WWII - Barren County Schools
... -argued Germans needed more lebenscraum, living space (Polish, Russian territory) ...
... -argued Germans needed more lebenscraum, living space (Polish, Russian territory) ...
Beginning of WWII and Main Events
... • w/ the armistice, Germany had direct control over northern and western 60% of France • French gov’t would keep control of the rest of France, but it was set up as a puppet gov’t collaborating w/ Germans (Vichy Gov’t) • Charles de Gaulle (a French general refuses the Vichy Gov’t and creates Free Fr ...
... • w/ the armistice, Germany had direct control over northern and western 60% of France • French gov’t would keep control of the rest of France, but it was set up as a puppet gov’t collaborating w/ Germans (Vichy Gov’t) • Charles de Gaulle (a French general refuses the Vichy Gov’t and creates Free Fr ...
Secretary Hull`s Reciprocal Trade Agreements
... with the German dictator—the Hitler-Stalin pact meant that Hitler could now wage war on Poland and the Western democracies, without fear of the Soviet Union turning against him The Soviet dictator was plotting to turn his German accomplice against the West democracies, the two warring camps would th ...
... with the German dictator—the Hitler-Stalin pact meant that Hitler could now wage war on Poland and the Western democracies, without fear of the Soviet Union turning against him The Soviet dictator was plotting to turn his German accomplice against the West democracies, the two warring camps would th ...
World War II Crossword
... 1. American general who commanded Allied forces in Africa before becoming Supreme Commander of Allied Forces in Europe (17-3) 3. nation whose invasion triggered World War II (17-1) 4. provided economic aid to European nations attempting to rebuild after world War II (17-5) 5. Soviet city under siege ...
... 1. American general who commanded Allied forces in Africa before becoming Supreme Commander of Allied Forces in Europe (17-3) 3. nation whose invasion triggered World War II (17-1) 4. provided economic aid to European nations attempting to rebuild after world War II (17-5) 5. Soviet city under siege ...
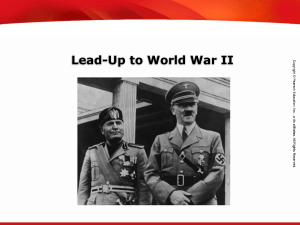
The interwar years - Plain Local Schools
... Fascism: Complete devotion to your country. Nothing is better or more important than the nation Mussolini had the goal of creating a new Roman Empire and found himself involved in several foreign affairs to accomplish this goal None was more important than Ethiopia in 1935 ...
... Fascism: Complete devotion to your country. Nothing is better or more important than the nation Mussolini had the goal of creating a new Roman Empire and found himself involved in several foreign affairs to accomplish this goal None was more important than Ethiopia in 1935 ...
How did the use of propaganda affect the
... that, however skilled, Goebbels was little more than a clever ranter who won support from his countrymen by appealing to base feelings of envy, revenge, conceit and arrogant pride” (Weber, “Goebbels’ Place in History”). Weber shows that some people did not find Goebbels or his propaganda methods eff ...
... that, however skilled, Goebbels was little more than a clever ranter who won support from his countrymen by appealing to base feelings of envy, revenge, conceit and arrogant pride” (Weber, “Goebbels’ Place in History”). Weber shows that some people did not find Goebbels or his propaganda methods eff ...
World War II 1941 to 1945
... maintaining peace in Europe. Hitler promised that he would be good from now on and follow all the rules. After the conference, Hitler took all of Czechoslovakia. Britain and France did nothing to Germany. However, they did begin to build up their military. Chamberlain realized that a war with German ...
... maintaining peace in Europe. Hitler promised that he would be good from now on and follow all the rules. After the conference, Hitler took all of Czechoslovakia. Britain and France did nothing to Germany. However, they did begin to build up their military. Chamberlain realized that a war with German ...
The 1920`s and the Great Depression
... Nazism – A. Mein Kampf – B. Hitler explained Nazism in three parts: 1. Extreme Nationalism – Germany above all. 2. Aryan Supremacy – master race and inferior races 3. National Expansion – to secure more “living space” for GER C. 1932 – 6 million Germans were unemployed and turned to Hitler for answe ...
... Nazism – A. Mein Kampf – B. Hitler explained Nazism in three parts: 1. Extreme Nationalism – Germany above all. 2. Aryan Supremacy – master race and inferior races 3. National Expansion – to secure more “living space” for GER C. 1932 – 6 million Germans were unemployed and turned to Hitler for answe ...
World War II
... 7. Why did Franco and his Nationalist forces ultimately win? 8. What were the political, economic, and military effects for Spain and the rest of Europe of the Spanish Civil War? 9. How did Austria become part of the Third Reich? 10. What was the ‘the Sudetenland problem’? How was it resolved? 11. W ...
... 7. Why did Franco and his Nationalist forces ultimately win? 8. What were the political, economic, and military effects for Spain and the rest of Europe of the Spanish Civil War? 9. How did Austria become part of the Third Reich? 10. What was the ‘the Sudetenland problem’? How was it resolved? 11. W ...
WWII
... conquers Ethiopia (1936) • Germany takes over Rhineland, shock French who take no action • Germany, Italy, their allies form alliance known as the Axis • Supported by Hitler and Mussolini, fascist forces take over Spain • Hitler invades Austria (1938), welcomed by many Germans, Austrians ...
... conquers Ethiopia (1936) • Germany takes over Rhineland, shock French who take no action • Germany, Italy, their allies form alliance known as the Axis • Supported by Hitler and Mussolini, fascist forces take over Spain • Hitler invades Austria (1938), welcomed by many Germans, Austrians ...
Chapter 17 Section 1
... • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. ...
... • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. ...
Class Notes_PDF - Jessamine County Schools
... A Pact for the Sudetenland…and the Appeasement Goes On…- Following the easy annexation of Austria, Hitler set his eyes on uniting some 3 million Germanspeaking people living in the resource rich, mountainous western region of Czechoslovakia, called the Sudetenland. Hitler charged that the Czechs w ...
... A Pact for the Sudetenland…and the Appeasement Goes On…- Following the easy annexation of Austria, Hitler set his eyes on uniting some 3 million Germanspeaking people living in the resource rich, mountainous western region of Czechoslovakia, called the Sudetenland. Hitler charged that the Czechs w ...
Chapter 27: World War II and Its Aftermath: 1939 – 1945 More than
... Austria pay for World War I damages. This destroyed the economies of these two countries. These hard times encouraged the rise of dictators. People were willing to follow leaders who promised a better way of life. Third, the three Axis countries were totalitarian dictatorships. They did not believe ...
... Austria pay for World War I damages. This destroyed the economies of these two countries. These hard times encouraged the rise of dictators. People were willing to follow leaders who promised a better way of life. Third, the three Axis countries were totalitarian dictatorships. They did not believe ...
World War II
... Fascism: a political philosophy, movement, or regime that exalts nation and often race above the individual and that stands for a centralizedautocratic government headed by a dictatorial leader, severe economic and social regimentation, and forcible suppression of opposition ...
... Fascism: a political philosophy, movement, or regime that exalts nation and often race above the individual and that stands for a centralizedautocratic government headed by a dictatorial leader, severe economic and social regimentation, and forcible suppression of opposition ...
Slide 1
... In 1933, Hitler started to put his plan into action – He left the League of Nations – Gradually he started to increase the size of the military – He tested to see if France and Britain would stop Germany from using their military – 1939 he invades Czechoslovakia and Poland ...
... In 1933, Hitler started to put his plan into action – He left the League of Nations – Gradually he started to increase the size of the military – He tested to see if France and Britain would stop Germany from using their military – 1939 he invades Czechoslovakia and Poland ...
22_The Consequences of World War II
... As the map demonstrates, the Auschwitz complex served as a concentration camp and an industrial centre for the exploitation of brutal slave labour - but it was the perpetration of genocide that became ...
... As the map demonstrates, the Auschwitz complex served as a concentration camp and an industrial centre for the exploitation of brutal slave labour - but it was the perpetration of genocide that became ...
The Treaty of Versailles
... contributed to the defense of our nation, often overlooked in our remembrances are the valiant efforts of African Americans. Throughout the war years they repeatedly had to battle adversaries on two fronts: the enemy overseas and racism at home. Black Americans recognized the paradox of fighting a w ...
... contributed to the defense of our nation, often overlooked in our remembrances are the valiant efforts of African Americans. Throughout the war years they repeatedly had to battle adversaries on two fronts: the enemy overseas and racism at home. Black Americans recognized the paradox of fighting a w ...
The Treaty of Versailles - Easy Peasy All-in
... contributed to the defense of our nation, often overlooked in our remembrances are the valiant efforts of African Americans. Throughout the war years they repeatedly had to battle adversaries on two fronts: the enemy overseas and racism at home. Black Americans recognized the paradox of fighting a w ...
... contributed to the defense of our nation, often overlooked in our remembrances are the valiant efforts of African Americans. Throughout the war years they repeatedly had to battle adversaries on two fronts: the enemy overseas and racism at home. Black Americans recognized the paradox of fighting a w ...
Hitler`s Aggressions
... The Sudentenland – the area around the rim of Czechoslovakia – had a large population of Germanspeaking people. Taking the Sudenten would leave the country defenseless. ...
... The Sudentenland – the area around the rim of Czechoslovakia – had a large population of Germanspeaking people. Taking the Sudenten would leave the country defenseless. ...
PRIMARY - Le Mémorial de Caen
... imposes his dictatorship on Germany. The Third Reich replaces the Republic of Weimar. Look at the photos on the wall. Can you tell that Germany is getting ready for the war? ...
... imposes his dictatorship on Germany. The Third Reich replaces the Republic of Weimar. Look at the photos on the wall. Can you tell that Germany is getting ready for the war? ...
Causes of World War II
... Fascism: a political philosophy, movement, or regime that exalts nation and often race above the individual and that stands for a centralized autocratic government headed by a dictatorial leader, severe economic and social regimentation, and forcible suppression of opposition ...
... Fascism: a political philosophy, movement, or regime that exalts nation and often race above the individual and that stands for a centralized autocratic government headed by a dictatorial leader, severe economic and social regimentation, and forcible suppression of opposition ...
File - Tennessee Geographic Alliance
... During the night of June 5-6, 1944, Marie-Louise's sleep is disrupted by the sound of cannon fire and aircraft overhead. The commotion intensifies and the Germans start packing equipment into trucks in preparation of leaving the area. Confused, Marie-Louise is unsure whether the aircraft and gunfire ...
... During the night of June 5-6, 1944, Marie-Louise's sleep is disrupted by the sound of cannon fire and aircraft overhead. The commotion intensifies and the Germans start packing equipment into trucks in preparation of leaving the area. Confused, Marie-Louise is unsure whether the aircraft and gunfire ...
9th WWII UPDATED
... 1937 – Hitler plans to absorb Austria and Czechoslovakia into the Third Reich. “Since WWI, Czechoslovakia had developed into a prosperous democracy with a strong army and a defense treaty with France. But 3 million German-speaking people lived in the Sudetenland - a western border region of Czechos ...
... 1937 – Hitler plans to absorb Austria and Czechoslovakia into the Third Reich. “Since WWI, Czechoslovakia had developed into a prosperous democracy with a strong army and a defense treaty with France. But 3 million German-speaking people lived in the Sudetenland - a western border region of Czechos ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.