
... Aryabhatta - was born in 476 A.D., and is widely recognized as the father of Indian astronomy. When he was about 25 years old, he presented astronomical and mathematical theories in which the Earth was taken to be spinning on its axis and the periods of the planets were given with respect to the Sun ...
... Aryabhatta - was born in 476 A.D., and is widely recognized as the father of Indian astronomy. When he was about 25 years old, he presented astronomical and mathematical theories in which the Earth was taken to be spinning on its axis and the periods of the planets were given with respect to the Sun ...
Chapter 21 Study Guide
... 12. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called an _____________________________. 13. Name one reason why astronomers have built large telescopes on the tops of mountains. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Hubble Space Telesco ...
... 12. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called an _____________________________. 13. Name one reason why astronomers have built large telescopes on the tops of mountains. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Hubble Space Telesco ...
Astronomy Syllabus - Jefferson Forest High School
... Absent 6+ days, you will need to talk with me to establish a date for the work to be completed. ...
... Absent 6+ days, you will need to talk with me to establish a date for the work to be completed. ...
White Dwarf star. Are
... 13.7 billion years. The solar system is 4.6 billion years old. The solar system is not the same age as the entire universe. ...
... 13.7 billion years. The solar system is 4.6 billion years old. The solar system is not the same age as the entire universe. ...
Star Name __Direction ___ Degrees
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
Friday, August 28 - Otterbein University
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
100 X size of Sun - East Penn School District
... stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon fixed distance of ten parsecs (about 32.6 light years) • How is brig ...
... stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon fixed distance of ten parsecs (about 32.6 light years) • How is brig ...
Introducing Astronomy
... “Latitude” is measured as Declination, a positive (above) or negative (below) degree from the Celestial Equator ...
... “Latitude” is measured as Declination, a positive (above) or negative (below) degree from the Celestial Equator ...
Astro history 1
... • With no street lights and no alarm clocks… • The Night sky was a great glowing question… • Who are we? (no answer yet?) • Why are we here (not clear on that one either…?) • Where are we? • Humans have been working on that one for a long time! ...
... • With no street lights and no alarm clocks… • The Night sky was a great glowing question… • Who are we? (no answer yet?) • Why are we here (not clear on that one either…?) • Where are we? • Humans have been working on that one for a long time! ...
astronomy - Mars Rover Celebration
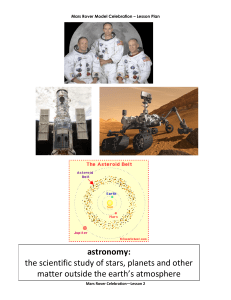
... space)”. Let’s look at some pictures that will help us understand the word “astronomy”. The first picture shows the crew of Apollo 11, the first astronauts to land on the moon. Astronauts are highly trained scientists who study astronomy. The next pictures show some of the scientific tools that astr ...
... space)”. Let’s look at some pictures that will help us understand the word “astronomy”. The first picture shows the crew of Apollo 11, the first astronauts to land on the moon. Astronauts are highly trained scientists who study astronomy. The next pictures show some of the scientific tools that astr ...
Space Part1
... A satellite is any object that orbits another object. The Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth and is kept in orbit by the attraction of the Earth’s gravity and by its motion. An artificial satellite is an object made by, and put into orbit by, humans. Why do you think satellites stay in orbit, ...
... A satellite is any object that orbits another object. The Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth and is kept in orbit by the attraction of the Earth’s gravity and by its motion. An artificial satellite is an object made by, and put into orbit by, humans. Why do you think satellites stay in orbit, ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.