Trophic network models explain instability of Early Triassic terrestrial
... incorporated the demographic properties and interactions of populations. In theory, combined topological and dynamic extinctions could be written in terms of classical interspecific dynamics, but the sheer number of interactions quickly renders this approach intractable for communities of even modes ...
... incorporated the demographic properties and interactions of populations. In theory, combined topological and dynamic extinctions could be written in terms of classical interspecific dynamics, but the sheer number of interactions quickly renders this approach intractable for communities of even modes ...
Linking Dynamic Economic and Ecological General Equilibrium
... A representative plant or animal and its species may have positive, zero or negative net energy in equilibrium. Positive (zero, negative) net energy is associated with greater (constant, lesser) fitness and an increasing (constant, decreasing) population between periods. (The analogy in a competitiv ...
... A representative plant or animal and its species may have positive, zero or negative net energy in equilibrium. Positive (zero, negative) net energy is associated with greater (constant, lesser) fitness and an increasing (constant, decreasing) population between periods. (The analogy in a competitiv ...
Observations on the Eastern Blackneck Garter Snake (Thamnophis
... I have spent many hours actively searching for these snakes for several years and recording my findings. Under normal circumstances, they begin to appear in late February through late March, weather permitting. In temperatures above 60F, blacknecks are alert. Whether or not they appear aboveground d ...
... I have spent many hours actively searching for these snakes for several years and recording my findings. Under normal circumstances, they begin to appear in late February through late March, weather permitting. In temperatures above 60F, blacknecks are alert. Whether or not they appear aboveground d ...
Food Webs, Competition Graphs, and Habitat Formation
... Through the various interactions in a food web, energy gets transferred from one organism to another. Food webs, through both direct and indirect interactions, describe the flow of energy through an ecosystem. By tracking the energy flow, you can derive where the energy from your last meal came from ...
... Through the various interactions in a food web, energy gets transferred from one organism to another. Food webs, through both direct and indirect interactions, describe the flow of energy through an ecosystem. By tracking the energy flow, you can derive where the energy from your last meal came from ...
From Populations to the Biosphere
... 2. Biotic factors are the parts of the environment that are alive, or were alive and then died, such as plants, animals, and their remains. Biotic factors, like organisms, interact with abiotic factors. For example, all animals (biotic factors) breathe in oxygen (abiotic factor). All plants (biotic ...
... 2. Biotic factors are the parts of the environment that are alive, or were alive and then died, such as plants, animals, and their remains. Biotic factors, like organisms, interact with abiotic factors. For example, all animals (biotic factors) breathe in oxygen (abiotic factor). All plants (biotic ...
Reconciling Ecosystems: Reversing Declines in Native Species
... biggest single cause was construction of dams, starting in the late 19th century. California’s dams, large and small, denied winter-run Chinook access to all their upstream spawning and rearing areas, barred spring-run Chinook and late-fall Chinook from more than 90 percent of their upstream spawnin ...
... biggest single cause was construction of dams, starting in the late 19th century. California’s dams, large and small, denied winter-run Chinook access to all their upstream spawning and rearing areas, barred spring-run Chinook and late-fall Chinook from more than 90 percent of their upstream spawnin ...
Research paper: Food webs in the ocean: Who eats whom and how
... increases as the size of the web (i.e. number of species) increases. This implies that the number of prey that a predator will eat increases in proportion to the total number of species in that community. However, the number of links relative to all possible links (connectance) decreases as the numb ...
... increases as the size of the web (i.e. number of species) increases. This implies that the number of prey that a predator will eat increases in proportion to the total number of species in that community. However, the number of links relative to all possible links (connectance) decreases as the numb ...
Transactions of the American Fisheries Society High Diet Overlap
... well as among habitats and across seasons with dynamic food resource availability and foraging conditions. Thus, evaluating the potential for competition based on diet overlap may require comprehensive assessment of fish diets across both space and time. The dearth of such investigations for small f ...
... well as among habitats and across seasons with dynamic food resource availability and foraging conditions. Thus, evaluating the potential for competition based on diet overlap may require comprehensive assessment of fish diets across both space and time. The dearth of such investigations for small f ...
A PRELIMINARY ECOREGION CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR
... This assessment should also consider the size and flow of the stream in terms of its sensitivity to water quality changes. A decrease in the natural flow volume may, for example, result in a diminished assimilative capacity (in the situation where effluent forms part of the total flow volume) or may ...
... This assessment should also consider the size and flow of the stream in terms of its sensitivity to water quality changes. A decrease in the natural flow volume may, for example, result in a diminished assimilative capacity (in the situation where effluent forms part of the total flow volume) or may ...
Chapter 1. Threats to freshwater biodiversity globally and in
... waters are hotspots of threatened species demonstrates how exploitation and degradation of inland waters have outpaced our best attempts at management, and the degree to which current practices are unsustainable. Extinctions are likely to continue over the next few decades, regardless of actions tak ...
... waters are hotspots of threatened species demonstrates how exploitation and degradation of inland waters have outpaced our best attempts at management, and the degree to which current practices are unsustainable. Extinctions are likely to continue over the next few decades, regardless of actions tak ...
CRCT Practice
... 45. Why are photosynthetic plankton found only near the surface of the oceanic zone? A. They are too light to sink deeper B. This region of the ocean is very shallow C. Large organisms along the ocean floor eat them D. Sunlight penetrates only for a few hundred meters ...
... 45. Why are photosynthetic plankton found only near the surface of the oceanic zone? A. They are too light to sink deeper B. This region of the ocean is very shallow C. Large organisms along the ocean floor eat them D. Sunlight penetrates only for a few hundred meters ...
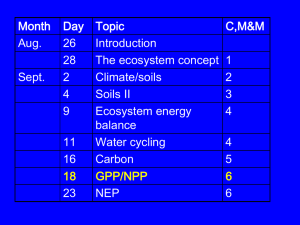
Net Primary Productivity - Sonoma Valley High School
... • Demonstrates species biotic potential. • Unlimited resources. • Only occurs in rare cases. Can this growth curve occur for long periods of time? Why ...
... • Demonstrates species biotic potential. • Unlimited resources. • Only occurs in rare cases. Can this growth curve occur for long periods of time? Why ...
Body size distributions in North American freshwater fish: smallscale
... Irvine 2007) being rarer, so species size also contains, admittedly crude, abundance information. As Post et al. (2007) make clear, defining ecosystem size is not straightforward. In all but the smallest lakes, water depth has a significant structuring influence (Moss 1998). When testing the hypothesis ...
... Irvine 2007) being rarer, so species size also contains, admittedly crude, abundance information. As Post et al. (2007) make clear, defining ecosystem size is not straightforward. In all but the smallest lakes, water depth has a significant structuring influence (Moss 1998). When testing the hypothesis ...
MARELAC ` BOTANY` 3
... - soil formation by trapping debris (aerial roots!! + filamentous algae); - filter land run-off -> removing terrestrial organic matter; - habitats for many faunal species (nursery function!); - producers of detritus -> offshore productivity. • Mangrove loss: soil reclamation for aquaculture (shrimps ...
... - soil formation by trapping debris (aerial roots!! + filamentous algae); - filter land run-off -> removing terrestrial organic matter; - habitats for many faunal species (nursery function!); - producers of detritus -> offshore productivity. • Mangrove loss: soil reclamation for aquaculture (shrimps ...
The Community Builder: Beaver`s Role in the Ecological Community
... Beaver build dams across low order streams to pond water, which provides deep water refuges for protection from predators, extends foraging areas and territories, and allows for food storage during winter (Baker and Hill, 2003). They construct their dens in the form of lodges made of sticks, twigs, ...
... Beaver build dams across low order streams to pond water, which provides deep water refuges for protection from predators, extends foraging areas and territories, and allows for food storage during winter (Baker and Hill, 2003). They construct their dens in the form of lodges made of sticks, twigs, ...
Download, PDF, 2.2 mb - Water`s Journey: Everglades
... ecosystems provide a haven for juveniles of open-ocean species. You may remember from Chapter 5 that mangrove swamps contribute to the health of coral reefs in this way. Human activities have wide-ranging potential effects on coastal ecosystems.The effects are both varied and immediately at hand. Hi ...
... ecosystems provide a haven for juveniles of open-ocean species. You may remember from Chapter 5 that mangrove swamps contribute to the health of coral reefs in this way. Human activities have wide-ranging potential effects on coastal ecosystems.The effects are both varied and immediately at hand. Hi ...
Baited technique improves censuses of cryptic fish in complex habitats
... 1986). This makes destructive sampling non-repeatable and therefore unsuitable for examining temporal variation at a particular site. On the other hand, destructive sampling is generally thought to be the best technique for estimating the abundance of small and cryptic fish. A third alternative is t ...
... 1986). This makes destructive sampling non-repeatable and therefore unsuitable for examining temporal variation at a particular site. On the other hand, destructive sampling is generally thought to be the best technique for estimating the abundance of small and cryptic fish. A third alternative is t ...
`Alkborough Managed Realignment` Measure analysis 30 in the
... but is now stabilising to some extent. Average accretion ranged from 0.02 m to 0.09 m, compared to values of up to 0.06 m during the first year. Maximum accretion is predominantly around the distribution channel and it is suspected that a high level of accretion has also occurred within the channel. ...
... but is now stabilising to some extent. Average accretion ranged from 0.02 m to 0.09 m, compared to values of up to 0.06 m during the first year. Maximum accretion is predominantly around the distribution channel and it is suspected that a high level of accretion has also occurred within the channel. ...
Soft-bottom intertidal ecosystems shaped by ecosystem engineers
... effect of reef-building bivalves. In Chapters 2, 3 and 5, it is demonstrated that reefbuilding bivalves also facilitate macrofaunal species across different trophic levels, not only on the reef itself but also in the surrounding area. The observed facilitation effects are most likely caused by (1) i ...
... effect of reef-building bivalves. In Chapters 2, 3 and 5, it is demonstrated that reefbuilding bivalves also facilitate macrofaunal species across different trophic levels, not only on the reef itself but also in the surrounding area. The observed facilitation effects are most likely caused by (1) i ...