Section 5.3
... • Properties such as the size of an atom (atomic radius), the energy required to remove an electron from an atom (ionization energy), and the energy associated with the addition of an electron to a gaseous atom (electron affinity) can be understood in terms of the electron configuration of the atom ...
... • Properties such as the size of an atom (atomic radius), the energy required to remove an electron from an atom (ionization energy), and the energy associated with the addition of an electron to a gaseous atom (electron affinity) can be understood in terms of the electron configuration of the atom ...
Medical Chemistry Lecture I
... = ATOMIC number ( Z ) Element = mixture of atoms with the same number of protons (the atomic number) The chemical properties of any given element are determined by the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. ...
... = ATOMIC number ( Z ) Element = mixture of atoms with the same number of protons (the atomic number) The chemical properties of any given element are determined by the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. ...
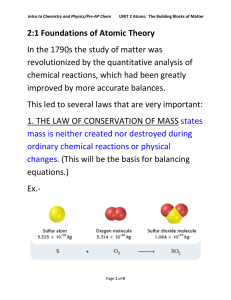
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... and it is radioactive. It exists in very small amounts in nature but can be artificially prepared. ...
... and it is radioactive. It exists in very small amounts in nature but can be artificially prepared. ...
Atomic Structure
... 3) Atoms of different elements can chemically combine with one another in simple whole number ratios (compounds) 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are separated, joined, and rearranged. Atoms of one element are never ...
... 3) Atoms of different elements can chemically combine with one another in simple whole number ratios (compounds) 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are separated, joined, and rearranged. Atoms of one element are never ...
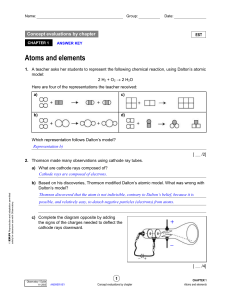
Name: Period: ______ Date: Atom Models Elements are made up of
... 2. By looking at the atomic number, figure out how many protons it has 3. Draw those number of protons inside the nucleus Number of neutrons: 4. Then, subtract the number of protons from the atomic mass (look on the periodic table) to find the number of neutrons the atom contains 5. Draw those numbe ...
... 2. By looking at the atomic number, figure out how many protons it has 3. Draw those number of protons inside the nucleus Number of neutrons: 4. Then, subtract the number of protons from the atomic mass (look on the periodic table) to find the number of neutrons the atom contains 5. Draw those numbe ...
Atoms and Bonding - Academic Computer Center
... • After gold foil experiment, atomic model changes to one with + charges (protons) in dense center with – charges (electrons) surrounding the center • 1932 – Chadwick: discovers the missing mass in the atom comes from neutral particles named neutrons ...
... • After gold foil experiment, atomic model changes to one with + charges (protons) in dense center with – charges (electrons) surrounding the center • 1932 – Chadwick: discovers the missing mass in the atom comes from neutral particles named neutrons ...
atoms.
... contains the same atoms in the same ratio. 4. In chemical reactions, atoms from one or more compounds or elements redistribute or rearrange in relation to other atoms to form one or more new compounds. Atoms themselves do not undergo a change of identity in chemical reactions. Copyright © 2007 Pears ...
... contains the same atoms in the same ratio. 4. In chemical reactions, atoms from one or more compounds or elements redistribute or rearrange in relation to other atoms to form one or more new compounds. Atoms themselves do not undergo a change of identity in chemical reactions. Copyright © 2007 Pears ...
Chemistry Note PowerPoint
... • An atom’s valance electrons are those that have the highest energy levels and are held most loosely. • The number of valance electrons determine many properties of that element, including the ways in which the atom combines with other atoms ...
... • An atom’s valance electrons are those that have the highest energy levels and are held most loosely. • The number of valance electrons determine many properties of that element, including the ways in which the atom combines with other atoms ...
Atomic Theory and Structure Notes
... positively-charged nucleus, containing nearly all the atom’s mass, surrounded by electrons traveling in specific allowed orbits, like the planets around a star—sometimes called the “planetary” model. ...
... positively-charged nucleus, containing nearly all the atom’s mass, surrounded by electrons traveling in specific allowed orbits, like the planets around a star—sometimes called the “planetary” model. ...
Name: Period: _____ Date
... 8. _____ average mass of all the isotopes of an element 9. _____ any charged particle, an atom that has gained or lost electrons 10. _____ s, p, d, f…sublevels of the electron cloud 11. _____ any element that tends to take electrons and get a negative charge 12. _____ part of an atom with a negative ...
... 8. _____ average mass of all the isotopes of an element 9. _____ any charged particle, an atom that has gained or lost electrons 10. _____ s, p, d, f…sublevels of the electron cloud 11. _____ any element that tends to take electrons and get a negative charge 12. _____ part of an atom with a negative ...
Slide 1 - Images
... • The positively charged proton is located in a very small space at the center of an atom. • Most of an atom is empty space occupied by nearly massless electrons. • Electrically neutral particles, neutrons, are also located in the nucleus. • The number of electrons equals the number of protons in an ...
... • The positively charged proton is located in a very small space at the center of an atom. • Most of an atom is empty space occupied by nearly massless electrons. • Electrically neutral particles, neutrons, are also located in the nucleus. • The number of electrons equals the number of protons in an ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... b. calcium sulfide c. iron (III) oxide 30. Be able to convert between gramsmolesatoms. a. How many grams of Al2S3 are in 2.00 moles of Al2S3? b. How many atoms are found in 1.00 moles of Na? c. How many atoms are found in 1.00 moles of NaF? 31. What is Avogadro’s Number? 32. How many atoms are in ...
... b. calcium sulfide c. iron (III) oxide 30. Be able to convert between gramsmolesatoms. a. How many grams of Al2S3 are in 2.00 moles of Al2S3? b. How many atoms are found in 1.00 moles of Na? c. How many atoms are found in 1.00 moles of NaF? 31. What is Avogadro’s Number? 32. How many atoms are in ...
2 - grade11chemistry
... • Putting all this together, we get B-R diagrams • To draw them you must know the # of protons, neutrons, and electrons (2,8,8,2 filling order) • Draw protons (p+), (n0) in circle (i.e. “nucleus”) • Draw electrons around in shells ...
... • Putting all this together, we get B-R diagrams • To draw them you must know the # of protons, neutrons, and electrons (2,8,8,2 filling order) • Draw protons (p+), (n0) in circle (i.e. “nucleus”) • Draw electrons around in shells ...
11129_evl_ch1_ste_corr
... electron shells. Some of them (boron, nitrogen, fluorine and neon) have two electron shells; others (sodium and magnesium) have three. ...
... electron shells. Some of them (boron, nitrogen, fluorine and neon) have two electron shells; others (sodium and magnesium) have three. ...
Particulate View of Matter
... Compound Pure substance formed when two or more different elements combine. Cannot be broken down into simpler compounds or elements by physical means but can be broken down by chemical means. Molecule Two or more atoms chemically bonded together by sharing electrons ...
... Compound Pure substance formed when two or more different elements combine. Cannot be broken down into simpler compounds or elements by physical means but can be broken down by chemical means. Molecule Two or more atoms chemically bonded together by sharing electrons ...
Atoms, Electrons and Periodicity test - A
... Identify the seventh element in the fourth period. State which block this element is in. element ................................................ block ................................................. ...
... Identify the seventh element in the fourth period. State which block this element is in. element ................................................ block ................................................. ...
PreAP Chemistry
... • Explain the relationship between unstable nuclei and radioactive decay. • Characterize alpha, beta, and gamma radiation in terms of mass and charge. Main Idea: __________________ atoms emit __________________ to gain stability. Radioactivity • __________________ reactions can change one element in ...
... • Explain the relationship between unstable nuclei and radioactive decay. • Characterize alpha, beta, and gamma radiation in terms of mass and charge. Main Idea: __________________ atoms emit __________________ to gain stability. Radioactivity • __________________ reactions can change one element in ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions I. Atomic Theory A. Dalton`s Postulates
... 1. relative charge +1 2. relative mass 1.00728 amu or actual mass of 1.6726 x 10-27 g The Neutron- discovered by Chadwick(1932) 1. relative charge : neutral 1. relative mass 1.00867 amu or 1.6749 x 10-27 g If the Houston Astrodome was an atom, a marble placed in the stadium would be the size of th ...
... 1. relative charge +1 2. relative mass 1.00728 amu or actual mass of 1.6726 x 10-27 g The Neutron- discovered by Chadwick(1932) 1. relative charge : neutral 1. relative mass 1.00867 amu or 1.6749 x 10-27 g If the Houston Astrodome was an atom, a marble placed in the stadium would be the size of th ...
Section 12.1 - CPO Science
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
Chemistry Nomenclature Notes
... Charges must balance because one element gives up electrons and the other one accepts these same electrons. The formula is the ratio of one ion to another. Example 1: Sodium atoms tend to lose an electron to form the cation, Na1+. Chlorine atoms tend to gain electrons to form an anion, Cl1-. When th ...
... Charges must balance because one element gives up electrons and the other one accepts these same electrons. The formula is the ratio of one ion to another. Example 1: Sodium atoms tend to lose an electron to form the cation, Na1+. Chlorine atoms tend to gain electrons to form an anion, Cl1-. When th ...
12.1 Structure of the Atom - appleg8
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
Isotope PPT - MrsPage.com
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
chemistry i - surrattchemistry
... nucleuselectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus b. The atom is a hard sphereelectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleusmost of the atom is empty space with a small dense nucleus. c. Most of the atom is empty space with a small, dense nucleuselectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucl ...
... nucleuselectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus b. The atom is a hard sphereelectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleusmost of the atom is empty space with a small dense nucleus. c. Most of the atom is empty space with a small, dense nucleuselectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucl ...
The Modern View of Atomic Structure
... The atom consists of positive, negative, and neutral entities (protons, electrons, and neutrons). Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, which is small. Most of the mass of the atom is due to the nucleus. Electrons are located outside of the nucleus. Most of the volume of the a ...
... The atom consists of positive, negative, and neutral entities (protons, electrons, and neutrons). Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, which is small. Most of the mass of the atom is due to the nucleus. Electrons are located outside of the nucleus. Most of the volume of the a ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint
... nucleus in the electron cloud where electrons can reside • Lewis dot structure -A model that uses electron-dot structures to show how electrons are arranged in molecules. Pairs of dots or lines represent bonding pairs • Noble gas configuration -An electron structure of an atom or ion in which the ou ...
... nucleus in the electron cloud where electrons can reside • Lewis dot structure -A model that uses electron-dot structures to show how electrons are arranged in molecules. Pairs of dots or lines represent bonding pairs • Noble gas configuration -An electron structure of an atom or ion in which the ou ...