Discovering History in - The National WWII Museum
... Battle of Stalingrad ends with Soviet victory over Germany; more than 1,000,000 deaths ...
... Battle of Stalingrad ends with Soviet victory over Germany; more than 1,000,000 deaths ...
File - In The Front Seat
... • September 1938 Ger. demanded Czechoslovakia cede (give) the Sudetenland – Munich Conference – Chamberlin gave in ...
... • September 1938 Ger. demanded Czechoslovakia cede (give) the Sudetenland – Munich Conference – Chamberlin gave in ...
1 The World at War 1914
... The Treaty of Versailles Signed in Versailles, French palace (France’s vision) Germany was forced to pay war reparations Germany was forced to limit its military and return all of its land it conquered German lands were taken and Poland was formed. The treaty crippled the Germans and would ...
... The Treaty of Versailles Signed in Versailles, French palace (France’s vision) Germany was forced to pay war reparations Germany was forced to limit its military and return all of its land it conquered German lands were taken and Poland was formed. The treaty crippled the Germans and would ...
Friday, November 20, 2015
... War II, the world—from individual nations to the United Nations; from religious leaders to professionals in fields as diverse as law, medicine, and science; from presidents and prime ministers to private citizens—confronted its legacy. In light of the moral failures that allowed the Holocaust to hap ...
... War II, the world—from individual nations to the United Nations; from religious leaders to professionals in fields as diverse as law, medicine, and science; from presidents and prime ministers to private citizens—confronted its legacy. In light of the moral failures that allowed the Holocaust to hap ...
The Fall of Berlin
... ● 4 May 1945 General Kinzel and Admiral H. G. von Friedeburg signed the surrender paperwork relating to german forces in the Netherlands, Northwest Germany, Friesian Islands, Heligoland and Schleswig-Holstein. ● The final documents signed by Field Marshal Keitel (Wehrmacht), Admiral Friedeburg (Krie ...
... ● 4 May 1945 General Kinzel and Admiral H. G. von Friedeburg signed the surrender paperwork relating to german forces in the Netherlands, Northwest Germany, Friesian Islands, Heligoland and Schleswig-Holstein. ● The final documents signed by Field Marshal Keitel (Wehrmacht), Admiral Friedeburg (Krie ...
Leisure in Nazi Germany
... • Also a full tour of Italy was offered for 155 marks for the most wealthy Nazi workers. ...
... • Also a full tour of Italy was offered for 155 marks for the most wealthy Nazi workers. ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... Japan and Germany kept fighting long after their defeat in the war was certain. This prolonged fighting gave the Allies time to make plans for a postwar world. In February 1945, Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin met at Yalta on the Black Sea. They discussed final strategy and the future of Germany, E ...
... Japan and Germany kept fighting long after their defeat in the war was certain. This prolonged fighting gave the Allies time to make plans for a postwar world. In February 1945, Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin met at Yalta on the Black Sea. They discussed final strategy and the future of Germany, E ...
World War II
... Hitler and Stalin had divided Poland between them in the Non-aggression Pact With Stalin’s approval, Hitler’s mobile army moved into Poland on September 1, 1939 Hitler’s Luftwaffe (air force) bombed Polish cities His Panzer tank divisions stormed into Poland This swift attack style is called Blitzkr ...
... Hitler and Stalin had divided Poland between them in the Non-aggression Pact With Stalin’s approval, Hitler’s mobile army moved into Poland on September 1, 1939 Hitler’s Luftwaffe (air force) bombed Polish cities His Panzer tank divisions stormed into Poland This swift attack style is called Blitzkr ...
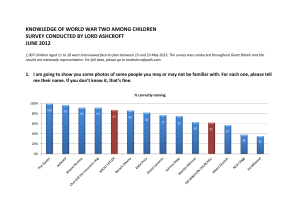
summary of the survey results
... 40% of those aged 17-18 said they didn’t know what happened on D-Day. ...
... 40% of those aged 17-18 said they didn’t know what happened on D-Day. ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... avoid involvement in a war, rather than to prevent one. While the Western democracies sought to avoid war, Germany, Italy, and Japan formed an alliance. It became known as the Axis powers. In Spain, a new, more liberal government passed reforms that upset conservatives. General Francisco Franco, who ...
... avoid involvement in a war, rather than to prevent one. While the Western democracies sought to avoid war, Germany, Italy, and Japan formed an alliance. It became known as the Axis powers. In Spain, a new, more liberal government passed reforms that upset conservatives. General Francisco Franco, who ...
Note Taking Study Guide
... avoid involvement in a war, rather than to prevent one. While the Western democracies sought to avoid war, Germany, Italy, and Japan formed an alliance. It became known as the Axis powers. In Spain, a new, more liberal government passed reforms that upset conservatives. General Francisco Franco, who ...
... avoid involvement in a war, rather than to prevent one. While the Western democracies sought to avoid war, Germany, Italy, and Japan formed an alliance. It became known as the Axis powers. In Spain, a new, more liberal government passed reforms that upset conservatives. General Francisco Franco, who ...
Teacher Notes for Holocaust Definition Prezi
... by the racial hygienists, she and her family were detained and word was sent to Berlin to determine what should be done. The response was the Theresia should be allowed to continue the pregnancy on condition that the babies would be turned over, upon their birth, to the clinic at the University of W ...
... by the racial hygienists, she and her family were detained and word was sent to Berlin to determine what should be done. The response was the Theresia should be allowed to continue the pregnancy on condition that the babies would be turned over, upon their birth, to the clinic at the University of W ...
Bade - WWII and the Postwar decade
... were foreign forced labourers, and mining (36 per cent). In companies with low qualification demands, up to 80 per cent of all workers came from abroad. There were also some extremely specialized fields with a very high level of foreign workers. In the aviation industry, the level of foreign workers ...
... were foreign forced labourers, and mining (36 per cent). In companies with low qualification demands, up to 80 per cent of all workers came from abroad. There were also some extremely specialized fields with a very high level of foreign workers. In the aviation industry, the level of foreign workers ...
WWII & the Holocaust
... 2nd violation of TOV; Hitler sends troops to Rhineland (permanent DMZ- Fr.& GB protest but tale no action) Mussolini completes conquest of Ethiopia Outbreak of the Spanish Civil War: 19361939 – Francisco Franco’s uprising against Demo. Leaders is supplied with $ and supplies by Hitler and Mussolini ...
... 2nd violation of TOV; Hitler sends troops to Rhineland (permanent DMZ- Fr.& GB protest but tale no action) Mussolini completes conquest of Ethiopia Outbreak of the Spanish Civil War: 19361939 – Francisco Franco’s uprising against Demo. Leaders is supplied with $ and supplies by Hitler and Mussolini ...
Chapter 16 A People`s War by Howard Zinn
... Wiped out six million European Jews and millions of other non-aryans “Hitler's Germany was extending totalitarianism, racism, militarism, and overt aggressive warfare beyond what an already cynical world had experienced.” (Zinn, pg.407) (Zinn Pg.407) Page 4 ...
... Wiped out six million European Jews and millions of other non-aryans “Hitler's Germany was extending totalitarianism, racism, militarism, and overt aggressive warfare beyond what an already cynical world had experienced.” (Zinn, pg.407) (Zinn Pg.407) Page 4 ...
Unit 5- WWII Study Guide
... 18. Describe growing Japanese aggression in the 1930s, leading up to Pearl Harbor. 19. What were the possible motives for the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? 20. What was the result of Pearl Harbor? Significance? 21. What measures did the government take to mobilize public support for the war effor ...
... 18. Describe growing Japanese aggression in the 1930s, leading up to Pearl Harbor. 19. What were the possible motives for the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? 20. What was the result of Pearl Harbor? Significance? 21. What measures did the government take to mobilize public support for the war effor ...
WWII Study Guide
... 18. Describe growing Japanese aggression in the 1930s, leading up to Pearl Harbor. 19. What were the possible motives for the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? 20. What was the result of Pearl Harbor? Significance? 21. What measures did the government take to mobilize public support for the war effor ...
... 18. Describe growing Japanese aggression in the 1930s, leading up to Pearl Harbor. 19. What were the possible motives for the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? 20. What was the result of Pearl Harbor? Significance? 21. What measures did the government take to mobilize public support for the war effor ...
Chapter 27: The Rise of Dictators and World War II
... -Mussolini took power in Italy -he started Fascism, a form of nationalism tinged with racism -he took complete control of the country -Adolf Hitler came to power in Germany -he was also a fascist who preached about the racial superiority of Germans -was elected by the people, but then became a dicta ...
... -Mussolini took power in Italy -he started Fascism, a form of nationalism tinged with racism -he took complete control of the country -Adolf Hitler came to power in Germany -he was also a fascist who preached about the racial superiority of Germans -was elected by the people, but then became a dicta ...
Road to world war ii
... Proclaimed U.S. could not remain neutral: its independence had never been in such danger Nazi war aim was world domination Many feel this speech marked entrance of U.S. into the war The U.S. would become the "Great Warehouse" of the Allies ...
... Proclaimed U.S. could not remain neutral: its independence had never been in such danger Nazi war aim was world domination Many feel this speech marked entrance of U.S. into the war The U.S. would become the "Great Warehouse" of the Allies ...
The Steady March Toward War in Europe
... Versailles set the board for a nationalistic rise of dictators in Europe and Asia. The “peace” brought by the war to end all wars was a farce. Germany and Russia were pawns in the imperialistic game of revenge of the Allied nations. Although their economies would fall into depression and ruin, both ...
... Versailles set the board for a nationalistic rise of dictators in Europe and Asia. The “peace” brought by the war to end all wars was a farce. Germany and Russia were pawns in the imperialistic game of revenge of the Allied nations. Although their economies would fall into depression and ruin, both ...
WWII Note Packet (13-14)
... - both sides just “sit” there, staring at each other for weeks, not fighting b. Stalin annexes Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania; defeats Finland c. 1940, Hitler invades Denmark, Norway, then Low Countries (Netherlands, Belgium, etc.) C. France and Britain Fight On 1. The Fall of France a. German army goes ...
... - both sides just “sit” there, staring at each other for weeks, not fighting b. Stalin annexes Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania; defeats Finland c. 1940, Hitler invades Denmark, Norway, then Low Countries (Netherlands, Belgium, etc.) C. France and Britain Fight On 1. The Fall of France a. German army goes ...
Chapter 26 Study Guide
... 9. Compared to the other nations that fought in the war, the United States fared much better. Why did the U.S. lose fewer lives than other nations that fought? Why did the U.S. economy come out of the war stronger than ...
... 9. Compared to the other nations that fought in the war, the United States fared much better. Why did the U.S. lose fewer lives than other nations that fought? Why did the U.S. economy come out of the war stronger than ...
AKS 47: World War II
... Early Challenges to World Peace Munich Conference (1938) Italy, France, Great Britain, Germany meet Allies follow policy of appeasement Hitler promises to halt expansionist efforts British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain (1869-1940) promises “peace for our time” Hitler signs secret Russian-Germa ...
... Early Challenges to World Peace Munich Conference (1938) Italy, France, Great Britain, Germany meet Allies follow policy of appeasement Hitler promises to halt expansionist efforts British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain (1869-1940) promises “peace for our time” Hitler signs secret Russian-Germa ...
Ch. 17 – World War II
... – Growth of dictatorships in Europe & Japan (and their invasion of other countries). – Japanese attack on U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor (December 7th 1941). World War II would be a fight between the: – Allies – United States, Great Britain, Soviet Union (and France, China) – Axis Powers – German ...
... – Growth of dictatorships in Europe & Japan (and their invasion of other countries). – Japanese attack on U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor (December 7th 1941). World War II would be a fight between the: – Allies – United States, Great Britain, Soviet Union (and France, China) – Axis Powers – German ...
Unit 4 Selfcheck #1 Answers
... and right wing parties in Germany at the time? The left wing party was the communist party, and the right wing party was the NAZI party. There were also other right wing parties referred to as nationalist parties. 3. When Hitler was elected in 1932, what became his title? Hitler’s new title was Chan ...
... and right wing parties in Germany at the time? The left wing party was the communist party, and the right wing party was the NAZI party. There were also other right wing parties referred to as nationalist parties. 3. When Hitler was elected in 1932, what became his title? Hitler’s new title was Chan ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.