B LOG - Science Centre
... more. Appears as a hazy patch in binoculars . Telescopes at low magnification may resolve individual stars. 17,000 lightyears away. ...
... more. Appears as a hazy patch in binoculars . Telescopes at low magnification may resolve individual stars. 17,000 lightyears away. ...
File - the ridgeway ASTRONOMY page
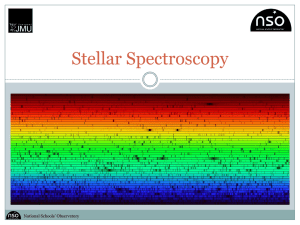
... Using the information provided in this presentation, and by making comparisons to the spectra you have already plotted, try to classify the mystery stars. ...
... Using the information provided in this presentation, and by making comparisons to the spectra you have already plotted, try to classify the mystery stars. ...
Lecture 9 - Notes on Galileo
... convinced by proof of something it was made then a sin to believe.” Cardinal Robert Bellarmine was the chief theologian of the Church, who took an instrumentalist view of the question, saying that mathematical hypotheses had nothing to do with physical reality. He was also concerned about raising an ...
... convinced by proof of something it was made then a sin to believe.” Cardinal Robert Bellarmine was the chief theologian of the Church, who took an instrumentalist view of the question, saying that mathematical hypotheses had nothing to do with physical reality. He was also concerned about raising an ...
equato equator - Universal Workshop
... of the ecliptic. It keeps occulting a certain star at intervals of a sidereal month, a longer series of such occultations if the star is closer to the ecliptic; the series ends, and then takes place again 18.6 years ...
... of the ecliptic. It keeps occulting a certain star at intervals of a sidereal month, a longer series of such occultations if the star is closer to the ecliptic; the series ends, and then takes place again 18.6 years ...
key - Scioly.org
... 57. What does not occur to a AM CVn system as it ages? [2] (a) Angular momentum is lost through gravitational waves (b) The orbital period increases (c) The orbital radius decreases (d) Matter is transferred from the less massive to the more massive star (e) The speed at which matter is transferred ...
... 57. What does not occur to a AM CVn system as it ages? [2] (a) Angular momentum is lost through gravitational waves (b) The orbital period increases (c) The orbital radius decreases (d) Matter is transferred from the less massive to the more massive star (e) The speed at which matter is transferred ...
MCWP 3-16.7 Chapter 7: Astronomy
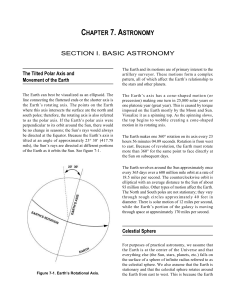
... The Earth’s axis has a cone-shaped motion (or precession) making one turn in 25,800 solar years or one platonic year (great year). This is caused by torque imposed on the Earth mostly by the Moon and Sun. Visualize it as a spinning top. As the spinning slows, the top begins to wobble creating a cone ...
... The Earth’s axis has a cone-shaped motion (or precession) making one turn in 25,800 solar years or one platonic year (great year). This is caused by torque imposed on the Earth mostly by the Moon and Sun. Visualize it as a spinning top. As the spinning slows, the top begins to wobble creating a cone ...
Sky-High 2015 - Irish Astronomical Society
... it looks otherwise and it is easier to describe things as we see them for our immediate purpose. The fact that the Earth turns on its axis about every 24 hours causes the Sun to rise in the east and set in the west, and it is due south at noon. A similar situation applies to all the other heavenly b ...
... it looks otherwise and it is easier to describe things as we see them for our immediate purpose. The fact that the Earth turns on its axis about every 24 hours causes the Sun to rise in the east and set in the west, and it is due south at noon. A similar situation applies to all the other heavenly b ...
the entire issue as one large (23
... brute-force star counts and methods of statistical analysis, such as those developed by Kapteyn. The basic idea was simple: as one counted stars, the number of stars would rise in the vicinity of a spiral arm and then drop off beyond it. No one applied these methods more diligently than Oort’s forme ...
... brute-force star counts and methods of statistical analysis, such as those developed by Kapteyn. The basic idea was simple: as one counted stars, the number of stars would rise in the vicinity of a spiral arm and then drop off beyond it. No one applied these methods more diligently than Oort’s forme ...
Here - Amateur Observers` Society of New York
... viewed from the earth. A lunar eclipse occurs when, on passing between the sun and the moon, the earth is closely enough aligned to hide at least some of the moon. For both solar and lunar eclipses, use the predictions listed in The Beginner’s Observing Guide and The Observer's Handbook to plan your ...
... viewed from the earth. A lunar eclipse occurs when, on passing between the sun and the moon, the earth is closely enough aligned to hide at least some of the moon. For both solar and lunar eclipses, use the predictions listed in The Beginner’s Observing Guide and The Observer's Handbook to plan your ...
the magellanic clouds newsletter - Keele University Astrophysics
... We present the Planck catalogue of Galactic Cold Clumps (PGCC), an all-sky catalogue of Galactic cold clump candidates detected by Planck. This catalogue is the full version of the Early Cold Core (ECC) catalogue, which was made available in 2011 with the Early Release Compact Source Catalogue (ERCS ...
... We present the Planck catalogue of Galactic Cold Clumps (PGCC), an all-sky catalogue of Galactic cold clump candidates detected by Planck. This catalogue is the full version of the Early Cold Core (ECC) catalogue, which was made available in 2011 with the Early Release Compact Source Catalogue (ERCS ...
New Almagest - University of Notre Dame
... observable phenomena. These phenomena were, in fact, not observed. Thus the Earth must not rotate. These are the physical and “physicomathematical” demonstrations Riccioli mentions in his main conclusion about which “hypothesis” can be asserted as being true. A second anti-Copernican argument—one th ...
... observable phenomena. These phenomena were, in fact, not observed. Thus the Earth must not rotate. These are the physical and “physicomathematical” demonstrations Riccioli mentions in his main conclusion about which “hypothesis” can be asserted as being true. A second anti-Copernican argument—one th ...
Kepler File
... of the heavenly spheres,” he was ready and able to throw out his most beloved theories if they did not agree with observations. 3. He introduced physical causality into astronomy. His major work (Astronomia Nova) in which he describes his first and second laws is subtitled “a new astronomy based upn ...
... of the heavenly spheres,” he was ready and able to throw out his most beloved theories if they did not agree with observations. 3. He introduced physical causality into astronomy. His major work (Astronomia Nova) in which he describes his first and second laws is subtitled “a new astronomy based upn ...
ASTRONOMICAL BINOCULARS
... years, so they may be seen edge-on (like a thin line) or broadside (like giant “ears” on each side of the planet). You will need a good steady atmosphere to achieve a worthwhile view of Saturn. If you look closely enough, you can see the Cassini division - a thin, dark gap in the rings. You can also ...
... years, so they may be seen edge-on (like a thin line) or broadside (like giant “ears” on each side of the planet). You will need a good steady atmosphere to achieve a worthwhile view of Saturn. If you look closely enough, you can see the Cassini division - a thin, dark gap in the rings. You can also ...
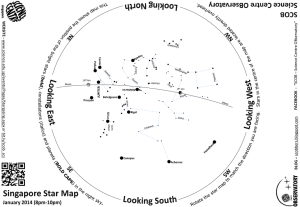
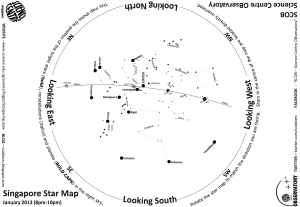
Star Map - Science Centre
... The Big Dipper is one of the most famous asterisms (star patterns) throughout history. In some places of the Northern Hemisphere, its seven brightest stars can be seen all year round. Further South near the equator, it is only visible for a few months. Merak and Dubhe are known as The Pointers, poin ...
... The Big Dipper is one of the most famous asterisms (star patterns) throughout history. In some places of the Northern Hemisphere, its seven brightest stars can be seen all year round. Further South near the equator, it is only visible for a few months. Merak and Dubhe are known as The Pointers, poin ...
Finding the Most Distant Quasars Using Bayesian Selection Methods
... been almost completely ionised, as the first generations of stars—and quasars—emitted sufficient ultraviolet radiation to separate electrons from protons. The rest-frame wavelength of the break is at 0.1216 µm, but the wavelength of all light is increased by the cosmological expansion; the Universe ...
... been almost completely ionised, as the first generations of stars—and quasars—emitted sufficient ultraviolet radiation to separate electrons from protons. The rest-frame wavelength of the break is at 0.1216 µm, but the wavelength of all light is increased by the cosmological expansion; the Universe ...
10 September: Faint Stars and Bright Stars
... Absolute Magnitude: a measure of the intrinsic brilliance of a star • Pick a star (any star) • Imagine moving it to a distance of 10 parsecs • The apparent magnitude it would have is its absolute magnitude • The absolute magnitude is a distanceindependent quantity • Look at Appendix 12 and Appendix ...
... Absolute Magnitude: a measure of the intrinsic brilliance of a star • Pick a star (any star) • Imagine moving it to a distance of 10 parsecs • The apparent magnitude it would have is its absolute magnitude • The absolute magnitude is a distanceindependent quantity • Look at Appendix 12 and Appendix ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.