Highlights in astronomical polarimetry
... capable of transforming linear into circular polrization and viceversa (the so-called Fresnel rhomb). ...
... capable of transforming linear into circular polrization and viceversa (the so-called Fresnel rhomb). ...
Insights into the Universe: Astronomy with Haystack’s Radio Telescope »
... Laboratory facility, and its original staff members were transferred from the Laboratory. The organizations share a deep bond and a long history of close cooperation on the site. Personnel are frequently shared between the two, and Lincoln Laboratory and observatory staff have worked shoulder to sho ...
... Laboratory facility, and its original staff members were transferred from the Laboratory. The organizations share a deep bond and a long history of close cooperation on the site. Personnel are frequently shared between the two, and Lincoln Laboratory and observatory staff have worked shoulder to sho ...
ATTENTION: Epreuve non définitive!!!
... for observed irregularities and determined a position based on an orbit in the ecliptic plane and Bode’s Law that suggested a radius twice that of Uranus. In his third memoir, read on 31 August 1846, le Verrier gave more precise limits within which one should look for the new planet and even predict ...
... for observed irregularities and determined a position based on an orbit in the ecliptic plane and Bode’s Law that suggested a radius twice that of Uranus. In his third memoir, read on 31 August 1846, le Verrier gave more precise limits within which one should look for the new planet and even predict ...
Ch13_Lecture - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • Consequently, absorption lines will be present or absent depending on the presence or absence of an electron at the right energy level and this is very much dependent on temperature • Adjusting for temperature, a star’s composition can be found – interestingly, virtually all stars have composition ...
... • Consequently, absorption lines will be present or absent depending on the presence or absence of an electron at the right energy level and this is very much dependent on temperature • Adjusting for temperature, a star’s composition can be found – interestingly, virtually all stars have composition ...
Ch. 1 - Astro1010
... Earth’s Orbital Motion Daily cycle, noon to noon, is diurnal motion – solar day Stars aren’t in quite the same place 24 hours later, though, due to Earth’s revolution around Sun; when they are, one sidereal day has passed ...
... Earth’s Orbital Motion Daily cycle, noon to noon, is diurnal motion – solar day Stars aren’t in quite the same place 24 hours later, though, due to Earth’s revolution around Sun; when they are, one sidereal day has passed ...
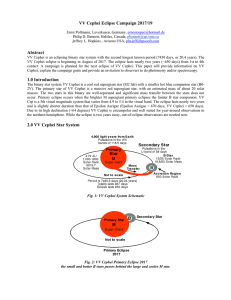
VV Cephei Eclipse Campaign 2017/19
... The binary star system VV Cephei is a cool red supergiant star (M2 Iab) with a smaller hot blue companion star (B02V). The primary star of VV Cephei is a massive red supergiant star, with an estimated mass of about 20 solar masses. The two stars in this binary are well-separated and significant mass ...
... The binary star system VV Cephei is a cool red supergiant star (M2 Iab) with a smaller hot blue companion star (B02V). The primary star of VV Cephei is a massive red supergiant star, with an estimated mass of about 20 solar masses. The two stars in this binary are well-separated and significant mass ...
Galaxies Astronomy 1 — Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College Spring F2015
... A. never had blue stars in the galaxy. B. had blue stars that are not present anymore but were at one time long ago. C. has been around long enough for blue stars to all evolve into the red main sequence stars we see. D. never contained enough gas to have blue stars develop. E. as blue stars that ar ...
... A. never had blue stars in the galaxy. B. had blue stars that are not present anymore but were at one time long ago. C. has been around long enough for blue stars to all evolve into the red main sequence stars we see. D. never contained enough gas to have blue stars develop. E. as blue stars that ar ...
Comets in ancient India
... Archaeoastronomical arguments indicate that vedas have preserved even older traditions. In vedic texts, nakshatras or ‘lunar mansion’ (bright stars and constellations lying along Moon’s path) have an exalted status (Subbarayappa 2008). Krittika (Pleiades) is often listed as the first asterism among ...
... Archaeoastronomical arguments indicate that vedas have preserved even older traditions. In vedic texts, nakshatras or ‘lunar mansion’ (bright stars and constellations lying along Moon’s path) have an exalted status (Subbarayappa 2008). Krittika (Pleiades) is often listed as the first asterism among ...
Building a model astrolabe - In-The
... On the rete appears a planispheric projection of the brightest stars in the northern sky; I have used the Yale Bright Star Catalogue11 to mark all stars brighter than fourth magnitude. The projection used here is the same as is used on modern planispheres: if a star has right ascension α and declina ...
... On the rete appears a planispheric projection of the brightest stars in the northern sky; I have used the Yale Bright Star Catalogue11 to mark all stars brighter than fourth magnitude. The projection used here is the same as is used on modern planispheres: if a star has right ascension α and declina ...
The Marine Sextant
... • A sextant is used to determine the sextant altitude (hs) of a celestial body. • First, we have to decide which stars to observe; this is done using a Rude Starfinder or other methods. • When making an observation, the star should look as shown in the next slide... ...
... • A sextant is used to determine the sextant altitude (hs) of a celestial body. • First, we have to decide which stars to observe; this is done using a Rude Starfinder or other methods. • When making an observation, the star should look as shown in the next slide... ...
`Magnificent Desolation` transcript
... gravity, this causes the water to swell up into a bulge. The oceans on the opposite side of the earth are pulled much less strongly and they move away from the moon, this is how we get two high tides and two low tides everyday. The tides cause friction against the earth, and this is actually slow ...
... gravity, this causes the water to swell up into a bulge. The oceans on the opposite side of the earth are pulled much less strongly and they move away from the moon, this is how we get two high tides and two low tides everyday. The tides cause friction against the earth, and this is actually slow ...
Expanding Earth and Static Universe: Two Papers of 1935
... Halm (1911) also studied the systematic motions of stars, finding evidence for a third class of “star streams” in addition to the two discovered by Jacobus C. Kapteyn. In this connection he argued that “the principle of equipartition of energy is applicable to the system of bodies constituting the v ...
... Halm (1911) also studied the systematic motions of stars, finding evidence for a third class of “star streams” in addition to the two discovered by Jacobus C. Kapteyn. In this connection he argued that “the principle of equipartition of energy is applicable to the system of bodies constituting the v ...
August, 2005 Observer - Fort Bend Astronomy Club
... dark rural site. The overall shape of the object is a face on spiral galaxy with two arms spiraling out from the center of the galaxy. One arm spirals out from the top and the other from the bottom of the galaxy. The core is bright and easy to detect. H2 regions can be seen throughout the galaxy and ...
... dark rural site. The overall shape of the object is a face on spiral galaxy with two arms spiraling out from the center of the galaxy. One arm spirals out from the top and the other from the bottom of the galaxy. The core is bright and easy to detect. H2 regions can be seen throughout the galaxy and ...
Trilogy Booklet for UN - with all graphics in low resolution
... know very well, that the stars we can see, are suns or even galaxies with different distances to our solar system. For observation purposes, though, one has to think of the distant stars as being ‘glued’ onto a huge sphere, which is the outer limit of our little imagined universe. The Sun’s journey ...
... know very well, that the stars we can see, are suns or even galaxies with different distances to our solar system. For observation purposes, though, one has to think of the distant stars as being ‘glued’ onto a huge sphere, which is the outer limit of our little imagined universe. The Sun’s journey ...
TNO Time Allocation Committee
... on three eclipsing WDMS binaries” with N. Sanguansak as the PI. The proposal was awarded three nights of observations using ULTRASPEC. Our target star was also observed several times during the GTO, carried out by our UK collaborators, as well as during other observing slots allocated to programs wi ...
... on three eclipsing WDMS binaries” with N. Sanguansak as the PI. The proposal was awarded three nights of observations using ULTRASPEC. Our target star was also observed several times during the GTO, carried out by our UK collaborators, as well as during other observing slots allocated to programs wi ...
1/20/09 301 Physics Chapter 12 The Family of Stars Triangulation
... • This information helps to understand the nature of stars as well as their life cycle • The light from stars received at Earth is all that is available for this analysis ...
... • This information helps to understand the nature of stars as well as their life cycle • The light from stars received at Earth is all that is available for this analysis ...
looking up! - Discover the universe
... • Shooting stars or meteors: Shooting stars are not stars, but space dust particles falling through the Earth’s atmosphere at high speed. The heat created when they pass through the atmosphere leaves a trail of light we can observe. • Milky Way: Under a very dark sky, away from city lights, it’s p ...
... • Shooting stars or meteors: Shooting stars are not stars, but space dust particles falling through the Earth’s atmosphere at high speed. The heat created when they pass through the atmosphere leaves a trail of light we can observe. • Milky Way: Under a very dark sky, away from city lights, it’s p ...
The Significance of Mega Stars
... Sirius is so close, in comparison with other stars, that it appears so bright. We can ask the question: How bright is Sirius objectively? In other words, if we were to place Sirius alongside our Sun, how bright would it appear in comparison with our Sun? This leads us to the concept of luminosity, w ...
... Sirius is so close, in comparison with other stars, that it appears so bright. We can ask the question: How bright is Sirius objectively? In other words, if we were to place Sirius alongside our Sun, how bright would it appear in comparison with our Sun? This leads us to the concept of luminosity, w ...
AN ATTEMPT To prove the MOTION OF THE EARTH FROM
... particularly of this subject, that there never was any sensible Parallax discovered by the best observations of this supposed annual motion of the Earth about the Sun as its center, though moved in an Orb whose Diameter is by the greatest number of Astronomers reckoned between 11 and 12 hundred Diam ...
... particularly of this subject, that there never was any sensible Parallax discovered by the best observations of this supposed annual motion of the Earth about the Sun as its center, though moved in an Orb whose Diameter is by the greatest number of Astronomers reckoned between 11 and 12 hundred Diam ...
Lesson Plan G2 The Stars
... All stars form from cold clouds of hydrogen gas that collapse under their own gravity. The center of the cloud heats up from the resulting increase in pressure and friction. Eventually the heat and pressure are great enough to force hydrogen nuclei to fuse together and form helium nuclei. This nucle ...
... All stars form from cold clouds of hydrogen gas that collapse under their own gravity. The center of the cloud heats up from the resulting increase in pressure and friction. Eventually the heat and pressure are great enough to force hydrogen nuclei to fuse together and form helium nuclei. This nucle ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... see the celestial equator cross the local meridian looking south, while an observer in the southern hemisphere will see the celestial equator cross the local meridian looking north. The altitude of the celestial equator, where it crosses the observer’s meridian, is equal to the absolute value of 90° ...
... see the celestial equator cross the local meridian looking south, while an observer in the southern hemisphere will see the celestial equator cross the local meridian looking north. The altitude of the celestial equator, where it crosses the observer’s meridian, is equal to the absolute value of 90° ...
Unit 2―The Stars and Their Diurnal Motion
... Ursa Major point to the North Star. If you use them to point in the other direction, or as we say, “downward on the Celestial Sphere,” you will cut off the tail of Leo the Lion”― a constellation you might wish to find if your birthday is in August. Again, notice how one memory device leads to locati ...
... Ursa Major point to the North Star. If you use them to point in the other direction, or as we say, “downward on the Celestial Sphere,” you will cut off the tail of Leo the Lion”― a constellation you might wish to find if your birthday is in August. Again, notice how one memory device leads to locati ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.