Marine Calcifiers in a High-CO Ocean
... 10. D. M. Iglesias-Rodríguez, O. M. Schofield, J. Batley, L. K. Medlin, P. K. Hayes, J. Phycol. 42, 526 (2006). 11. J. C. Cubillos et al., Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 348, 47 (2007). ...
... 10. D. M. Iglesias-Rodríguez, O. M. Schofield, J. Batley, L. K. Medlin, P. K. Hayes, J. Phycol. 42, 526 (2006). 11. J. C. Cubillos et al., Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 348, 47 (2007). ...
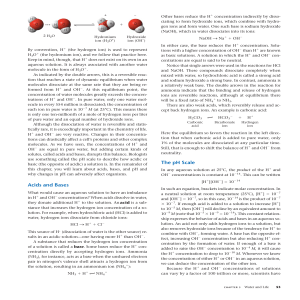
Acids and Bases The pH Scale
... compounds into the atmosphere. When certain of these compounds react with water, the water becomes more acidic, altering the delicate balance of conditions for life on Earth. Carbon dioxide is the main product of fossil fuel combustion. About 25% of human-generated CO2 is absorbed by the oceans. In ...
... compounds into the atmosphere. When certain of these compounds react with water, the water becomes more acidic, altering the delicate balance of conditions for life on Earth. Carbon dioxide is the main product of fossil fuel combustion. About 25% of human-generated CO2 is absorbed by the oceans. In ...
8_Ocean126_2006
... Ridges devoid of sediment Oceanic ridges and associated structures account for 22% of the world’s surface (compare to all land which is 29%!) < 60% of their length is at the center of basins Youngest rocks at spreading centers Steeper ridges at slower spreading centers ...
... Ridges devoid of sediment Oceanic ridges and associated structures account for 22% of the world’s surface (compare to all land which is 29%!) < 60% of their length is at the center of basins Youngest rocks at spreading centers Steeper ridges at slower spreading centers ...
Atmosphere_Ocean_Currents
... Comets brought water and organic molecules. Oxygen did not appear in the atmosphere until after the first bacteria evolved. Early plants released oxygen as a waste product and helped to build the atmosphere. Once oxygen was present in the atmosphere, ozone could form, blocking out the Sun’s ultravio ...
... Comets brought water and organic molecules. Oxygen did not appear in the atmosphere until after the first bacteria evolved. Early plants released oxygen as a waste product and helped to build the atmosphere. Once oxygen was present in the atmosphere, ozone could form, blocking out the Sun’s ultravio ...
CHAPTER 1
... for the progressive evolution of coral reefs into atolls. - One of the leading marine biologists of the 19 th century was Edward Forbes. Forbes believed the oceans could be divided vertically into zones, each of which was home to a characteristic group of organisms. He suggested that there was no li ...
... for the progressive evolution of coral reefs into atolls. - One of the leading marine biologists of the 19 th century was Edward Forbes. Forbes believed the oceans could be divided vertically into zones, each of which was home to a characteristic group of organisms. He suggested that there was no li ...
Oceanography Final Study Guide
... 20. What ships were built just for marine science work? 21. What did submersibles and self-contained diving contribute to the study of the ocean? 22. What types of submersibles have been used for underwater research? 23. What are the advantages and disadvantages of submersibles compared to scuba? 24 ...
... 20. What ships were built just for marine science work? 21. What did submersibles and self-contained diving contribute to the study of the ocean? 22. What types of submersibles have been used for underwater research? 23. What are the advantages and disadvantages of submersibles compared to scuba? 24 ...
Chemical and Physical Properties of Seawater
... In some locations, large volumes of water may sink or rise. Water sinks due to changes in temperature and salinity – this is known as an area of down-welling. Down-welling brings gases from the surface to deeper layers. Areas of upwelling come from currents that push deeper waters toward the surface ...
... In some locations, large volumes of water may sink or rise. Water sinks due to changes in temperature and salinity – this is known as an area of down-welling. Down-welling brings gases from the surface to deeper layers. Areas of upwelling come from currents that push deeper waters toward the surface ...
Document
... is just a veneer of warmth over a cold ocean; typical deep ocean temperature vary from –1° to 3°C. The sharp drop off in temperature with depth is called the thermocline. The warm surface water is generally saltier than the cooler deep or polar waters. The halocline marks the drop of salinity with d ...
... is just a veneer of warmth over a cold ocean; typical deep ocean temperature vary from –1° to 3°C. The sharp drop off in temperature with depth is called the thermocline. The warm surface water is generally saltier than the cooler deep or polar waters. The halocline marks the drop of salinity with d ...
Marine Science - US Satellite Laboratory
... Foundations of NGSS and Marine Science: The Dynamic Ocean Nature of Science (NOS) A deep understanding of the NOS is essential to a strong science education and highly valued in Marine Science: The Dynamic Ocean. The text directly addresses important NOS terminology and contextualizes examples of ho ...
... Foundations of NGSS and Marine Science: The Dynamic Ocean Nature of Science (NOS) A deep understanding of the NOS is essential to a strong science education and highly valued in Marine Science: The Dynamic Ocean. The text directly addresses important NOS terminology and contextualizes examples of ho ...
Global Variations of Chemical Composition of Oceans
... demonstrate a reverse situation). As a result, there are no conditions for formation of ...
... demonstrate a reverse situation). As a result, there are no conditions for formation of ...
plate-tectonics-pre-test-study-guide
... a. past each other b. towards each other c. away from each other ...
... a. past each other b. towards each other c. away from each other ...
Statement on Educational Backgrounds of Marine
... most fruitful avenues for them to pursue. Such a transition is a natural outcome of intellectual curiosity and investigation, and they find that they must acquire a knowledge of oceanography in order to proceed with their research. Oceanography is replete with examples of scientists from other disci ...
... most fruitful avenues for them to pursue. Such a transition is a natural outcome of intellectual curiosity and investigation, and they find that they must acquire a knowledge of oceanography in order to proceed with their research. Oceanography is replete with examples of scientists from other disci ...
FacultyBackgrounds - USF College of Marine Science
... most fruitful avenues for them to pursue. Such a transition is a natural outcome of intellectual curiosity and investigation, and they find that they must acquire a knowledge of oceanography in order to proceed with their research. Oceanography is replete with examples of scientists from other disci ...
... most fruitful avenues for them to pursue. Such a transition is a natural outcome of intellectual curiosity and investigation, and they find that they must acquire a knowledge of oceanography in order to proceed with their research. Oceanography is replete with examples of scientists from other disci ...
Ocean Currents (10.3) PPT
... right or left that is caused by Earth’s rotation. It causes fluids such as air and water to curve to the right in the Northern hemisphere, in a clockwise direction. The Coriolis effect also cases fluids to curve to the left in the southern hemisphere, in a counterclockwise direction. ...
... right or left that is caused by Earth’s rotation. It causes fluids such as air and water to curve to the right in the Northern hemisphere, in a clockwise direction. The Coriolis effect also cases fluids to curve to the left in the southern hemisphere, in a counterclockwise direction. ...
South East Asia Time-Series Station (SEATS)
... As there are various types of physical forcing, the SCS is an ideal site for the study of their effects on the ecosystem. It is also potentially sensitive to climate change due to its juxtaposition to the climate driving engines. The large shelf to interior ratio provides an opportunity to examine t ...
... As there are various types of physical forcing, the SCS is an ideal site for the study of their effects on the ecosystem. It is also potentially sensitive to climate change due to its juxtaposition to the climate driving engines. The large shelf to interior ratio provides an opportunity to examine t ...
05_2_Sci_Earth_T1 (05_2_Sci_Earth_T1)
... 9. The natural process of rocks gradually breaking up and being worn away over time is known as A. weathering. B. cementing. C. sedimentation. D. melting. 10. A moving portion of Earth's crust and upper mantle is called a A. fault. B. fold. C. plate. D. ridge. ...
... 9. The natural process of rocks gradually breaking up and being worn away over time is known as A. weathering. B. cementing. C. sedimentation. D. melting. 10. A moving portion of Earth's crust and upper mantle is called a A. fault. B. fold. C. plate. D. ridge. ...
OCR ASA Level Geography Exploring Oceans Learner Resource 1
... Ocean trench = Long narrow depressions on the sea floor, some of the deepest places on ...
... Ocean trench = Long narrow depressions on the sea floor, some of the deepest places on ...
Lecture 7. Marine Sediments
... The average depth of the ocean is about 4000 meters. The Mariana Trench is 11,022 m deep, the deepest spot on the planet. 8 tons per sq. in. Mt. Everest is “only” ~8667 m above sea level ...
... The average depth of the ocean is about 4000 meters. The Mariana Trench is 11,022 m deep, the deepest spot on the planet. 8 tons per sq. in. Mt. Everest is “only” ~8667 m above sea level ...
Palau Declaration on The Ocean Life and Future
... Palau Declaration on ‘The Ocean: Life and Future’ Charting a course to sustainability Importance of the Ocean to us 1. As Leaders of the Pacific Islands Forum, we have and will continue to play a central role in the stewardship of one of the greatest natural endowments in the world – the Pacific Oce ...
... Palau Declaration on ‘The Ocean: Life and Future’ Charting a course to sustainability Importance of the Ocean to us 1. As Leaders of the Pacific Islands Forum, we have and will continue to play a central role in the stewardship of one of the greatest natural endowments in the world – the Pacific Oce ...
Notes: The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... rate (less than ______ cm/yr), and the ______ ________ _______ near Easter Island, in the South Pacific about 3,400 km west of Chile, has the _________ rate (more than ____ cm/yr). Geologists eventually discovered that Earth’s ______ was cracked into many _______, called _________, that are in con ...
... rate (less than ______ cm/yr), and the ______ ________ _______ near Easter Island, in the South Pacific about 3,400 km west of Chile, has the _________ rate (more than ____ cm/yr). Geologists eventually discovered that Earth’s ______ was cracked into many _______, called _________, that are in con ...
Restless Continents
... continents were once one large landmass (Pangaea) that has broken up and drifted apart. – Alfred Wegener ...
... continents were once one large landmass (Pangaea) that has broken up and drifted apart. – Alfred Wegener ...
Ocean acidification

Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's oceans, caused by the uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. An estimated 30–40% of the carbon dioxide from human activity released into the atmosphere dissolves into oceans, rivers and lakes. To achieve chemical equilibrium, some of it reacts with the water to form carbonic acid. Some of these extra carbonic acid molecules react with a water molecule to give a bicarbonate ion and a hydronium ion, thus increasing ocean acidity (H+ ion concentration). Between 1751 and 1994 surface ocean pH is estimated to have decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14, representing an increase of almost 30% in H+ ion concentration in the world's oceans. Since current and projected ocean pH levels are above 7.0, the oceans are technically alkaline now and will remain so; referring to this effect as ""decreasing ocean alkalinity"" would be equally correct if less politically useful. Earth System Models project that within the last decade ocean acidity exceeded historical analogs and in combination with other ocean biogeochemical changes could undermine the functioning of marine ecosystems and disrupt the provision of many goods and services associated with the ocean.Increasing acidity is thought to have a range of possibly harmful consequences, such as depressing metabolic rates and immune responses in some organisms, and causing coral bleaching. This also causes decreasing oxygen levels as it kills off algae.Other chemical reactions are triggered which result in a net decrease in the amount of carbonate ions available. This makes it more difficult for marine calcifying organisms, such as coral and some plankton, to form biogenic calcium carbonate, and such structures become vulnerable to dissolution. Ongoing acidification of the oceans threatens food chains connected with the oceans. As members of the InterAcademy Panel, 105 science academies have issued a statement on ocean acidification recommending that by 2050, global CO2 emissions be reduced by at least 50% compared to the 1990 level.Ocean acidification has been called the ""evil twin of global warming"" and ""the other CO2 problem"".Ocean acidification has occurred previously in Earth's history. The most notable example is the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which occurred approximately 56 million years ago. For reasons that are currently uncertain, massive amounts of carbon entered the ocean and atmosphere, and led to the dissolution of carbonate sediments in all ocean basins.