3D View of a Comet`s Neighborhood
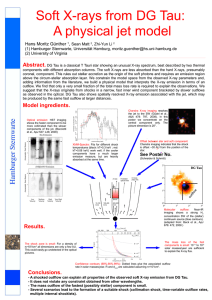
... fluids in the vicinity of the comet. Electrons from the solar wind and from the cometary ions exchange roles cleanly as the four fluids interact. This yields distinct streams of heterogeneous plasma, downwind from the comet, with different sources for the ions and electrons in each stream (Fig. 1). ...
... fluids in the vicinity of the comet. Electrons from the solar wind and from the cometary ions exchange roles cleanly as the four fluids interact. This yields distinct streams of heterogeneous plasma, downwind from the comet, with different sources for the ions and electrons in each stream (Fig. 1). ...
Pallavicini - IASF Milano
... GO programmes, are starting to cover the full age-metallicity plane of nearby open clusters. They allow addressing the question whether a cluster of a given age is representative of all clusters with the same age. ...
... GO programmes, are starting to cover the full age-metallicity plane of nearby open clusters. They allow addressing the question whether a cluster of a given age is representative of all clusters with the same age. ...
The Sun and How to Observe It For further volumes: www.springer.com/series/5338
... released deep within the Sun’s core. The first part of this book will give an overview of these topics. We will begin by looking at the differences and similarities between the Sun and other stars, how the Sun was born, and how energy makes its way from the Sun’s core to our backyards. Once that bas ...
... released deep within the Sun’s core. The first part of this book will give an overview of these topics. We will begin by looking at the differences and similarities between the Sun and other stars, how the Sun was born, and how energy makes its way from the Sun’s core to our backyards. Once that bas ...
Powerpoint
... pulsar of < 5 ms period if rotation and B-fields are to matter. This is much faster than observed in common pulsars. A concern: If calculate the presupernova evolution with the same efficient magnetic field generating algorithms as used in some core collapse simulations, will it be rotating at all? ...
... pulsar of < 5 ms period if rotation and B-fields are to matter. This is much faster than observed in common pulsars. A concern: If calculate the presupernova evolution with the same efficient magnetic field generating algorithms as used in some core collapse simulations, will it be rotating at all? ...
Formation of the Solar System
... changes in the sky form this star – the astrometric technique, but this is difficult. • Since 1995, this Doppler Technique has found evidence of over 200 planets orbiting stars in the near vicinity of the Sun. • Some of the extrasolar planets can be detected when the transit the star. The star’s bri ...
... changes in the sky form this star – the astrometric technique, but this is difficult. • Since 1995, this Doppler Technique has found evidence of over 200 planets orbiting stars in the near vicinity of the Sun. • Some of the extrasolar planets can be detected when the transit the star. The star’s bri ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... C: They have much greater density than adjacent regions D: They have much higher temperature than adjacent regions ...
... C: They have much greater density than adjacent regions D: They have much higher temperature than adjacent regions ...
Evolution of interplanetary coronal mass ejections for different solar
... Expansion from analysis of different ICMEs at different solar distances D Expansion from analysis of a MC at fixed D (non-dimensional rate along S/C path) Comparison of expansion for different SW conditions: -MC in a clean SW / Overtaken MC by fast SW Anisotropy of expansion (axial and radial ex ...
... Expansion from analysis of different ICMEs at different solar distances D Expansion from analysis of a MC at fixed D (non-dimensional rate along S/C path) Comparison of expansion for different SW conditions: -MC in a clean SW / Overtaken MC by fast SW Anisotropy of expansion (axial and radial ex ...
Neutron Star Crustal Emission: a basic, unanswered question.
... But: if some objects have not accreted much gas: we may detect thermal emission directly from the iron surface layers depending on B the outer layers of RX J1856.5-3754 might be in form of condensed matter ! ...
... But: if some objects have not accreted much gas: we may detect thermal emission directly from the iron surface layers depending on B the outer layers of RX J1856.5-3754 might be in form of condensed matter ! ...
plasmas and fusion reactions
... matter that contains enough free charged particles for its dynamical behavior to be dominated by electrodynamics forces. The field largely covers ionized gases, even though it encompasses the solid state, where electrons in metals and semiconductors fall under this category. At a very low level of 0 ...
... matter that contains enough free charged particles for its dynamical behavior to be dominated by electrodynamics forces. The field largely covers ionized gases, even though it encompasses the solid state, where electrons in metals and semiconductors fall under this category. At a very low level of 0 ...
Physics: Particles from Space - Advice for Practitioners (Revised
... atmosphere they produce secondary particles, which go on to produce more collisions and particles, resulting in a shower of particles that is detected at ground level. The primary cosmic rays can usually only be detected directly in space, for example by detectors on satellites, although very high e ...
... atmosphere they produce secondary particles, which go on to produce more collisions and particles, resulting in a shower of particles that is detected at ground level. The primary cosmic rays can usually only be detected directly in space, for example by detectors on satellites, although very high e ...
Astronomy Glossary Key
... Gravity is an attractive force produced bal all things with mass. The more massive an object is, the greater the force of gravity, the closer the object is the greater the force. In 1925 Hubble was first to notice that the light from hydrogen starlight was shifted towards the red end of the spectrum ...
... Gravity is an attractive force produced bal all things with mass. The more massive an object is, the greater the force of gravity, the closer the object is the greater the force. In 1925 Hubble was first to notice that the light from hydrogen starlight was shifted towards the red end of the spectrum ...
poster
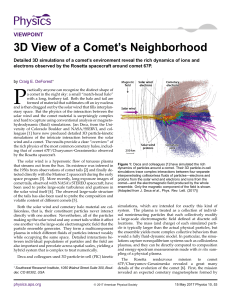
... Abstract. DG Tau is a classical T Tauri star showing an unusual X-ray spectrum, best described by two thermal components with different absorption columns. The soft X-rays are less absorbed than the hard X-rays, presumably coronal, component. This rules out stellar accretion as the origin of the sof ...
... Abstract. DG Tau is a classical T Tauri star showing an unusual X-ray spectrum, best described by two thermal components with different absorption columns. The soft X-rays are less absorbed than the hard X-rays, presumably coronal, component. This rules out stellar accretion as the origin of the sof ...
Summary - Chandra X
... for hard state. But nonthermal high energy excess requires a weak B-field. I.e. must have two spatially separated regions. Nowak: Cyg X-1 hard state in all (6) X-ray satellites – simultaneously! Modeling requires accounting for absorption by blobs in accretion stream and dust scattering halo. VERY b ...
... for hard state. But nonthermal high energy excess requires a weak B-field. I.e. must have two spatially separated regions. Nowak: Cyg X-1 hard state in all (6) X-ray satellites – simultaneously! Modeling requires accounting for absorption by blobs in accretion stream and dust scattering halo. VERY b ...
Plasma physics, space research and the origin of the solar system
... meteoroid impact on the lunar surface are another important source of knowledge. In these cases, however, we do not gain very much information about the structure of the grains in space, because the particles we recover have either passed the terrestrial atmosphere or been destroyed by impact on the ...
... meteoroid impact on the lunar surface are another important source of knowledge. In these cases, however, we do not gain very much information about the structure of the grains in space, because the particles we recover have either passed the terrestrial atmosphere or been destroyed by impact on the ...
Electromagnetic Waves - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Electromagnetic Waves • Waves of energy that travel through matter or space by electric and magnetic fields. ...
... Electromagnetic Waves • Waves of energy that travel through matter or space by electric and magnetic fields. ...
Secrets of the Sun
... The bright displays of light in the night sky that result from charged particles from the Sun hitting the Earth’s atmosphere. Also known as aurora (plural = aurorae). ...
... The bright displays of light in the night sky that result from charged particles from the Sun hitting the Earth’s atmosphere. Also known as aurora (plural = aurorae). ...
solar system notes
... Exercise: Using the zoom function to find the time period that corresponds to the peak in power and write them down for each of the planets. How do these values compare to the orbital period of each planet (Table 2)? Better still type [xx,yy]=ginput on the MATLAB command line and using the mouse, cl ...
... Exercise: Using the zoom function to find the time period that corresponds to the peak in power and write them down for each of the planets. How do these values compare to the orbital period of each planet (Table 2)? Better still type [xx,yy]=ginput on the MATLAB command line and using the mouse, cl ...
imaging_wkshp_all - Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
... • Coordinated Ulysses and SOHO observations of another CME in Nov. 2002 found similar high Fe charge states both in the corona and at 4 AU – thus following for the first time the hot parcels of CME plasma from their origin to ...
... • Coordinated Ulysses and SOHO observations of another CME in Nov. 2002 found similar high Fe charge states both in the corona and at 4 AU – thus following for the first time the hot parcels of CME plasma from their origin to ...
1 Planetary-Spin heat, Jupiter- Saturn-Solar Tidal
... Spring tide on Earth-Moon-Sun System) or on opposite sides of the sun, also known as Spring tide . This occurs every 10.7 years approximately. Because of Jupiter’s mass, the Jupiter- Sun center of gravity position falls 7% outside our sun and has a great tidal effect on the sun. ...
... Spring tide on Earth-Moon-Sun System) or on opposite sides of the sun, also known as Spring tide . This occurs every 10.7 years approximately. Because of Jupiter’s mass, the Jupiter- Sun center of gravity position falls 7% outside our sun and has a great tidal effect on the sun. ...
Propagation of Charged Particles through Helical
... Cartesian spaces. Figure 2 left shows how eq.6 is graphically represented for each particle, and Figure 2 right shows the momentum vector field for a flux of particles traveling in the x2 direction. The code written for this project allows a flux of particles to travel in any one of the three princi ...
... Cartesian spaces. Figure 2 left shows how eq.6 is graphically represented for each particle, and Figure 2 right shows the momentum vector field for a flux of particles traveling in the x2 direction. The code written for this project allows a flux of particles to travel in any one of the three princi ...
Two-Layer Solar Interior Model Presentation
... the left is just for cosmetics. You do not need to read it. It is a visual reminder that if an astronomer understands the reactions that go on within the Sun and the pressure and temperature conditions that control those reactions, they can calculate the properties of the interior of the Sun with gr ...
... the left is just for cosmetics. You do not need to read it. It is a visual reminder that if an astronomer understands the reactions that go on within the Sun and the pressure and temperature conditions that control those reactions, they can calculate the properties of the interior of the Sun with gr ...
The Sun The Sun is a very typical main sequence star. It contains 100
... imagines a local element of gas that becomes ho_er than its surroundings, such that it expands slightly. The lower density of the gas element compared to its surroundings causes it to experience ...
... imagines a local element of gas that becomes ho_er than its surroundings, such that it expands slightly. The lower density of the gas element compared to its surroundings causes it to experience ...
The Sun
... Because of the Sun’s huge influence on Earth, many early cultures saw the Sun as a __________________. For example, Ancient Egyptians had a sun god called Ra while in Aztec mythology there is a sun god named Tonatiuh. The Sun produces a solar _________________ which contains charged particles such a ...
... Because of the Sun’s huge influence on Earth, many early cultures saw the Sun as a __________________. For example, Ancient Egyptians had a sun god called Ra while in Aztec mythology there is a sun god named Tonatiuh. The Sun produces a solar _________________ which contains charged particles such a ...
Is our solar system unique?
... where it’s cold) the cores are bigger. If big enough, they’ll suck gas out of the disk and form giant planets • Moons form via collision or capture or in mini disks ...
... where it’s cold) the cores are bigger. If big enough, they’ll suck gas out of the disk and form giant planets • Moons form via collision or capture or in mini disks ...
How did the Solar System form?
... where it’s cold) the cores are bigger. If big enough, they’ll suck gas out of the disk and form giant planets • Moons form via collision or capture or in mini disks ...
... where it’s cold) the cores are bigger. If big enough, they’ll suck gas out of the disk and form giant planets • Moons form via collision or capture or in mini disks ...
Corona

A corona (Latin, 'crown') is an aura of plasma that surrounds the sun and other celestial bodies. The Sun's corona extends millions of kilometres into space and is most easily seen during a total solar eclipse, but it is also observable with a coronagraph. The word ""corona"" is a Latin word meaning ""crown"", from the Ancient Greek κορώνη (korōnē, “garland, wreath”).The high temperature of the Sun's corona gives it unusual spectral features, which led some in the 19th century to suggest that it contained a previously unknown element, ""coronium"". Instead, these spectral features have since been explained by highly ionized iron (Fe-XIV). Bengt Edlén, following the work of Grotrian (1939), first identified the coronal lines in 1940 (observed since 1869) as transitions from low-lying metastable levels of the ground configuration of highly ionised metals (the green Fe-XIV line at 5303 Å, but also the red line Fe-X at 6374 Å). These high stages of ionisation indicate a plasma temperature in excess of 1,000,000 kelvin, much hotter than the surface of the sun.Light from the corona comes from three primary sources, which are called by different names although all of them share the same volume of space. The K-corona (K for kontinuierlich, ""continuous"" in German) is created by sunlight scattering off free electrons; Doppler broadening of the reflected photospheric absorption lines completely obscures them, giving the spectral appearance of a continuum with no absorption lines. The F-corona (F for Fraunhofer) is created by sunlight bouncing off dust particles, and is observable because its light contains the Fraunhofer absorption lines that are seen in raw sunlight; the F-corona extends to very high elongation angles from the Sun, where it is called the zodiacal light. The E-corona (E for emission) is due to spectral emission lines produced by ions that are present in the coronal plasma; it may be observed in broad or forbidden or hot spectral emission lines and is the main source of information about the corona's composition.