Station 1 - The Periodic Table, Molecules and Molecular
... 1. What is the distinction between atomic number and mass number? Between mass number and atomic mass? 2. Distinguish between the terms family and period in connection with the periodic table. For which of these is the term group also used. 3. When metals react with nonmetals, an ionic compound gene ...
... 1. What is the distinction between atomic number and mass number? Between mass number and atomic mass? 2. Distinguish between the terms family and period in connection with the periodic table. For which of these is the term group also used. 3. When metals react with nonmetals, an ionic compound gene ...
Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
... Each person represents a subatomic particle: Proton = Red Neutron = Blue Electron = Yellow ...
... Each person represents a subatomic particle: Proton = Red Neutron = Blue Electron = Yellow ...
Atoms, and Elements
... 1. relative charge +1 2. relative mass 1.00728 amu or actual mass of 1.6726 x 10 -24 g The Neutron- discovered by Chadwick(1932) 1. relative charge : neutral 1. relative mass 1.00867 amu or 1.6749 x 10-24 g If the Houston Astrodome was an atom, a marble placed in the stadium would be the size of t ...
... 1. relative charge +1 2. relative mass 1.00728 amu or actual mass of 1.6726 x 10 -24 g The Neutron- discovered by Chadwick(1932) 1. relative charge : neutral 1. relative mass 1.00867 amu or 1.6749 x 10-24 g If the Houston Astrodome was an atom, a marble placed in the stadium would be the size of t ...
SECTION 3.1 Atomic Structure
... paths around the nucleus much like planets orbit the sun. Each electron has a certain path known as the energy level. However, the modern model determined that electrons did not orbit the nucleus in set paths but behaved more like waves on a vibrating string It is impossible to determine both ...
... paths around the nucleus much like planets orbit the sun. Each electron has a certain path known as the energy level. However, the modern model determined that electrons did not orbit the nucleus in set paths but behaved more like waves on a vibrating string It is impossible to determine both ...
Chapter 1 - Manual Science Chemistry/Physics
... Solid – definite volume and definite shape; lowest amount of energy Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape Gas – neither definite volume or shape Plasma – high temperature physical state in which atoms lose most of their electrons; highest amount of energy Chemical Properties – a su ...
... Solid – definite volume and definite shape; lowest amount of energy Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape Gas – neither definite volume or shape Plasma – high temperature physical state in which atoms lose most of their electrons; highest amount of energy Chemical Properties – a su ...
periodic table elements
... the center of each atom lies the atomic __________________, which consists of _____________and__________. The atomic number refers to the number of ______________ in the nucleus of the atom. Atoms typically have the same number of electrons as the number of protons. All atoms of the same element hav ...
... the center of each atom lies the atomic __________________, which consists of _____________and__________. The atomic number refers to the number of ______________ in the nucleus of the atom. Atoms typically have the same number of electrons as the number of protons. All atoms of the same element hav ...
Chapter 5 – Atomic Structure
... 4th Century BC Coined the term “atom” Could not prove because no scientific research was being done ...
... 4th Century BC Coined the term “atom” Could not prove because no scientific research was being done ...
Atoms - cloudfront.net
... (1) All matter is composed of atoms and (2) Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element, remain unchanged. ...
... (1) All matter is composed of atoms and (2) Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element, remain unchanged. ...
syllabus for entrance examination - NTU.edu
... reactions and of multi-step processes with a rate-determining step, for which n and m are both integral and are either 0, 1 or 2. The use of the integrated forms of first- and second-order rate equations is not required but the use of constancy of half-life as a test for first order kinetics is incl ...
... reactions and of multi-step processes with a rate-determining step, for which n and m are both integral and are either 0, 1 or 2. The use of the integrated forms of first- and second-order rate equations is not required but the use of constancy of half-life as a test for first order kinetics is incl ...
Atomic Mass Lab (Flaskum)
... 2. To distinguish between atoms of the same element and those of a different element. 3. To calculate the average atomic mass of an imaginary element. ...
... 2. To distinguish between atoms of the same element and those of a different element. 3. To calculate the average atomic mass of an imaginary element. ...
Chemistry 1 Revision: Metals and their uses
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
... Complete the following using the periodic table to help: H2O: ........... atoms of h.......................... .......... atoms of o....................... ...
File
... • The symbol for the positive element is written first, followed by the symbol of the negative element • Subscripts are used to indicate the numbers of ions needed to produce an electrically neutral compound. ...
... • The symbol for the positive element is written first, followed by the symbol of the negative element • Subscripts are used to indicate the numbers of ions needed to produce an electrically neutral compound. ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... • Atomic mass of an element is a weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. • Example: Silver has an atomic mass of 107.87. – This means that a sample of Silver will have some Ag-107, Ag-108, Ag-109, etc., and that the average of those atoms is 107.87 ...
... • Atomic mass of an element is a weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. • Example: Silver has an atomic mass of 107.87. – This means that a sample of Silver will have some Ag-107, Ag-108, Ag-109, etc., and that the average of those atoms is 107.87 ...
An atom - Ms. Buicke maths and science
... Electrons whizz around the nucleus in energy levels called shells or orbitals. The first shell can hold two electrons. The second and third shell can hold 8 electrons each Electrons fill up the shells one by one, starting with the first shell. When a shell is full, they start a new ...
... Electrons whizz around the nucleus in energy levels called shells or orbitals. The first shell can hold two electrons. The second and third shell can hold 8 electrons each Electrons fill up the shells one by one, starting with the first shell. When a shell is full, they start a new ...
Unit 3C Standards for Quiz
... Unit 2C Standards Quiz on Monday, November 24. It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structur ...
... Unit 2C Standards Quiz on Monday, November 24. It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structur ...
Objectives: early history, laws for calculations, atoms, molecules
... α particles: charge +2 (|e|), m = 7100 me (electron masses) these are charged and thus dangerous for health, but they do not penetrate deeply. A piece of paper between a man and α particle radiation is enough to save him. But: if α ray emitting dust is inhaled by breathing or otherwise taken into th ...
... α particles: charge +2 (|e|), m = 7100 me (electron masses) these are charged and thus dangerous for health, but they do not penetrate deeply. A piece of paper between a man and α particle radiation is enough to save him. But: if α ray emitting dust is inhaled by breathing or otherwise taken into th ...
Chapter 3
... 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
... 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
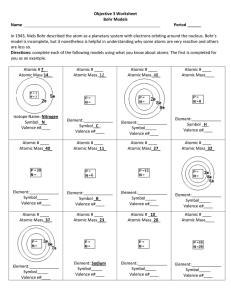
Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name Period In 1943, Niels
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
Discussion Notes (cont.)
... How can atoms of the same element be different? • Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. • The average atomic mass of an element listed in the periodic table is the weighted average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of that elem ...
... How can atoms of the same element be different? • Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. • The average atomic mass of an element listed in the periodic table is the weighted average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of that elem ...
LBC1_Sec3_Unit01_Alchemy
... How can atoms of the same element be different? • Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. • The average atomic mass of an element listed in the periodic table is the weighted average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of that elem ...
... How can atoms of the same element be different? • Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. • The average atomic mass of an element listed in the periodic table is the weighted average mass of the naturally occurring isotopes of that elem ...
File - 7th Grade Science
... Neutrons and Isotopes • Isotopes – atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Mass number – the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom ...
... Neutrons and Isotopes • Isotopes – atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons • Mass number – the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom ...
Section 5.3
... • Properties such as the size of an atom (atomic radius), the energy required to remove an electron from an atom (ionization energy), and the energy associated with the addition of an electron to a gaseous atom (electron affinity) can be understood in terms of the electron configuration of the atom ...
... • Properties such as the size of an atom (atomic radius), the energy required to remove an electron from an atom (ionization energy), and the energy associated with the addition of an electron to a gaseous atom (electron affinity) can be understood in terms of the electron configuration of the atom ...
Medical Chemistry Lecture I
... = ATOMIC number ( Z ) Element = mixture of atoms with the same number of protons (the atomic number) The chemical properties of any given element are determined by the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. ...
... = ATOMIC number ( Z ) Element = mixture of atoms with the same number of protons (the atomic number) The chemical properties of any given element are determined by the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. ...