The initial conditions: Orion GMC
... out rapidly by moving electric charges. In contrast, the required currents for large scale B can be set up by tiny drifts between electrons and ions. Maxwell’s equations: a B field of 3 muG requires e-i drift of only 10-3 cm/s ...
... out rapidly by moving electric charges. In contrast, the required currents for large scale B can be set up by tiny drifts between electrons and ions. Maxwell’s equations: a B field of 3 muG requires e-i drift of only 10-3 cm/s ...
Slide 1
... nightside magnetosphere). This results in pitch angle dependent heating exactly analogously to the radial heat cycle. That combined with isothermal scatter can result in net azimuthal heating, as illustrating in Figure 5. ...
... nightside magnetosphere). This results in pitch angle dependent heating exactly analogously to the radial heat cycle. That combined with isothermal scatter can result in net azimuthal heating, as illustrating in Figure 5. ...
The Sun and Energy
... Sunspot appearance has been linked to an 11 year cycle. Believed that magnetic field lines of the sunare getting wrapped up and twisted, because of differential rotation, i.e. Middle rotates faster than top. Sunspots occur when bunched up magnetic field pops upward through the photosphere. This cont ...
... Sunspot appearance has been linked to an 11 year cycle. Believed that magnetic field lines of the sunare getting wrapped up and twisted, because of differential rotation, i.e. Middle rotates faster than top. Sunspots occur when bunched up magnetic field pops upward through the photosphere. This cont ...
The solar dynamo(s) - Center for Magnetic Self Organization
... Any three-dimensional, turbulent (chaotic) flow with high magnetic Reynolds number is (extremely) likely to be a dynamo. • Reflectionally symmetric flows: – Small-scale dynamo action – Disordered fields; same correlation length/time as turbulence ...
... Any three-dimensional, turbulent (chaotic) flow with high magnetic Reynolds number is (extremely) likely to be a dynamo. • Reflectionally symmetric flows: – Small-scale dynamo action – Disordered fields; same correlation length/time as turbulence ...
The Electric Climate versus Flat-Earth Science
... too small to be visible (1/100th of it), located on an orbit 2 inches in diameter. Pluto, being far off, would be located on an orbit 3.5 feet in diameter, about as far as a person can reach across. All the other planets would have their orbits in the space in-between. On this scale the nearest star ...
... too small to be visible (1/100th of it), located on an orbit 2 inches in diameter. Pluto, being far off, would be located on an orbit 3.5 feet in diameter, about as far as a person can reach across. All the other planets would have their orbits in the space in-between. On this scale the nearest star ...
Real Properties of Electromagnetic Fields and
... a neutral point can be created. The field structure that is shown in Fig. 1 lies within the small rectangle at the center of Fig. 2. The two dark circles with central Xs in Fig. 2 represent two straight equal-amplitude electric currents I flowing away from the viewer (into the page). A clockwise-dir ...
... a neutral point can be created. The field structure that is shown in Fig. 1 lies within the small rectangle at the center of Fig. 2. The two dark circles with central Xs in Fig. 2 represent two straight equal-amplitude electric currents I flowing away from the viewer (into the page). A clockwise-dir ...
Chandra Emission Line Diagnostics of Sco
... majority of lines were wider than can be explained by thermal broadening. However the implied velocities were significantly less then those observed for the wind itself from the UV spectrum. A qualitative comparison to similar spectra taken from several stars supported this quantitative analysis. In ...
... majority of lines were wider than can be explained by thermal broadening. However the implied velocities were significantly less then those observed for the wind itself from the UV spectrum. A qualitative comparison to similar spectra taken from several stars supported this quantitative analysis. In ...
Scientific Analysis within SEPServer
... The acceleration mechanisms and transport processes of solar energetic particles (SEP) constitute up-to-date highly important scientific issues. SEP events and their transport through interplanetary (IP) space offer a unique opportunity to analyze their acceleration mechanisms and their sources whil ...
... The acceleration mechanisms and transport processes of solar energetic particles (SEP) constitute up-to-date highly important scientific issues. SEP events and their transport through interplanetary (IP) space offer a unique opportunity to analyze their acceleration mechanisms and their sources whil ...
Folie 1
... higher opacity and blocks photons and thus stores energy. When the star expands the density decreases and neutral helium is ionized by the emerging radiation. The opacity then decreases. This mechanism is reponsible for the 5 minute oscillations in the Sun. ...
... higher opacity and blocks photons and thus stores energy. When the star expands the density decreases and neutral helium is ionized by the emerging radiation. The opacity then decreases. This mechanism is reponsible for the 5 minute oscillations in the Sun. ...
contributed talk in splinter session
... observations) is as much of a puzzle as the mass accretion rate that they carry. Mass and angular momentum are not only gained by the star in the process of accretion, but also lost in either jets or winds. Linking all these different features is the magnetic field. Recent observations suggest the p ...
... observations) is as much of a puzzle as the mass accretion rate that they carry. Mass and angular momentum are not only gained by the star in the process of accretion, but also lost in either jets or winds. Linking all these different features is the magnetic field. Recent observations suggest the p ...
Properties of Stars
... Keeping this in mind, we can divide the sun into four parts: the solar interior; the visible surface, or photosphere; and two atmospheric layers, the chromosphere and corona. ...
... Keeping this in mind, we can divide the sun into four parts: the solar interior; the visible surface, or photosphere; and two atmospheric layers, the chromosphere and corona. ...
Observations of ubiquitous compressive waves in the Sun`s
... structures are the fibrils and shorter structures are the mottles. Recent advances in the modelling of Hα line formation suggest the dark structures are regions of enhanced density that closely follow the magnetic field structure [22]. The nature of the bright fine structures are less clear, althoug ...
... structures are the fibrils and shorter structures are the mottles. Recent advances in the modelling of Hα line formation suggest the dark structures are regions of enhanced density that closely follow the magnetic field structure [22]. The nature of the bright fine structures are less clear, althoug ...
A Simple Planetary Evolution Model Using the Solar Nebular Theory
... are theorized to be the locations where the planets should form. The effects of a varying distance on pressure are observed along with a varying constant of the wave equation and varying time. Finally, the effects of a varying density throughout the proto-planetary disc are briefly discussed. INTROD ...
... are theorized to be the locations where the planets should form. The effects of a varying distance on pressure are observed along with a varying constant of the wave equation and varying time. Finally, the effects of a varying density throughout the proto-planetary disc are briefly discussed. INTROD ...
Astronomy Lecture 3b
... D.subduction of hydrogen into the Sun's surface E.rising plumes of dark, hot material ___ 16. The atmosphere of ? is mostly molecular nitrogen; it may have a liquid nitrogen, ethane and methane ocean up to a depth of one kilometer, beneath which may be a layer of acetylene. A.Iapetus B.Triton C.Mir ...
... D.subduction of hydrogen into the Sun's surface E.rising plumes of dark, hot material ___ 16. The atmosphere of ? is mostly molecular nitrogen; it may have a liquid nitrogen, ethane and methane ocean up to a depth of one kilometer, beneath which may be a layer of acetylene. A.Iapetus B.Triton C.Mir ...
Protecting planets from their stars
... fast solar wind emerges from the polar regions where magnetic field lines are open (coronal holes) and the slow solar wind emerges above the low-latitude active regions (latitudes of up to 30–35° around the equator). In contrast, during periods of maximum activity, the topology of the field becomes ...
... fast solar wind emerges from the polar regions where magnetic field lines are open (coronal holes) and the slow solar wind emerges above the low-latitude active regions (latitudes of up to 30–35° around the equator). In contrast, during periods of maximum activity, the topology of the field becomes ...
The Sun powerpoint
... The chromosphere, a thin red layer, is sometimes visible during a solar eclipse. The upper atmosphere of the sun is called the corona. This layer is a tenuous layer that is larger than the sun itself. The corona can reach a temperature of several million K. Changes within the corona cause solar wind ...
... The chromosphere, a thin red layer, is sometimes visible during a solar eclipse. The upper atmosphere of the sun is called the corona. This layer is a tenuous layer that is larger than the sun itself. The corona can reach a temperature of several million K. Changes within the corona cause solar wind ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS
... n the late 1950s, the study of the sun concentrated on the mapping in detail the intensity distribution in the umbrae and penumbrae of sunspots in relation to the brightness of the photosphere. The solar tower telescope completed and installed at the Kodaikanal Observatory in 1960 with an f/90 objec ...
... n the late 1950s, the study of the sun concentrated on the mapping in detail the intensity distribution in the umbrae and penumbrae of sunspots in relation to the brightness of the photosphere. The solar tower telescope completed and installed at the Kodaikanal Observatory in 1960 with an f/90 objec ...
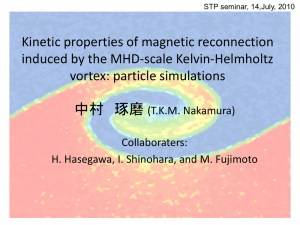
Kinetic aspects of the vortex-induced
... (T~80)Finally, the KH vortex is highly rolled-up as a large magnetic island. ...
... (T~80)Finally, the KH vortex is highly rolled-up as a large magnetic island. ...
Turbulent Origins of the Solar Wind
... • Several ideas exist; one powerful one relates the spatial dependence of the heating to the location of the Parker critical point; this determines how the “available” heating affects the plasma (e.g., Leer & Holzer 1980): SUPERSONIC coronal heating: subsonic region is unaffected. Energy flux has no ...
... • Several ideas exist; one powerful one relates the spatial dependence of the heating to the location of the Parker critical point; this determines how the “available” heating affects the plasma (e.g., Leer & Holzer 1980): SUPERSONIC coronal heating: subsonic region is unaffected. Energy flux has no ...
Turbulent Origins of the Solar Wind
... • Several ideas exist; one powerful one relates the spatial dependence of the heating to the location of the Parker critical point; this determines how the “available” heating affects the plasma (e.g., Leer & Holzer 1980): SUPERSONIC coronal heating: subsonic region is unaffected. Energy flux has no ...
... • Several ideas exist; one powerful one relates the spatial dependence of the heating to the location of the Parker critical point; this determines how the “available” heating affects the plasma (e.g., Leer & Holzer 1980): SUPERSONIC coronal heating: subsonic region is unaffected. Energy flux has no ...
File
... down to its original level, releasing the amount of energy it gained in the form of photons. ...
... down to its original level, releasing the amount of energy it gained in the form of photons. ...
Hard X-Ray Polarization – a Diagnostic of Electron
... •Electrons spiral around magnetic field lines •Must average over θ and φ •Result is that bremsstrahlung cross-section really depends on –ε and E –direction (θ’,φ’) of guiding magnetic field –polarization relative to plane containing B and line to observer ...
... •Electrons spiral around magnetic field lines •Must average over θ and φ •Result is that bremsstrahlung cross-section really depends on –ε and E –direction (θ’,φ’) of guiding magnetic field –polarization relative to plane containing B and line to observer ...
Solar radioastronomy with the LOFAR (LOw Frequency ARray) radio
... LOFAR will operate as an interferometric array consisting of a large number of dipoles grouped into 100 “stations” each consisting of 100 - 1000 dipoles spread over an area 100 m in diameter. The large number of dipoles is necessary to achieve sufficient effective collecting area in order to reach t ...
... LOFAR will operate as an interferometric array consisting of a large number of dipoles grouped into 100 “stations” each consisting of 100 - 1000 dipoles spread over an area 100 m in diameter. The large number of dipoles is necessary to achieve sufficient effective collecting area in order to reach t ...
impulsive electron acceleration by gravitational waves
... relatively low energy particles (Fig. 1d). The chaotic part of the phase space is called ‘‘the chaotic sea.’’ The dynamics, presented by the Poincaré sections in Figure 1, are typical for the majority of parameter values. Generally, the critical values ac and c determine the conditions for possibl ...
... relatively low energy particles (Fig. 1d). The chaotic part of the phase space is called ‘‘the chaotic sea.’’ The dynamics, presented by the Poincaré sections in Figure 1, are typical for the majority of parameter values. Generally, the critical values ac and c determine the conditions for possibl ...
Corona

A corona (Latin, 'crown') is an aura of plasma that surrounds the sun and other celestial bodies. The Sun's corona extends millions of kilometres into space and is most easily seen during a total solar eclipse, but it is also observable with a coronagraph. The word ""corona"" is a Latin word meaning ""crown"", from the Ancient Greek κορώνη (korōnē, “garland, wreath”).The high temperature of the Sun's corona gives it unusual spectral features, which led some in the 19th century to suggest that it contained a previously unknown element, ""coronium"". Instead, these spectral features have since been explained by highly ionized iron (Fe-XIV). Bengt Edlén, following the work of Grotrian (1939), first identified the coronal lines in 1940 (observed since 1869) as transitions from low-lying metastable levels of the ground configuration of highly ionised metals (the green Fe-XIV line at 5303 Å, but also the red line Fe-X at 6374 Å). These high stages of ionisation indicate a plasma temperature in excess of 1,000,000 kelvin, much hotter than the surface of the sun.Light from the corona comes from three primary sources, which are called by different names although all of them share the same volume of space. The K-corona (K for kontinuierlich, ""continuous"" in German) is created by sunlight scattering off free electrons; Doppler broadening of the reflected photospheric absorption lines completely obscures them, giving the spectral appearance of a continuum with no absorption lines. The F-corona (F for Fraunhofer) is created by sunlight bouncing off dust particles, and is observable because its light contains the Fraunhofer absorption lines that are seen in raw sunlight; the F-corona extends to very high elongation angles from the Sun, where it is called the zodiacal light. The E-corona (E for emission) is due to spectral emission lines produced by ions that are present in the coronal plasma; it may be observed in broad or forbidden or hot spectral emission lines and is the main source of information about the corona's composition.