The Nature of Molecules
... ***Inner energy shells (those closest to the nucleus) contain electrons with lower energy than the outer energy shells ***important concept as it will be discussed in the Light Dependent reaction of Photosynthesis ...
... ***Inner energy shells (those closest to the nucleus) contain electrons with lower energy than the outer energy shells ***important concept as it will be discussed in the Light Dependent reaction of Photosynthesis ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... When a molecule contains two or more atoms of different elements, it is called a compound. CO2 ...
... When a molecule contains two or more atoms of different elements, it is called a compound. CO2 ...
Chemical Basis of Life
... Kinetic: energy of motion Potential: energy due to location or structure; capability ...
... Kinetic: energy of motion Potential: energy due to location or structure; capability ...
Surface Characterization by Spectroscopy and Microscopy
... vapor at low temperature, effectively has an interface that is one atomic distance in width. A more diffuse interface is present in the extreme case, where we may consider a system near its critical point, such as a liquid in contact and hence at equilibrium with its own vapor at high temperature an ...
... vapor at low temperature, effectively has an interface that is one atomic distance in width. A more diffuse interface is present in the extreme case, where we may consider a system near its critical point, such as a liquid in contact and hence at equilibrium with its own vapor at high temperature an ...
Bonding in Atoms
... • Polyatomic ions are IONS that consist of multiple atoms • Polyatomic ions are used in ionic bonding because there is still an exchange in electrons ...
... • Polyatomic ions are IONS that consist of multiple atoms • Polyatomic ions are used in ionic bonding because there is still an exchange in electrons ...
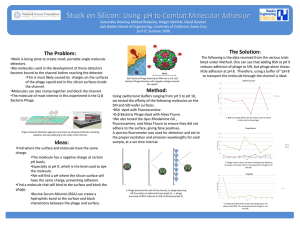
Adhesion

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another (cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another). The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are certain emergent mechanical effects that will also be discussed at the end of the article.