Constrained cost-coupled stochastic games with independent state
... function, and has constraints over other time-average cost functions. Both the cost that is minimized as well as those defining the constraints depend on the state and actions of all players. We study in this paper the existence of a Nash equilibrium. Examples in power control in wireless communicat ...
... function, and has constraints over other time-average cost functions. Both the cost that is minimized as well as those defining the constraints depend on the state and actions of all players. We study in this paper the existence of a Nash equilibrium. Examples in power control in wireless communicat ...
Introduction to Game Theory: Static Games
... In his will it states the two sons must each specify an amount si that they are willing to accept. If s1 + s2 ≤ 1000, then each gets the money he asked for and the remainder goes to a church. If s1 + s2 > 1000, then neither son receives any money and $1000 goes to a church. Assume (a) the two men ca ...
... In his will it states the two sons must each specify an amount si that they are willing to accept. If s1 + s2 ≤ 1000, then each gets the money he asked for and the remainder goes to a church. If s1 + s2 > 1000, then neither son receives any money and $1000 goes to a church. Assume (a) the two men ca ...
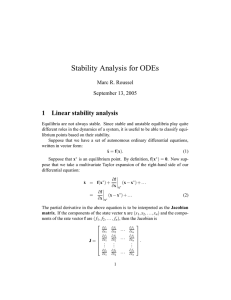
Lecture 2: Stability analysis for ODEs
... Linear stability analysis tells us how a system behaves near an equilibrium point. It does not however tell us anything about what happens farther away from equilibrium. Phase-plane analysis combined with linear stability analysis can generally give us a full picture of the dynamics, but things beco ...
... Linear stability analysis tells us how a system behaves near an equilibrium point. It does not however tell us anything about what happens farther away from equilibrium. Phase-plane analysis combined with linear stability analysis can generally give us a full picture of the dynamics, but things beco ...
A Recurrent Neural Network for Game Theoretic Decision Making
... and, once activated, sustain their activation. Theorem 2. If exists a stable state each layer for which ...
... and, once activated, sustain their activation. Theorem 2. If exists a stable state each layer for which ...
1 Mixed strategies in 2 ! 2 games 2 Maximin Strategies in zero sum
... points in the other region the column player would prefer to play b rather than a. To identify the regions, we take a vertex of the triangle which is not on the indi¤erence line and determine to which of the two regions it belongs. For instance, the vertex (0; 0) is not on the indi¤erence line and c ...
... points in the other region the column player would prefer to play b rather than a. To identify the regions, we take a vertex of the triangle which is not on the indi¤erence line and determine to which of the two regions it belongs. For instance, the vertex (0; 0) is not on the indi¤erence line and c ...
Beyond Normal Form Invariance: First Mover Advantage in Two-Stage Games
... participants made helpful comments, though their views may not be at all well represented here. Research support from the National Science Foundation at that time is gratefully acknowledged. The earlier paper had a serious flaw, however, because its “sophisticated” equilibria could fail to be Nash. ...
... participants made helpful comments, though their views may not be at all well represented here. Research support from the National Science Foundation at that time is gratefully acknowledged. The earlier paper had a serious flaw, however, because its “sophisticated” equilibria could fail to be Nash. ...
New complexity results about Nash equilibria
... 2. Brief review of reductions and complexity A key concept in computational complexity theory is that of a reduction from one problem A to another problem B. Informally, a reduction maps every instance of computational problem A to a corresponding instance of computational problem B, in such a way t ...
... 2. Brief review of reductions and complexity A key concept in computational complexity theory is that of a reduction from one problem A to another problem B. Informally, a reduction maps every instance of computational problem A to a corresponding instance of computational problem B, in such a way t ...