Term 2 Exam 2 Study Guide Pt 2 File
... What are 2 types of insects that sometimes spread human diseases? What do termites eat? What is a pollinator? Why is it bad for some plants if the number of bees keeps going down? ...
... What are 2 types of insects that sometimes spread human diseases? What do termites eat? What is a pollinator? Why is it bad for some plants if the number of bees keeps going down? ...
Packet 10 Classification F13(2).
... dry conditions or during the heat of the day plants can close these holes to prevent water loss. If a plant has an excess of water, then the holes remain open and water can exit the leaves through the holes. ...
... dry conditions or during the heat of the day plants can close these holes to prevent water loss. If a plant has an excess of water, then the holes remain open and water can exit the leaves through the holes. ...
GHSGT BIOLOGY REVIEW
... Mass extinction- massive changes cause the extinction of many species REPRODUCTION Asexual reproduction- requires only one parent, reproduction without sex Sexual reproduction- requires cells from two parents Gametes- sex cells, the cells involved in the formation of offspring Spermatozoan or sperm ...
... Mass extinction- massive changes cause the extinction of many species REPRODUCTION Asexual reproduction- requires only one parent, reproduction without sex Sexual reproduction- requires cells from two parents Gametes- sex cells, the cells involved in the formation of offspring Spermatozoan or sperm ...
Ch. 33 1. Which of the following regarding sponges is true? a
... Rotifers are the type of lophotrocozoan that does parthenogenesis. Parthenogenesis refers to the type of asexual reproduction during which a species of only females produce more females from unfertilized eggs. Under certain conditions, a female will produce eggs that become males also so that sexual ...
... Rotifers are the type of lophotrocozoan that does parthenogenesis. Parthenogenesis refers to the type of asexual reproduction during which a species of only females produce more females from unfertilized eggs. Under certain conditions, a female will produce eggs that become males also so that sexual ...
Name
... 1. __________________________ command center of the cell; contains DNA 2. __________________________ small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 3. __________________________ the site of protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. __________________________ transport system of the cel ...
... 1. __________________________ command center of the cell; contains DNA 2. __________________________ small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 3. __________________________ the site of protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. __________________________ transport system of the cel ...
Nervous System
... Energy produced in one cell is transported to another cell If a multi-cellular organism has a single cell damaged it can survive and make new cells. Different cell types of the organism perform different functions in a multicellular organism The organism has the ability to produce offspring . Simple ...
... Energy produced in one cell is transported to another cell If a multi-cellular organism has a single cell damaged it can survive and make new cells. Different cell types of the organism perform different functions in a multicellular organism The organism has the ability to produce offspring . Simple ...
Moore 1 Timothy Moore Life Science: Unit 3, Lesson 16 22
... 17. In a plant, roots absorb water and nutrients. Those materials are then transported to other parts of the plant. What system in the human body functions in a similar way? Compare these two systems. The system that takes care of transport in the body is the cardiovascular system, also known as the ...
... 17. In a plant, roots absorb water and nutrients. Those materials are then transported to other parts of the plant. What system in the human body functions in a similar way? Compare these two systems. The system that takes care of transport in the body is the cardiovascular system, also known as the ...
Classifying Organisms Study Guide
... ______________________ are multi-celled organisms that are ______________________ (absorb food from living or dead organisms). They live off dead or living organisms (like dead trees)-decomposers. ...
... ______________________ are multi-celled organisms that are ______________________ (absorb food from living or dead organisms). They live off dead or living organisms (like dead trees)-decomposers. ...
Biology SOL Review Packet
... body or apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, centriole, cell wall, cytoplasm, chloroplast, lysosomes, cell membrane 1. _____________________- command center of the cell; DNA in the form of chromosomes is here 2. _____________________- small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 4. __ ...
... body or apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, centriole, cell wall, cytoplasm, chloroplast, lysosomes, cell membrane 1. _____________________- command center of the cell; DNA in the form of chromosomes is here 2. _____________________- small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 4. __ ...
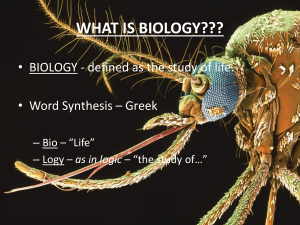
The Study of Life
... • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic unit of life – The smallest organisms are made of only one cell ...
... • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic unit of life – The smallest organisms are made of only one cell ...
Power Reviews PPT
... The same groups of embryonic cells develop in the same order and in similar patterns to produce tissues & organs. ...
... The same groups of embryonic cells develop in the same order and in similar patterns to produce tissues & organs. ...
Name Science Red/Gray - Crestwood Local Schools
... from which it is made). 2. Function is the _______________ the part does. a. The structure of the lungs is a large, spongy sac. b. In the lungs, there are millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli. c. Blood vessels wrap around the alveoli. d. Oxygen from air in the alveoli enters the blood, which bri ...
... from which it is made). 2. Function is the _______________ the part does. a. The structure of the lungs is a large, spongy sac. b. In the lungs, there are millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli. c. Blood vessels wrap around the alveoli. d. Oxygen from air in the alveoli enters the blood, which bri ...
EOCT Review Sheet
... B crossing over C deletion D insertion 7. In Mendel’s experiments with a single trait, the trait that disappeared in the first generation and reappeared in the next generation is called the ...
... B crossing over C deletion D insertion 7. In Mendel’s experiments with a single trait, the trait that disappeared in the first generation and reappeared in the next generation is called the ...
Reproduction Gas exchange Growth Take in energy
... They decompose dead organisms and waste from the environment. ...
... They decompose dead organisms and waste from the environment. ...
Section 1: Characteristics of Animals
... Only their gametes (egg and sperm) are haploid. A great advantage of diploidy is that it permits an animal to exchange genes between the two copies of a set of chromosomes, creating new combinations of genes. ...
... Only their gametes (egg and sperm) are haploid. A great advantage of diploidy is that it permits an animal to exchange genes between the two copies of a set of chromosomes, creating new combinations of genes. ...
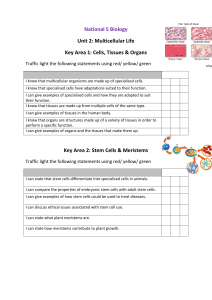
National 5 Biology Unit 2: Multicellular Life Key Area 1: Cells
... I know that examples of discrete variation are usually only controlled by one gene. I know that examples of continuous variation are normally controlled by more than one gene (polygenic inheritance). I know that offspring receive one set of chromosomes from each parent. I understand that information ...
... I know that examples of discrete variation are usually only controlled by one gene. I know that examples of continuous variation are normally controlled by more than one gene (polygenic inheritance). I know that offspring receive one set of chromosomes from each parent. I understand that information ...
Animal Systems
... Ovaries - FEMALE reproductive gland in which EGGS are formed and hormones are produced. Testes -- MALE reproductive gland that produces SPERM and TESTOSTERONE. ...
... Ovaries - FEMALE reproductive gland in which EGGS are formed and hormones are produced. Testes -- MALE reproductive gland that produces SPERM and TESTOSTERONE. ...
Recognize and apply the definition of diffusion
... Identify the levels of organization in the biosphere including cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems, as well as organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems Organisms: an individual living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds to stimuli, grows and develops P ...
... Identify the levels of organization in the biosphere including cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems, as well as organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems Organisms: an individual living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds to stimuli, grows and develops P ...
Life Science: Session 4
... A short account of advantages of asexual reproduction in plants is provided in the article below. One should, however, note that this form of reproduction though, offers shortterm benefits, sexual reproduction always scores over it. A type of reproduction in which fertilization and other processes l ...
... A short account of advantages of asexual reproduction in plants is provided in the article below. One should, however, note that this form of reproduction though, offers shortterm benefits, sexual reproduction always scores over it. A type of reproduction in which fertilization and other processes l ...
Lesson 1-AsexualInPlants
... develops or grows from a single parent. • There is no fusion of cells from two different parents. ...
... develops or grows from a single parent. • There is no fusion of cells from two different parents. ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.