![Cartoon History [Part I]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010027059_1-be202f9d96a8b0acdc9c259e604c080f-300x300.png)
Cartoon History [Part I]
... The first important attack on Galileo began in 1610, when he announced that his telescope had revealed the moons of the planet Jupiter. The enemy saw that this took the Copernican theory out of the realm of hypothesis, and they gave battle immediately . . . In vain did Galileo try to prove the exis ...
... The first important attack on Galileo began in 1610, when he announced that his telescope had revealed the moons of the planet Jupiter. The enemy saw that this took the Copernican theory out of the realm of hypothesis, and they gave battle immediately . . . In vain did Galileo try to prove the exis ...
Giuseppe Piazzi and the Discovery of Ceres
... Piazzi, who had not yet received any reaction either from Bode or Oriani, was obliged to send his complete set of observations to Lalande. It should be understood that Lalande was not only a good friend of Piazzi but was also the Gran Maestro of the Lodge of the Neuf Seurs; Piazzi himself was a free ...
... Piazzi, who had not yet received any reaction either from Bode or Oriani, was obliged to send his complete set of observations to Lalande. It should be understood that Lalande was not only a good friend of Piazzi but was also the Gran Maestro of the Lodge of the Neuf Seurs; Piazzi himself was a free ...
Makeup labs will be done this week (requires permission from TA).
... electromagnetic radiation (light). Additional important information will be provided in the “Lab and Discussion Syllabus” given during the first week of lab and discussion. Instructions on how to subscribe to our Listserver, MILKYWAY, will be provided in the first lab. The Discussion/Lab Schedule ca ...
... electromagnetic radiation (light). Additional important information will be provided in the “Lab and Discussion Syllabus” given during the first week of lab and discussion. Instructions on how to subscribe to our Listserver, MILKYWAY, will be provided in the first lab. The Discussion/Lab Schedule ca ...
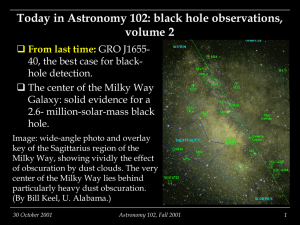
Today in Astronomy 102: black hole observations, v.2
... neighborhood of Sgr A*’s black hole to provide a quasarlike luminosity. This would also explain the lack of jets. It’s also not quite massive enough for quasar-size luminosity, as we shall see. 30 October 2001 ...
... neighborhood of Sgr A*’s black hole to provide a quasarlike luminosity. This would also explain the lack of jets. It’s also not quite massive enough for quasar-size luminosity, as we shall see. 30 October 2001 ...
about Stars
... Magnitudes • Astronomers use “magnitudes” to describe how bright stars are • Small numbers are brighter, large numbers fainter. • The brightest naked-eye stars are around magnitude zero. • The faintest naked-eye stars are around magnitude six • 5 magnitudes are a factor of 100 in brightness (a 6th ...
... Magnitudes • Astronomers use “magnitudes” to describe how bright stars are • Small numbers are brighter, large numbers fainter. • The brightest naked-eye stars are around magnitude zero. • The faintest naked-eye stars are around magnitude six • 5 magnitudes are a factor of 100 in brightness (a 6th ...
Determination of Latitude
... – Know the information that can be obtained from the practice of celestial navigation at sea. – Know the correct procedures for computing times of sunrise, sunset, and twilight. ...
... – Know the information that can be obtained from the practice of celestial navigation at sea. – Know the correct procedures for computing times of sunrise, sunset, and twilight. ...
Mathematics in Art and Architecture GEM1518K
... To warm Rudolph's frozen nose, Santa heads down to the equator (0 degrees latitude). At the equator, you see the celestial equator arcing from exactly east to the zenith to exactly west. The NCP is on your northern horizon. At the equator you see one-half of every star's total 24-hour path around y ...
... To warm Rudolph's frozen nose, Santa heads down to the equator (0 degrees latitude). At the equator, you see the celestial equator arcing from exactly east to the zenith to exactly west. The NCP is on your northern horizon. At the equator you see one-half of every star's total 24-hour path around y ...
The Star Finder Book - Starpath School of Navigation
... combinations. Navigators soon learn the value of the moon, Venus, or Jupiter for combination with star sights, since these three bodies can be seen during the brighter part of twilight when stars are faint but the horizon is still sharp. We also demonstrate how the Star Finder can be used to answer ...
... combinations. Navigators soon learn the value of the moon, Venus, or Jupiter for combination with star sights, since these three bodies can be seen during the brighter part of twilight when stars are faint but the horizon is still sharp. We also demonstrate how the Star Finder can be used to answer ...
section 17 powerpoint
... by 1 Astronomical Unit, A.U., at the distance of a star. In practice one can observe the annual displacement of a star resulting from Earth’s orbit about the Sun as 2π. Since all stars should exhibit parallax, measured values (trigonometric parallaxes) are of two types: πrel = relative parallax, is ...
... by 1 Astronomical Unit, A.U., at the distance of a star. In practice one can observe the annual displacement of a star resulting from Earth’s orbit about the Sun as 2π. Since all stars should exhibit parallax, measured values (trigonometric parallaxes) are of two types: πrel = relative parallax, is ...
2009, 1st. Quarter, Vol 24, No 1
... Observing Report on Saturn and Ceres By Bernie Kosher, BMAA I recently forwarded a challenge offered by Alan Daroff of the Willingboro Astronomical Society. The challenge was to see how soon after the last ring closing (the rings are now opening for a few months) one could pick out the dark sky b ...
... Observing Report on Saturn and Ceres By Bernie Kosher, BMAA I recently forwarded a challenge offered by Alan Daroff of the Willingboro Astronomical Society. The challenge was to see how soon after the last ring closing (the rings are now opening for a few months) one could pick out the dark sky b ...
PowerPoint - Herschel Space Observatory
... – The shape of the spectrum is always the same, but the peak wavelength changes with temperature. – But not all objects are black bodies. – Atoms, molecules and electrons emit radiation with a different ...
... – The shape of the spectrum is always the same, but the peak wavelength changes with temperature. – But not all objects are black bodies. – Atoms, molecules and electrons emit radiation with a different ...
identifying seasonal stars in kaurna astronomical traditions
... In Teichelmann and Schürmann (1840), Parnakkoyerli is mentioned directly after Tinniinyaranna, which suggests that the Aboriginal informant pointed out the stars of Tinniinyaranna, then probably moved to Rigel and said it was ‗their father‘. In this case, Parnakkoyerli is a descripttion rather than ...
... In Teichelmann and Schürmann (1840), Parnakkoyerli is mentioned directly after Tinniinyaranna, which suggests that the Aboriginal informant pointed out the stars of Tinniinyaranna, then probably moved to Rigel and said it was ‗their father‘. In this case, Parnakkoyerli is a descripttion rather than ...
Document
... observed in the interstellar medium • Many complex molecules have been observed, including progenitors of the basic amino acids required to build life • These complex molecules can only survive in space when they are shielded by dense, dark, giant clouds containing dust • These giant clouds are inte ...
... observed in the interstellar medium • Many complex molecules have been observed, including progenitors of the basic amino acids required to build life • These complex molecules can only survive in space when they are shielded by dense, dark, giant clouds containing dust • These giant clouds are inte ...
The Naked Eye Stars as Data Supporting Galileo`s
... Brief historical background is also included. ...
... Brief historical background is also included. ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.