Name: Period : ______ The Universe – Life and Death of a Star How
... 22. What does all that extra heat cause the Sun-like star to do? 23. When a Sun-like star begins to eject its outer layers of gas in “cosmic burps” it will send shells of gas illuminated by the hot central star and that will cause the __________________ nebula phenomenon. 24. When a star cools, it c ...
... 22. What does all that extra heat cause the Sun-like star to do? 23. When a Sun-like star begins to eject its outer layers of gas in “cosmic burps” it will send shells of gas illuminated by the hot central star and that will cause the __________________ nebula phenomenon. 24. When a star cools, it c ...
Star in a Box Worksheet - Beginning
... complete, you can click on “Data Table” (upper right) to see the final values for each stage in the lifecycle. 1. Describe how the Sun changes over its lifetime. 2. When will the Sun be at its brightest? 3. When will the Sun be at its hottest? 4. In which stage of its life does the Sun spend the lon ...
... complete, you can click on “Data Table” (upper right) to see the final values for each stage in the lifecycle. 1. Describe how the Sun changes over its lifetime. 2. When will the Sun be at its brightest? 3. When will the Sun be at its hottest? 4. In which stage of its life does the Sun spend the lon ...
Section 26.2 - CPO Science
... 26.2 Phases of the Moon The lighted side of the Moon faces away from Earth. How the moon appears to Earth dwellers at different positions in its orbit is shown below: ...
... 26.2 Phases of the Moon The lighted side of the Moon faces away from Earth. How the moon appears to Earth dwellers at different positions in its orbit is shown below: ...
Mirrored Image Sep06.pub - High Desert Astronomical Society
... in the direction in time for most to see it. It most likely hit the ground somewhere north of Barstow! There were so many objects to look at, one hardly knew where to start. Neptune through Dave Meyer's Celestron 14” scope was a beautiful turquoise dot, very pretty. There were four 10” dobs, Dave Fl ...
... in the direction in time for most to see it. It most likely hit the ground somewhere north of Barstow! There were so many objects to look at, one hardly knew where to start. Neptune through Dave Meyer's Celestron 14” scope was a beautiful turquoise dot, very pretty. There were four 10” dobs, Dave Fl ...
Star Maps and Constellations
... •However, in some cases (n.b. Ursa Major), Bayer named the stars not in order of brightness, but in order of location. ...
... •However, in some cases (n.b. Ursa Major), Bayer named the stars not in order of brightness, but in order of location. ...
Lecture 19 The Milky Way Galaxy
... • Romans called it ‘via lactia’ – milky road, or milky way • But what is it? • By the mid-18th century, astronomers new that it was made up of an enormous number of distant stars ...
... • Romans called it ‘via lactia’ – milky road, or milky way • But what is it? • By the mid-18th century, astronomers new that it was made up of an enormous number of distant stars ...
astronomy notes2013
... How we explained these motions: Assumptions of Early Models II. Models of the Universe A. Geocentric = _____________________________ 1. The Planets The usual motion of planets as they "wandered" on the celestial sphere was eastward against the background stars. This is called ______________________ ...
... How we explained these motions: Assumptions of Early Models II. Models of the Universe A. Geocentric = _____________________________ 1. The Planets The usual motion of planets as they "wandered" on the celestial sphere was eastward against the background stars. This is called ______________________ ...
North Celestial Pole
... the Earth's North Pole. • The South Celestial Pole is directly above the Earth's South Pole. • The star Polaris, in the constellation Ursa Minor, is located very close to the North Celestial Pole. • The celestial equator is directly above the Earth's equator. • Right ascention = Longitude (East – We ...
... the Earth's North Pole. • The South Celestial Pole is directly above the Earth's South Pole. • The star Polaris, in the constellation Ursa Minor, is located very close to the North Celestial Pole. • The celestial equator is directly above the Earth's equator. • Right ascention = Longitude (East – We ...
Unit 1 Test
... ____ 69. Frequency involves the number of pulses of energy past a certain point in a specific amount of time. ____ 70. A geocentric universe places the Earth at the center. ____ 71. The speed of light is also known as the cosmological constant. ____ 72. We can obviously see in the visible portion of ...
... ____ 69. Frequency involves the number of pulses of energy past a certain point in a specific amount of time. ____ 70. A geocentric universe places the Earth at the center. ____ 71. The speed of light is also known as the cosmological constant. ____ 72. We can obviously see in the visible portion of ...
The Celestial Sphere
... Earth. The celestial equator lies in the same plane as does the Earth's equator. An astronomer can only see half the sky at a time, that is, only half the sky is above the horizon at any time. But the sky keeps moving as the earth rotates. Just as the sun rises and sets every day, so does every star ...
... Earth. The celestial equator lies in the same plane as does the Earth's equator. An astronomer can only see half the sky at a time, that is, only half the sky is above the horizon at any time. But the sky keeps moving as the earth rotates. Just as the sun rises and sets every day, so does every star ...
Activities, In the Footsteps of Galileo
... be seen with the unaided eye, Galileo wrote: “Now those spots which are fairly dark and rather large are plain to everyone and have been seen throughout the ages; these I shall call the ‘large’ or ‘ancient’ spots, distinguishing them from others all over the lunar surface, and especially the lighter ...
... be seen with the unaided eye, Galileo wrote: “Now those spots which are fairly dark and rather large are plain to everyone and have been seen throughout the ages; these I shall call the ‘large’ or ‘ancient’ spots, distinguishing them from others all over the lunar surface, and especially the lighter ...
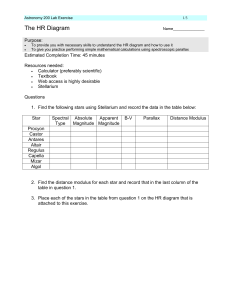
labex7
... Castor Antares Altair Regulus Capella Mizar Algol 5. Find the mass of each of the stars by using the Mass-Luminosity Relation (See online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the dista ...
... Castor Antares Altair Regulus Capella Mizar Algol 5. Find the mass of each of the stars by using the Mass-Luminosity Relation (See online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the dista ...
Slide 1
... Highlands = light colored areas (almost as high as Mt. Everest!) Mare (Maria, pl.) = dark smooth areas (ancient beds of lava) Rilles are valleys or trenches. Regolith = soil-like layer ...
... Highlands = light colored areas (almost as high as Mt. Everest!) Mare (Maria, pl.) = dark smooth areas (ancient beds of lava) Rilles are valleys or trenches. Regolith = soil-like layer ...
File
... Measuring the motion of the Moon around the Earth relative to the Sun leads us to what is called the synodic (pronounced si-nod-ik) period. The synodic period is the time required for a body within the solar system, such as a planet, the Moon, or an artificial Earth satellite, to return to the same ...
... Measuring the motion of the Moon around the Earth relative to the Sun leads us to what is called the synodic (pronounced si-nod-ik) period. The synodic period is the time required for a body within the solar system, such as a planet, the Moon, or an artificial Earth satellite, to return to the same ...
Phobos
... One of the largest stars known but W.Herschel did not know that when he discovered its variability in 1795. It is a semi-regular, reddish, looking naked-eye star that shows slow brightness changes. There are 3 stars that show the combined light some 380 light years away. It is about mag. 3.3 at pres ...
... One of the largest stars known but W.Herschel did not know that when he discovered its variability in 1795. It is a semi-regular, reddish, looking naked-eye star that shows slow brightness changes. There are 3 stars that show the combined light some 380 light years away. It is about mag. 3.3 at pres ...
Welcome to Astro 10! - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... • Average distance between the Earth and Sun is 150,000,000 km = 1.5 x 108 km = 1.5 x 1011 m. This is known as an “Astronomical Unit.” Stars and galaxies are much, much further away. • Convenient way to give distance: use the light travel time • The speed of light in a vacuum is constant and the lar ...
... • Average distance between the Earth and Sun is 150,000,000 km = 1.5 x 108 km = 1.5 x 1011 m. This is known as an “Astronomical Unit.” Stars and galaxies are much, much further away. • Convenient way to give distance: use the light travel time • The speed of light in a vacuum is constant and the lar ...
Astronomy Merit Badge Workshop
... same drawing, repeat this at the same time each day for the next three days, showing the height and shape of the moon for each observation. Note the date and time of your observations next to each sketch of the moon. If the sky is overcast and the moon is not visible, either extend the observations ...
... same drawing, repeat this at the same time each day for the next three days, showing the height and shape of the moon for each observation. Note the date and time of your observations next to each sketch of the moon. If the sky is overcast and the moon is not visible, either extend the observations ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.