Historical Overview of the Universe
... geometrical schemes to represent celestial motions (eccentrics, i.e. circles with the center displaced from the observer, and epicycles, i.e. small circles whose center is orbiting along a larger circle). Moreover, Hipparchus was himself a careful astronomical observer who also made systematic but c ...
... geometrical schemes to represent celestial motions (eccentrics, i.e. circles with the center displaced from the observer, and epicycles, i.e. small circles whose center is orbiting along a larger circle). Moreover, Hipparchus was himself a careful astronomical observer who also made systematic but c ...
04jan20.ppt
... Greeks did not think the stars could be that far away, and therefore rejected the correct explanation (1)… Thus setting the stage for the long, historical showdown between Earth-centered and Sun-centered systems. ...
... Greeks did not think the stars could be that far away, and therefore rejected the correct explanation (1)… Thus setting the stage for the long, historical showdown between Earth-centered and Sun-centered systems. ...
Superwind - The University of Sydney
... they are driven by minute dust grains, which form in the atmosphere of the star and absorb its light. The star light pushes the dust grains (silicates) away from the star. However, models show that this mechanism does not work well. The dust grains become too hot, and evaporate before they can be pu ...
... they are driven by minute dust grains, which form in the atmosphere of the star and absorb its light. The star light pushes the dust grains (silicates) away from the star. However, models show that this mechanism does not work well. The dust grains become too hot, and evaporate before they can be pu ...
Apparent Motions of Celestial Objects
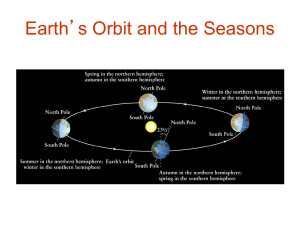
... In the Northern Hemisphere: The Sun rises north of east and sets north of west in the summer. The sun’s altitude at noon is highest during the year. The sun’s “apparent path” across the sky is at its longest (greater than 12 hours). ...
... In the Northern Hemisphere: The Sun rises north of east and sets north of west in the summer. The sun’s altitude at noon is highest during the year. The sun’s “apparent path” across the sky is at its longest (greater than 12 hours). ...
word - IMCCE
... and to the motion of the Earth. Indeed, all the distances in the solar system may be deduced from only one of them thanks to the laws from Kepler. The perturbations generated by the Moon and other planets on the Earth, are known only through a dynamic modeling of the solar system. One will avoid the ...
... and to the motion of the Earth. Indeed, all the distances in the solar system may be deduced from only one of them thanks to the laws from Kepler. The perturbations generated by the Moon and other planets on the Earth, are known only through a dynamic modeling of the solar system. One will avoid the ...
Constellations, Star Names, and Magnitudes
... figures along the ecliptic. D. They are 13 well defined sky regions along the ecliptic. ...
... figures along the ecliptic. D. They are 13 well defined sky regions along the ecliptic. ...
Shapes in the Sky
... class. What do you see? Possibly even use it outside beneath the "real" sky. The circle is the horizon and the center of the circle is the point overhead. Whatever direction you are facing, put that direction on the chart at the bottom, closest to the ground. 4. Discuss the idea of something being “ ...
... class. What do you see? Possibly even use it outside beneath the "real" sky. The circle is the horizon and the center of the circle is the point overhead. Whatever direction you are facing, put that direction on the chart at the bottom, closest to the ground. 4. Discuss the idea of something being “ ...
Homework Problems for Quiz 1 – AY 5 – Spring 2013
... a) What are the relative distances of the two stars? Star A has twice the parallax angle so is at 1/2 the distance of Star B b) what are the relative brightnesses of the two stars? Based on their relative luminosities, Star A would be twice as bright as Star B at the same distance. But, Star A is 1/ ...
... a) What are the relative distances of the two stars? Star A has twice the parallax angle so is at 1/2 the distance of Star B b) what are the relative brightnesses of the two stars? Based on their relative luminosities, Star A would be twice as bright as Star B at the same distance. But, Star A is 1/ ...
PS 224: Astronomy Fall 2014 Midterm (October 16, 2014)
... I would not believe this claim because this is a “very old” star with rare-earth elements. Such heavy elements are only produced in supernovae, so the earliest stars probably do not have those elements. So it is unlikely that a “very old” star has rare earth elements. To test this I would conduct sp ...
... I would not believe this claim because this is a “very old” star with rare-earth elements. Such heavy elements are only produced in supernovae, so the earliest stars probably do not have those elements. So it is unlikely that a “very old” star has rare earth elements. To test this I would conduct sp ...
Assignment 1 - utoledo.edu
... and has taken to going out into an open field and staring at the stars for hours, while slowly chanting the names of the 92 stable elements. But he gets very easily dizzy from watching the slow turning of the stars in the sky. Where in the sky would you advise him to look to see stars that are not ...
... and has taken to going out into an open field and staring at the stars for hours, while slowly chanting the names of the 92 stable elements. But he gets very easily dizzy from watching the slow turning of the stars in the sky. Where in the sky would you advise him to look to see stars that are not ...
CONSTELLATIONS
... of the night. It also changes every day of the year as Earth goes around the Sun. We start this numbering system at the Vernal Equinox i.e. the point in the sky where the Sun was at the time of the Spring Equinox. From that specific point on the Celestial Equator, they simply numbered the "hours" 0, ...
... of the night. It also changes every day of the year as Earth goes around the Sun. We start this numbering system at the Vernal Equinox i.e. the point in the sky where the Sun was at the time of the Spring Equinox. From that specific point on the Celestial Equator, they simply numbered the "hours" 0, ...
Exploring the Universe
... an H-R diagram where most stars spend 90% of their life. i. A diagonal band running from the bright, hot stars on the upper left to the dim, cool stars on the lower right ii. Example: The Sun lies in the main ...
... an H-R diagram where most stars spend 90% of their life. i. A diagonal band running from the bright, hot stars on the upper left to the dim, cool stars on the lower right ii. Example: The Sun lies in the main ...
Minerals
... A full moon occurs with the lineup sun – Earth – moon; the same lineup is required for a lunar eclipse. A new moon occurs with the lineup sun – moon – Earth; the same lineup is required for a solar eclipse. A full cycle of moon phases takes about a month; therefore there is about a week between each ...
... A full moon occurs with the lineup sun – Earth – moon; the same lineup is required for a lunar eclipse. A new moon occurs with the lineup sun – moon – Earth; the same lineup is required for a solar eclipse. A full cycle of moon phases takes about a month; therefore there is about a week between each ...
Consulting the Planetary Expert: You
... and predictable. They learned to tell the time of day, the date, the weather, their position and the occurrence of tides and eclipses. Many other events were thought to depend on the skies and astrologers were often employed to read the sky. This type of prediction has nothing to do with science how ...
... and predictable. They learned to tell the time of day, the date, the weather, their position and the occurrence of tides and eclipses. Many other events were thought to depend on the skies and astrologers were often employed to read the sky. This type of prediction has nothing to do with science how ...
here. - SUNY Oswego
... their apparent brightness as seen from Earth varies. Their intrinsic brightness is around 0.75 and their period is usually less than a day. They’re commonly found in globular clusters, though the stars involved in out research were field stars, and are used as standard candles which are astronomical ...
... their apparent brightness as seen from Earth varies. Their intrinsic brightness is around 0.75 and their period is usually less than a day. They’re commonly found in globular clusters, though the stars involved in out research were field stars, and are used as standard candles which are astronomical ...
Nov - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... Aries and continue it until you reach a faint parallelogram of stars that makes up the whale’s head. Brian provided the meeting with handouts to cover this talk and in this he mentioned a number of objects of interest to be found in the region. Mira otherwise known as Omicron Ceti, was one of the fi ...
... Aries and continue it until you reach a faint parallelogram of stars that makes up the whale’s head. Brian provided the meeting with handouts to cover this talk and in this he mentioned a number of objects of interest to be found in the region. Mira otherwise known as Omicron Ceti, was one of the fi ...
Bad Astronomy
... earth on the moon. Not true! Lunar eclipse happens when the moon passes behind the earth so the earth blocks the sun rays from striking the moon. ...
... earth on the moon. Not true! Lunar eclipse happens when the moon passes behind the earth so the earth blocks the sun rays from striking the moon. ...
Word version
... time of the flood helped the Egyptians regulate their resources, so they learned to watch the sky for a pattern that would repeat every year. Egyptian astronomers noticed that the bright star Sirius, in Orion’s hunting dog, made its first appearance just before sunrise at the same time each year—ju ...
... time of the flood helped the Egyptians regulate their resources, so they learned to watch the sky for a pattern that would repeat every year. Egyptian astronomers noticed that the bright star Sirius, in Orion’s hunting dog, made its first appearance just before sunrise at the same time each year—ju ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.