GCSE_C2_Revision_+_Exam_Questions
... Substances that consist of simple molecules have only weak forces between the molecules (intermolecular forces). It is these intermolecular forces that are overcome, not the covalent bonds, when the substance melts or boils. Substances that consist of simple molecules do not conduct electricity beca ...
... Substances that consist of simple molecules have only weak forces between the molecules (intermolecular forces). It is these intermolecular forces that are overcome, not the covalent bonds, when the substance melts or boils. Substances that consist of simple molecules do not conduct electricity beca ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... 2. Write the ionic equation showing the strong electrolytes completely dissociated into cations and anions. 3. Cancel the spectator ions on both sides of the ionic equation 4. Check that charges and number of atoms are balanced in the net ionic equation ...
... 2. Write the ionic equation showing the strong electrolytes completely dissociated into cations and anions. 3. Cancel the spectator ions on both sides of the ionic equation 4. Check that charges and number of atoms are balanced in the net ionic equation ...
1 Q. If ΔrH is positive, what can you say about the reaction? 2 Q If
... up (and so its container would get hot) because it is releasing energy from its surroundings. ...
... up (and so its container would get hot) because it is releasing energy from its surroundings. ...
Example 1-2
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
Week 1 NEPHAR 201- Analytical Chemistry II_Introduction_5
... A solution of sodium chloride, NaCl (500 mL) contains 20.0 g of NaCl. What is the molar concentration of NaCl in this solution? Describe how this ...
... A solution of sodium chloride, NaCl (500 mL) contains 20.0 g of NaCl. What is the molar concentration of NaCl in this solution? Describe how this ...
Chemistry of the Non
... SO2 in water produces sulfurous acid, H2SO3, a weak diprotic acid. SO2 is toxic to fungi and is used to sterilize dried fruit and wine. • Na2SO3 and NaHSO3 are used as preservatives. • Many people are allergic to these agents and must avoid foods treated with them. When sulfur burns in air both SO2 ...
... SO2 in water produces sulfurous acid, H2SO3, a weak diprotic acid. SO2 is toxic to fungi and is used to sterilize dried fruit and wine. • Na2SO3 and NaHSO3 are used as preservatives. • Many people are allergic to these agents and must avoid foods treated with them. When sulfur burns in air both SO2 ...
CBSE/12th Class/2010/CHEMISTRY
... Ionic solids Ionic solids are insulators in solid state but conductors in molten state and in aqueous solutions. Ans.2 In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to a given substance (such as reactant, catalyst or product) is defined as the index, or exponent, to which its concentratio ...
... Ionic solids Ionic solids are insulators in solid state but conductors in molten state and in aqueous solutions. Ans.2 In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to a given substance (such as reactant, catalyst or product) is defined as the index, or exponent, to which its concentratio ...
ch8 - Otterville R-VI School District
... BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s) iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS(aq) + HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl(aq) + NaOH NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
... BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s) iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS(aq) + HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl(aq) + NaOH NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2 KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) ...
Chapter 4 2013
... fluoride ion acetate ion cyanide ion nitrite ion carbonate ion sulfite ion phosphate ion oxalate ion ...
... fluoride ion acetate ion cyanide ion nitrite ion carbonate ion sulfite ion phosphate ion oxalate ion ...
158KB - NZQA
... Ammonia is a weak base, and so doesn’t ionise fully. This means that there are still many ammonia molecules in the reaction mixture with just some ammonium and hydroxide ions. Because all 3 species are present, the labels of ammonia or ammonium hydroxide are equally valid. ...
... Ammonia is a weak base, and so doesn’t ionise fully. This means that there are still many ammonia molecules in the reaction mixture with just some ammonium and hydroxide ions. Because all 3 species are present, the labels of ammonia or ammonium hydroxide are equally valid. ...
Chapter 4
... Weak acids are acids in which only some of the molecules are ionized in water; the rest remain as intact molecules The dissociation of a weak acid in solution is written using a double arrow to indicate that the dissociation does not go to completion ...
... Weak acids are acids in which only some of the molecules are ionized in water; the rest remain as intact molecules The dissociation of a weak acid in solution is written using a double arrow to indicate that the dissociation does not go to completion ...
Get Solutions - Iqraa group of institutes
... (i) Nitration is carried out in presence of concentrated HNO3 + concentrated H2SO4. (ii) Aniline acts as base. In presence of H2SO4 its protonation takes place and anilinium ion is formed ...
... (i) Nitration is carried out in presence of concentrated HNO3 + concentrated H2SO4. (ii) Aniline acts as base. In presence of H2SO4 its protonation takes place and anilinium ion is formed ...
1063-1069 - Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences
... formula C 2 2 H 2 2 O 1 0 +1. Another important peak at m/z=301 which means (M + -146) proving the presence of a deoxy sugar moiety attached to the aglycone. The 1 H and 1 3 C NMR spectrum showed the most important signals of diosmetin like (Nair et al., 1986; W u et al., 1983) OCH 3 protons appear ...
... formula C 2 2 H 2 2 O 1 0 +1. Another important peak at m/z=301 which means (M + -146) proving the presence of a deoxy sugar moiety attached to the aglycone. The 1 H and 1 3 C NMR spectrum showed the most important signals of diosmetin like (Nair et al., 1986; W u et al., 1983) OCH 3 protons appear ...
Differentiated Chemistry First Term Test Review
... A commercially valuable paint and adhesive stripper, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), (CH3)2SO, can be prepared by the reaction of oxygen with dimethyl sulfide, (CH3)2S, using a ratio of one mole oxygen to two moles of the sulfide: O2 + 2(CH3)2S → 2(CH3)2SO If this process has an 83% percent yield, how ma ...
... A commercially valuable paint and adhesive stripper, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), (CH3)2SO, can be prepared by the reaction of oxygen with dimethyl sulfide, (CH3)2S, using a ratio of one mole oxygen to two moles of the sulfide: O2 + 2(CH3)2S → 2(CH3)2SO If this process has an 83% percent yield, how ma ...
Elements (NonMetals)
... Lowest density of any chemical substance Used in blimps in 1930s but flammable Gas at room Temp B.P. –253°C (20K) and M.P.-259°C (14K) Insoluble in water: 2mL gas/ 1L of water Found in H2O, organic and biological molecules Most common element in universe H2 (H-H) isoelectronic with He H has a small ...
... Lowest density of any chemical substance Used in blimps in 1930s but flammable Gas at room Temp B.P. –253°C (20K) and M.P.-259°C (14K) Insoluble in water: 2mL gas/ 1L of water Found in H2O, organic and biological molecules Most common element in universe H2 (H-H) isoelectronic with He H has a small ...
Acids - Beck-Shop
... hydrogen atoms, but only the hydrogen atom on the COOH group is released as H+. Even then, only about one molecule in every hundred dissociates, so ethanoic acid is a weak acid. Most organic acids, like ethanoic acid, are weak acids. ...
... hydrogen atoms, but only the hydrogen atom on the COOH group is released as H+. Even then, only about one molecule in every hundred dissociates, so ethanoic acid is a weak acid. Most organic acids, like ethanoic acid, are weak acids. ...
Ionic bonding - Nidderdale High School
... Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up during the reaction. Different reactions need different catalysts. Catalysts are important in increasing the rates of chemical reactions used in industrial processes to reduce costs. Pressure: Increasing pressure increases ...
... Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up during the reaction. Different reactions need different catalysts. Catalysts are important in increasing the rates of chemical reactions used in industrial processes to reduce costs. Pressure: Increasing pressure increases ...
chlorobenzene/acetic acid 2:1 v/v msds
... Immediately remove contaminated clothing. Rinse the skin immediately with lots of water. Get medical attention immediately. EYE CONTACT May cause permanent damage if eye is not immediately irrigated. Make sure to remove any contact lenses from the eyes before rinsing. Promptly wash eyes with plenty ...
... Immediately remove contaminated clothing. Rinse the skin immediately with lots of water. Get medical attention immediately. EYE CONTACT May cause permanent damage if eye is not immediately irrigated. Make sure to remove any contact lenses from the eyes before rinsing. Promptly wash eyes with plenty ...
pdfInt 2 Homework Unit 2 1 MB
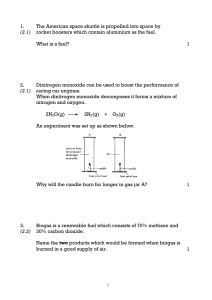
... Scientists have been experimenting to find ways of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. One of these ways involves placing concrete balls on the sea bed. They hope that green plants called algae will grow on the balls and this will help to reduce the carbon dioxide level. Give a reason why the ...
... Scientists have been experimenting to find ways of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. One of these ways involves placing concrete balls on the sea bed. They hope that green plants called algae will grow on the balls and this will help to reduce the carbon dioxide level. Give a reason why the ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.