Unit 6 Worksheet Package
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
Syllabus Of AMIE Exams Section A (Non Diploma Stream)
... Introduction to materials. Metal and alloys, ceramics, polymers and semi conducting materials-introduction and application as engineering materials. Defects in solids. Point, line and surface defects. Diffusion in solids. Phase diagrams. Mono-component and binary systems, non-equilibrium system, pha ...
... Introduction to materials. Metal and alloys, ceramics, polymers and semi conducting materials-introduction and application as engineering materials. Defects in solids. Point, line and surface defects. Diffusion in solids. Phase diagrams. Mono-component and binary systems, non-equilibrium system, pha ...
PowerPoint material for lecture 1 (September 4, 2012)
... other and move around randomly. Usually these are liquids. Solutions are usually transparent. ...
... other and move around randomly. Usually these are liquids. Solutions are usually transparent. ...
Chem Regents 2015 A Few Things
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
File
... valence shell) usually determine how an atom will react Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is full Atoms can gain or lose electrons to ...
... valence shell) usually determine how an atom will react Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is full Atoms can gain or lose electrons to ...
Nature of Atoms Atomic Structure Atomic number Atomic mass
... ◦ Cl atom gains an electron to become Cl– ◦ Opposite charges attract so that Na+ and Cl– remain associated as an ionic compound ...
... ◦ Cl atom gains an electron to become Cl– ◦ Opposite charges attract so that Na+ and Cl– remain associated as an ionic compound ...
Review 3rd Qtr KEY
... Filled & ½ filled orbital’s are more stable. 14. Complete the following question based upon Cobalt (#27) a) Give the noble gas electron configuration for this element: _________________________ b) What are the quantum numbers for this element? _____, _____, _____, _____ c) How many unpaired electron ...
... Filled & ½ filled orbital’s are more stable. 14. Complete the following question based upon Cobalt (#27) a) Give the noble gas electron configuration for this element: _________________________ b) What are the quantum numbers for this element? _____, _____, _____, _____ c) How many unpaired electron ...
Small Business Success on the Web
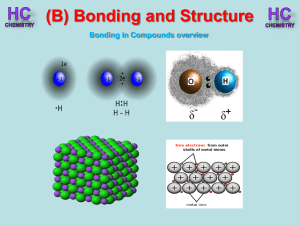
... Polar covalent bonds Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher electronegativity ...
... Polar covalent bonds Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher electronegativity ...
2nd Semester Exam Review
... • Gasses consist of small particles that take up little volume relative to the volume of empty space around them – Gas molecules are very far apart and therefore don’t experience attractive or repulsive forces. ...
... • Gasses consist of small particles that take up little volume relative to the volume of empty space around them – Gas molecules are very far apart and therefore don’t experience attractive or repulsive forces. ...
Adhesion

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another (cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another). The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are certain emergent mechanical effects that will also be discussed at the end of the article.