Nature of Atoms Atomic Structure
... – Cl atom gains an electron to become Cl– – Opposite charges attract so that Na+ and Cl– remain associated as an ionic compound ...
... – Cl atom gains an electron to become Cl– – Opposite charges attract so that Na+ and Cl– remain associated as an ionic compound ...
Introduction to spectroscopy
... Spectroscopy: Using a probe (radiation, ions or electrons) and sorting its content into energy bins to identify the materials response in each region of the spectrum Recall that any material system made up of atoms, molecules and electrons responds to external stimuli such as light or particles over ...
... Spectroscopy: Using a probe (radiation, ions or electrons) and sorting its content into energy bins to identify the materials response in each region of the spectrum Recall that any material system made up of atoms, molecules and electrons responds to external stimuli such as light or particles over ...
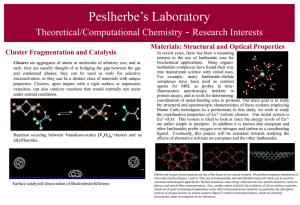
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... such, they are usually thought of as bridging the gap between the gas and condensed phases; they can be used as tools for selective microsolvation, or they can be a distinct class of materials with unique properties. Clusters, upon impact with a rigid surface at supersonic velocities, can also catal ...
... such, they are usually thought of as bridging the gap between the gas and condensed phases; they can be used as tools for selective microsolvation, or they can be a distinct class of materials with unique properties. Clusters, upon impact with a rigid surface at supersonic velocities, can also catal ...
Basics of Chemistry
... in another Can occur wherever an -OH exists in a larger molecule Weak bonds ...
... in another Can occur wherever an -OH exists in a larger molecule Weak bonds ...
chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... 2.2 Elements and Compounds • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
Adhesion

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another (cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another). The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are certain emergent mechanical effects that will also be discussed at the end of the article.