Latent Heat of Vaporization and Speci c Heat - Physlab
... We know that molecules are always on the move as they have kinetic energy, but the question is, how is this energy shared? James Clerk Maxwell solved this problem for a large number of molecules. He said that energy is equally divided in all the directions a molecule is free to move. The average ene ...
... We know that molecules are always on the move as they have kinetic energy, but the question is, how is this energy shared? James Clerk Maxwell solved this problem for a large number of molecules. He said that energy is equally divided in all the directions a molecule is free to move. The average ene ...
Atomic Structure
... plenty of cold drinks, which they wish to keep cold. They fill their cool box with _______ and put in their drinks. The temperature outside the cool box is much greater than the temperature inside. As the day progresses _______ energy is transferred through the cool box walls. The flow of thermal en ...
... plenty of cold drinks, which they wish to keep cold. They fill their cool box with _______ and put in their drinks. The temperature outside the cool box is much greater than the temperature inside. As the day progresses _______ energy is transferred through the cool box walls. The flow of thermal en ...
Chapter 20 Problems
... convection and conduction.) The filament has a surface area of 0.250 mm2 and an emissivity of 0.950. Find the filament’s ...
... convection and conduction.) The filament has a surface area of 0.250 mm2 and an emissivity of 0.950. Find the filament’s ...
paper - Indico
... Cryosorption pumps are used to achieve ultra-high vacuum in such harsh conditions. An important aspect in their development is the proper adhesion of the activated carbon granules onto the metallic cryopanel and their cooling to the lowest possible temperature by using high thermal conductivity adhe ...
... Cryosorption pumps are used to achieve ultra-high vacuum in such harsh conditions. An important aspect in their development is the proper adhesion of the activated carbon granules onto the metallic cryopanel and their cooling to the lowest possible temperature by using high thermal conductivity adhe ...
Basic Properties of the Atmosphere
... placed in contact with the parcel of air. Since the air is now 0.76 K warmer than the water, heat will flow from the air to the water until both objects reach the same temperature (somewhere around 288.4 K). After they are in equilibrium again, ~60% of the heat initially added to the air will have t ...
... placed in contact with the parcel of air. Since the air is now 0.76 K warmer than the water, heat will flow from the air to the water until both objects reach the same temperature (somewhere around 288.4 K). After they are in equilibrium again, ~60% of the heat initially added to the air will have t ...
chem 155 trial questions
... 34. An isolated system is best described by which one of the following statements? a. Neither matter nor heat can pass into or out of the system b. The system has a boundary which allows heat to be transferred but does not allow material to pass into or out of the system c. The system has a diatherm ...
... 34. An isolated system is best described by which one of the following statements? a. Neither matter nor heat can pass into or out of the system b. The system has a boundary which allows heat to be transferred but does not allow material to pass into or out of the system c. The system has a diatherm ...
The Mayer-Joule Principle: The Foundation of
... terms of heating times using a constant heating source. Bodies in thermal equilibrium would have the same temperature independent of size. Equally important, Black viewed heat as a measurable quantity, an impossibility with the heat asmotion-theory. He knew that the time required to boil water depen ...
... terms of heating times using a constant heating source. Bodies in thermal equilibrium would have the same temperature independent of size. Equally important, Black viewed heat as a measurable quantity, an impossibility with the heat asmotion-theory. He knew that the time required to boil water depen ...
Is there a negative absolute temperature?
... • It violates Third Law (when applied to a simple quantum oscillator, given a constant heat capacity) ...
... • It violates Third Law (when applied to a simple quantum oscillator, given a constant heat capacity) ...
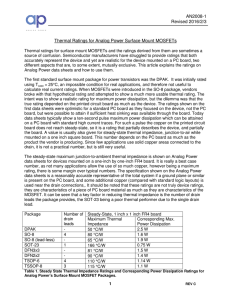
Thermal Ratings of Surface Mount Packages
... Thermal ratings for surface mount MOSFETs and the ratings derived from them are sometimes a source of confusion. Semiconductor manufacturers have struggled to provide ratings that both accurately represent the device and yet are realistic for the device mounted on a PC board, two different aspects t ...
... Thermal ratings for surface mount MOSFETs and the ratings derived from them are sometimes a source of confusion. Semiconductor manufacturers have struggled to provide ratings that both accurately represent the device and yet are realistic for the device mounted on a PC board, two different aspects t ...
Course Specifications
... 3 Be able to point out the relation between the basic mechanics (dealt with in Physics 1 I), and the physical principles studied in this course, be able to apply the principles 1 and techniques of the introductory mechanics when dealing with vibrations, waves, 1 optics, thermal physics. 4 Show ...
... 3 Be able to point out the relation between the basic mechanics (dealt with in Physics 1 I), and the physical principles studied in this course, be able to apply the principles 1 and techniques of the introductory mechanics when dealing with vibrations, waves, 1 optics, thermal physics. 4 Show ...
Physical Chemistry - School of Chemistry, University of Leeds
... Read the additional instructions with each set of apparatus before starting the run. Each run can be performed in any order. Measure 100 cm3 of the 80/20 water / acetone reaction solvent and pour this into the reaction vessel. Make sure the magnetic stirrer bar is rotating. Note the temperat ...
... Read the additional instructions with each set of apparatus before starting the run. Each run can be performed in any order. Measure 100 cm3 of the 80/20 water / acetone reaction solvent and pour this into the reaction vessel. Make sure the magnetic stirrer bar is rotating. Note the temperat ...
ESO201A: Thermodynamics
... Condition for minimum work associated with compression with intercooling, reversible adiabatic and reversible isothermal efficiencies of compressor, Introduction to the concept of exergy or work potential, definitions, dead state, forms of exergy, exergy of kinetic and potential energy. Lecture #27 ...
... Condition for minimum work associated with compression with intercooling, reversible adiabatic and reversible isothermal efficiencies of compressor, Introduction to the concept of exergy or work potential, definitions, dead state, forms of exergy, exergy of kinetic and potential energy. Lecture #27 ...
Study of Thermal Resistance Measurement Techniques
... Sometimes different thermocouple systems differed at certain temperatures but agree at other temperatures. To choose a thermocouple system, it is examined versus a precision thermometer. c) Current Sources: Making a perfect Current Source is difficult and can lead to oscillations due to the small lo ...
... Sometimes different thermocouple systems differed at certain temperatures but agree at other temperatures. To choose a thermocouple system, it is examined versus a precision thermometer. c) Current Sources: Making a perfect Current Source is difficult and can lead to oscillations due to the small lo ...
The laws of thermodynamics - Assets
... The quasistatic process is defined as a thermodynamic process which takes place unlimitedly slowly. In the theoretical formulation of thermodynamics it is customary to consider a sample of gas contained in a cylinder with a frictionless piston. The walls of the cylinder are made up of a diathermal, i ...
... The quasistatic process is defined as a thermodynamic process which takes place unlimitedly slowly. In the theoretical formulation of thermodynamics it is customary to consider a sample of gas contained in a cylinder with a frictionless piston. The walls of the cylinder are made up of a diathermal, i ...
Jeopardy Heat
... State the zeroth law of thermodynamics. If Body A in in thermal equilibrium with Body B & If Body B in in thermal equilibrium with Body T then Body A in in thermal equilibrium with Body T. ...
... State the zeroth law of thermodynamics. If Body A in in thermal equilibrium with Body B & If Body B in in thermal equilibrium with Body T then Body A in in thermal equilibrium with Body T. ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... As the temperature of a solid increases, the vibrations of the individual molecules become larger. When these vibrations become larger, the average distance between the molecules increases to accommodate these larger oscillations, and the solid expands. In a liquid or a gas, the individual molecul ...
... As the temperature of a solid increases, the vibrations of the individual molecules become larger. When these vibrations become larger, the average distance between the molecules increases to accommodate these larger oscillations, and the solid expands. In a liquid or a gas, the individual molecul ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... As the temperature of a solid increases, the vibrations of the individual molecules become larger. When these vibrations become larger, the average distance between the molecules increases to accommodate these larger oscillations, and the solid expands. In a liquid or a gas, the individual molecules ...
... As the temperature of a solid increases, the vibrations of the individual molecules become larger. When these vibrations become larger, the average distance between the molecules increases to accommodate these larger oscillations, and the solid expands. In a liquid or a gas, the individual molecules ...
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. An object with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. When the temperature of the body is greater than absolute zero, interatomic collisions cause the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules to change. This results in charge-acceleration and/or dipole oscillation which produces electromagnetic radiation, and the wide spectrum of radiation reflects the wide spectrum of energies and accelerations that occur even at a single temperature.Examples of thermal radiation include the visible light and infrared light emitted by an incandescent light bulb, the infrared radiation emitted by animals and detectable with an infrared camera, and the cosmic microwave background radiation. Thermal radiation is different from thermal convection and thermal conduction—a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold.Sunlight is part of thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and different spectral distribution (infrared rather than visible) because it is cooler. The Earth's absorption of solar radiation, followed by its outgoing thermal radiation are the two most important processes that determine the temperature and climate of the Earth.If a radiation-emitting object meets the physical characteristics of a black body in thermodynamic equilibrium, the radiation is called blackbody radiation. Planck's law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object's temperature. Wien's displacement law determines the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation, and the Stefan–Boltzmann law gives the radiant intensity.Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer.