Carbon Solutions Group - Australian Industry Group
... accuracy or completeness of any statement in it. The document does not purport to contain all of the information that clients or prospective investors may require or should obtain. To the maximum extent permitted by law, National Australia Bank Limited expressly disclaims all or any liability which ...
... accuracy or completeness of any statement in it. The document does not purport to contain all of the information that clients or prospective investors may require or should obtain. To the maximum extent permitted by law, National Australia Bank Limited expressly disclaims all or any liability which ...
Chemistry of the atmosphere
... Carbon footprint is the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases emitted over the lifetime of a product, service or event Carbon footprint is the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases emitted during the creation of a product, service or event Carbon footprint is the amount o ...
... Carbon footprint is the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases emitted over the lifetime of a product, service or event Carbon footprint is the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases emitted during the creation of a product, service or event Carbon footprint is the amount o ...
UN-DESA Policy Brief No. 26
... other environmental issues is crucial and could be undertaken immediately by the international community. Awareness raising efforts should build on support of scientific efforts such as the UNESCO-sponsored Monaco Symposium on the Ocean in a High-CO2 World and could include preparation of easy-to-un ...
... other environmental issues is crucial and could be undertaken immediately by the international community. Awareness raising efforts should build on support of scientific efforts such as the UNESCO-sponsored Monaco Symposium on the Ocean in a High-CO2 World and could include preparation of easy-to-un ...
Wake HM 1AR v MSU HR Ky semis
... with very little international trade, the growth in living standards-and thus "competitiveness" according to Tyson's definition -- would be determined almost entirely by domestic factors, primarily the rate of productivity growth. That's domestic productivity growth, period -- not productivity growt ...
... with very little international trade, the growth in living standards-and thus "competitiveness" according to Tyson's definition -- would be determined almost entirely by domestic factors, primarily the rate of productivity growth. That's domestic productivity growth, period -- not productivity growt ...
Carbon cycle dynamics - PAGES
... Atlantic heat transport and shifts in the rain belt of the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). These ”Dansgaard-Oeschger” and related Southern Hemisphere climate swings demonstrate that the climate system can switch into new states within decades – a potential for unpleasant future surprise. Sur ...
... Atlantic heat transport and shifts in the rain belt of the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). These ”Dansgaard-Oeschger” and related Southern Hemisphere climate swings demonstrate that the climate system can switch into new states within decades – a potential for unpleasant future surprise. Sur ...
Kudzu can release soil carbon, accelerate global warming
... In a paper published in the scientific journal New Phytologist, plant ecologist Nishanth Tharayil and This layer of decomposing knotweed will eventually form graduate student Mioko Tamura show that invasive soil organic matter in invaded ecosystems. plants can accelerate the greenhouse effect by rel ...
... In a paper published in the scientific journal New Phytologist, plant ecologist Nishanth Tharayil and This layer of decomposing knotweed will eventually form graduate student Mioko Tamura show that invasive soil organic matter in invaded ecosystems. plants can accelerate the greenhouse effect by rel ...
Activity 1C-Carbon Journey
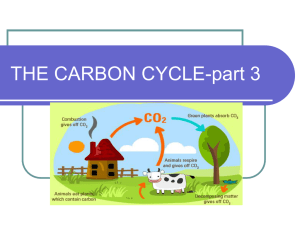
... anthropogenic (human) activities are releasing more CO2 into the atmosphere than has been previously recorded over the last half million years. Most of the increase in CO2 is due to the combustion of fossil fuels. Forest fires and the reduction in forest cover due to land use changes are also causin ...
... anthropogenic (human) activities are releasing more CO2 into the atmosphere than has been previously recorded over the last half million years. Most of the increase in CO2 is due to the combustion of fossil fuels. Forest fires and the reduction in forest cover due to land use changes are also causin ...
Implications of Climate Change on Ocean Living Resources off
... research effort. The origin of data varies: in Alaska - survey (RACE) and observer (NORPAC) databases; West Coast – NMFS bottom trawl surveys and observer programs; Gulf and Southeastern US - literature citations and fishery management council database; Northeast historical records, NMFS bottom traw ...
... research effort. The origin of data varies: in Alaska - survey (RACE) and observer (NORPAC) databases; West Coast – NMFS bottom trawl surveys and observer programs; Gulf and Southeastern US - literature citations and fishery management council database; Northeast historical records, NMFS bottom traw ...
Warming Deep Seas 0606 - Global Warming
... Decrease in sea ice delaying spring phytoplankton bloom to later in season, out of synch. with max. zooplankton growth. Consequence that spring phytoplankton bloom benefits primarily the benthic community; later zooplankton bloom benefits primarily the pelagic ecosystem. ...
... Decrease in sea ice delaying spring phytoplankton bloom to later in season, out of synch. with max. zooplankton growth. Consequence that spring phytoplankton bloom benefits primarily the benthic community; later zooplankton bloom benefits primarily the pelagic ecosystem. ...
Ocean acidification in the western tropical Pacific
... What is ocean acidification? Ocean acidification is a change in ocean chemistry that occurs when atmospheric carbon dioxide is taken up by the ocean, thereby increasing pH. Carbon dioxide is a weak acid, so when it enters the ocean it reacts with seawater, increasing acidity. Oceans absorb about 25% ...
... What is ocean acidification? Ocean acidification is a change in ocean chemistry that occurs when atmospheric carbon dioxide is taken up by the ocean, thereby increasing pH. Carbon dioxide is a weak acid, so when it enters the ocean it reacts with seawater, increasing acidity. Oceans absorb about 25% ...
6-7 Ocean Acidification and Sea Level Change 2.6.4bcd
... additional doubling to tripling of today's post-industrial acid concentrations) by 2100. These changes are predicted to continue rapidly as the oceans take up more anthropogenic CO2 from the atmosphere. ...
... additional doubling to tripling of today's post-industrial acid concentrations) by 2100. These changes are predicted to continue rapidly as the oceans take up more anthropogenic CO2 from the atmosphere. ...
File
... Geoengineering could reduce the monsoon rains in Asia, according to scientists at the National Centre for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Boulder, Colorado in the US. A study in October found that global warming caused by a massive increase in greenhouse gases would lead to 7 per cent more rain than ...
... Geoengineering could reduce the monsoon rains in Asia, according to scientists at the National Centre for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Boulder, Colorado in the US. A study in October found that global warming caused by a massive increase in greenhouse gases would lead to 7 per cent more rain than ...
File
... • As said Carbon is essential for life • Found in all living things, their dead bodies and wastes • Found in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide • Used in photosynthesis • There IS NOT AN ENDLESS SUPPLY • Fossils are the preserved remains of once living organisms • Fossils fuels are made form the carbo ...
... • As said Carbon is essential for life • Found in all living things, their dead bodies and wastes • Found in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide • Used in photosynthesis • There IS NOT AN ENDLESS SUPPLY • Fossils are the preserved remains of once living organisms • Fossils fuels are made form the carbo ...
Ocean acidification may cause many negative effects on a variety of
... Ocean acidification may cause many negative effects on a variety of marine species and ecosystems, which would have rippling consequences throughout the entire ocean. One of the most devastating impacts of rising ocean acidity could be the collapse of food webs. Caron ...
... Ocean acidification may cause many negative effects on a variety of marine species and ecosystems, which would have rippling consequences throughout the entire ocean. One of the most devastating impacts of rising ocean acidity could be the collapse of food webs. Caron ...
Link to statement. - Deep Ocean Stewardship Initiative
... and constitutes the ultimate sink for most anthropogenic carbon. The biogenic deep-sea carbon component is poorly quantified, but chemosynthetic ecosystems with high carbon fixation rates and vertical transport by pelagic species may significantly contribute to ‘blue carbon’ sequestration (Marlow et ...
... and constitutes the ultimate sink for most anthropogenic carbon. The biogenic deep-sea carbon component is poorly quantified, but chemosynthetic ecosystems with high carbon fixation rates and vertical transport by pelagic species may significantly contribute to ‘blue carbon’ sequestration (Marlow et ...
The oceans warm and cool much slower than land for a number of
... (3) The thermal capacity of the oceans is much higher because the water is considerably denser and has roughly four times the specific heat (the amount of heat required to warm a given volume 1 degree Celsius) as most land surfaces. This is why land warms more and much faster than the ocean in the s ...
... (3) The thermal capacity of the oceans is much higher because the water is considerably denser and has roughly four times the specific heat (the amount of heat required to warm a given volume 1 degree Celsius) as most land surfaces. This is why land warms more and much faster than the ocean in the s ...
Recent Warming of Antarctic Bottom Water in the South Atlantic
... Friday Harbor Laboratories, San Juan Island, WA ...
... Friday Harbor Laboratories, San Juan Island, WA ...
Atlantic Ocean
... Ballast waters are source of invasive species and also oil pollution. Discharges into coastal waters along with other sources of marine pollution have the potential to be toxic to marine plants, animals, and microorganisms causing alterations such as changes in growth, disruption of hormone cycles, ...
... Ballast waters are source of invasive species and also oil pollution. Discharges into coastal waters along with other sources of marine pollution have the potential to be toxic to marine plants, animals, and microorganisms causing alterations such as changes in growth, disruption of hormone cycles, ...
Elements of the climate
... storms, floods and droughts. (October 6, 2010) Among the new study’s more dramatic calculations: River runoff into the seas has been increasing by some 540 cubic kilometers per year, or about 1.5 percent annually over the period analyzed (1994 to 2006). While that may not sound like much, “over 20 ...
... storms, floods and droughts. (October 6, 2010) Among the new study’s more dramatic calculations: River runoff into the seas has been increasing by some 540 cubic kilometers per year, or about 1.5 percent annually over the period analyzed (1994 to 2006). While that may not sound like much, “over 20 ...
04 - PP - nc2p_u4l5_indicators_of_climate_change
... cm over the past century. This is caused by land glaciers melting and water expanding as it warms. ...
... cm over the past century. This is caused by land glaciers melting and water expanding as it warms. ...
Wood as energetic biomass - threats and opportunities
... landcover changes on climate are at least as important, and quite possibly more important than those of carbon dioxide," said ...
... landcover changes on climate are at least as important, and quite possibly more important than those of carbon dioxide," said ...
The Science and Ethics of Global warming
... taken up by plants in parts of the world where forests are growing, and dissolved into the oceans. Photosynthetic organisms (plants, algae and bacteria) take in about 120 Pg each year, while all living things breathe out a little less than this (accounting for the storage of carbon in growing thing ...
... taken up by plants in parts of the world where forests are growing, and dissolved into the oceans. Photosynthetic organisms (plants, algae and bacteria) take in about 120 Pg each year, while all living things breathe out a little less than this (accounting for the storage of carbon in growing thing ...
Advantage CP 2 7WK - Open Evidence Archive
... upgrade the public transportation system; $32 billion for building “smart grid” electrical transmissions systems that can, among other things, efficiently use power from renewable sources; and $8 billion for renewable energy research and commercialization (allowing that the exact allocations for var ...
... upgrade the public transportation system; $32 billion for building “smart grid” electrical transmissions systems that can, among other things, efficiently use power from renewable sources; and $8 billion for renewable energy research and commercialization (allowing that the exact allocations for var ...
Iron fertilization

Iron fertilization is the intentional introduction of iron to the upper ocean to stimulate a phytoplankton bloom. This is intended to enhance biological productivity, which can benefit the marine food chain and is under investigation in hopes of increasing carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere. Iron is a trace element necessary for photosynthesis in all plants. It is highly insoluble in sea water and is often the limiting nutrient for phytoplankton growth. Large algal blooms can be created by supplying iron to iron-deficient ocean waters.A number of ocean labs, scientists and businesses are exploring fertilization as a means to sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide in the deep ocean, and to increase marine biological productivity which is likely in decline as a result of climate change. Since 1993, thirteen international research teams have completed ocean trials demonstrating that phytoplankton blooms can be stimulated by iron addition. However, controversy remains over the effectiveness of atmospheric CO2 sequestration and ecological effects. The most recent open ocean trials of ocean iron fertilization were in 2009 (January to March) in the South Atlantic by project Lohafex, and in July 2012 in the North Pacific off the coast of British Columbia, Canada, by the Haida Salmon Restoration Corporation (HSRC).Fertilization also occurs naturally when upwellings bring nutrient-rich water to the surface, as occurs when ocean currents meet an ocean bank or a sea mount. This form of fertilization produces the world's largest marine habitats. Fertilization can also occur when weather carries wind blown dust long distances over the ocean, or iron-rich minerals are carried into the ocean by glaciers, rivers and icebergs.