Earth Geology
... A new theory was postulated to explain continental drift: “Plate Tectonics” • Earth’s surface divided into many plates that move slowly over the surface and interact with each other • Their movements are driven from below - internal heat and convection in the Earth (What is convection?) • This was ...
... A new theory was postulated to explain continental drift: “Plate Tectonics” • Earth’s surface divided into many plates that move slowly over the surface and interact with each other • Their movements are driven from below - internal heat and convection in the Earth (What is convection?) • This was ...
Abstract - Geological Society of America
... to form the new crust i.e. Proto North America. The remaining rift basin continued to widen to form a new ocean, i.e. Iapetus (Proto Atlantic). During this time an Island Arc with deep sea flysch deposits and differentiated volcanic and magmatic rocks (Hartland Formation) developed in the Iapetus oc ...
... to form the new crust i.e. Proto North America. The remaining rift basin continued to widen to form a new ocean, i.e. Iapetus (Proto Atlantic). During this time an Island Arc with deep sea flysch deposits and differentiated volcanic and magmatic rocks (Hartland Formation) developed in the Iapetus oc ...
Plate tectonics - pams
... The Real Issue……….. How could the continents move through the solid-rock bottoms of the oceans? In the 1950’s, scientists using better instruments found underwater mountain chains with rift valleys in their centers ...
... The Real Issue……….. How could the continents move through the solid-rock bottoms of the oceans? In the 1950’s, scientists using better instruments found underwater mountain chains with rift valleys in their centers ...
Sedimentary Rock
... •Metamorphic rock is formed as sedimentary rock is pushed deeper into the Earth’s surface. •Here it is heated due to the pressure from rocks layered above it and the surrounding temperatures in the mantle. •The temperature changes the chemical composition of the rock. •Sedimentary shale becomes meta ...
... •Metamorphic rock is formed as sedimentary rock is pushed deeper into the Earth’s surface. •Here it is heated due to the pressure from rocks layered above it and the surrounding temperatures in the mantle. •The temperature changes the chemical composition of the rock. •Sedimentary shale becomes meta ...
Our Earth
... mantle. it forces the cooler rock aside. What effect does this have on the crust above? 4. When a continent on the edge of a tectonic plate is forced against a sea floor on the edge of another plate, the sea floor is always the loser. It returns to the mantle. Why? 5. What example is shown in the pr ...
... mantle. it forces the cooler rock aside. What effect does this have on the crust above? 4. When a continent on the edge of a tectonic plate is forced against a sea floor on the edge of another plate, the sea floor is always the loser. It returns to the mantle. Why? 5. What example is shown in the pr ...
SCIENCE NOTES
... - Physical Weathering – This is when the crust is exposed to water, air, and temperature changes. - Chemical Weathering – This is when chemicals in the air or rain react to cause changes. How Can Wind and Ice Erode Rock? - Wind can push things along with it, but not as hard as water. - Ice from a gl ...
... - Physical Weathering – This is when the crust is exposed to water, air, and temperature changes. - Chemical Weathering – This is when chemicals in the air or rain react to cause changes. How Can Wind and Ice Erode Rock? - Wind can push things along with it, but not as hard as water. - Ice from a gl ...
Layers of the Earth Study Guide
... 6. It is composed (means made of) minerals and rocks and is mostly made of granite and basalt. 7. The part of the crust where the continents are is known as continental crust. This is the thickest part of the crust. 8. The part of the crust beneath the ocean water is known as the oceanic crust, th ...
... 6. It is composed (means made of) minerals and rocks and is mostly made of granite and basalt. 7. The part of the crust where the continents are is known as continental crust. This is the thickest part of the crust. 8. The part of the crust beneath the ocean water is known as the oceanic crust, th ...
Exam Study Guide
... formation (including climate) and deposition. (Small well sorted grains – far from source, poorly sorted far from source). E3.1d Explain how the crystal sizes of igneous rocks indicate the rate of cooling and whether the rock is extrusive (small grained) or intrusive (large grained). E3.1e Expla ...
... formation (including climate) and deposition. (Small well sorted grains – far from source, poorly sorted far from source). E3.1d Explain how the crystal sizes of igneous rocks indicate the rate of cooling and whether the rock is extrusive (small grained) or intrusive (large grained). E3.1e Expla ...
S6CS1
... d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. e. Explain that gravity is the force that governs the motion in the solar system. f. Describe the characteristics of comets, asteroids, and meteors. S6E2 Grade: 6 Description: S6E2 Students will understand the effec ...
... d. Explain the motion of objects in the day/night sky in terms of relative position. e. Explain that gravity is the force that governs the motion in the solar system. f. Describe the characteristics of comets, asteroids, and meteors. S6E2 Grade: 6 Description: S6E2 Students will understand the effec ...
The Lithosphere
... ________ or mineral matter that naturally occurs as part of our planet • Three types – _______________ – _______________ – _______________ ...
... ________ or mineral matter that naturally occurs as part of our planet • Three types – _______________ – _______________ – _______________ ...
Document
... Greenhouse Effect and the Atmosphere • Composition of the atmosphere is critical to maintain the greenhouse effect in balance • Even relatively small changes in chemical composition could alter global balance and result in a “runaway” cycle (as on Venus) – more contaminants more heating (due to ...
... Greenhouse Effect and the Atmosphere • Composition of the atmosphere is critical to maintain the greenhouse effect in balance • Even relatively small changes in chemical composition could alter global balance and result in a “runaway” cycle (as on Venus) – more contaminants more heating (due to ...
Document
... Greenhouse Effect and the Atmosphere • Composition of the atmosphere is critical to maintain the greenhouse effect in balance • Even relatively small changes in chemical composition could alter global balance and result in a “runaway” cycle (as on Venus) – more contaminants more heating (due to ...
... Greenhouse Effect and the Atmosphere • Composition of the atmosphere is critical to maintain the greenhouse effect in balance • Even relatively small changes in chemical composition could alter global balance and result in a “runaway” cycle (as on Venus) – more contaminants more heating (due to ...
File
... -The nature of the parent magma determines the composition of the igneous rock it produces. As such, it is important to understand how different types of magma are created! Magma Formation -Magma forms through the melting of solid rock in Earth’s crust and upper mantle due to: 1. Heat: -As we descen ...
... -The nature of the parent magma determines the composition of the igneous rock it produces. As such, it is important to understand how different types of magma are created! Magma Formation -Magma forms through the melting of solid rock in Earth’s crust and upper mantle due to: 1. Heat: -As we descen ...
Geologic History of South Yuba River State Park Bruce Pauly, Univ
... Continuing East along the trail, 60 ft. past the grotto, on your left (North side of the trail) is an outcrop of relatively light-colored rock with a prominent dark, vertical band (Figure 3). The lighter-colored rock unit of this outcrop appears to be more of the granitic, plutonic rock just seen at ...
... Continuing East along the trail, 60 ft. past the grotto, on your left (North side of the trail) is an outcrop of relatively light-colored rock with a prominent dark, vertical band (Figure 3). The lighter-colored rock unit of this outcrop appears to be more of the granitic, plutonic rock just seen at ...
Document
... ____ 7. A fault is classified by the A. number of earthquakes that occur along it B. type of plate boundary it occurs along C. directions in which rocks move along it D. distance that rocks on either side of the fault move ...
... ____ 7. A fault is classified by the A. number of earthquakes that occur along it B. type of plate boundary it occurs along C. directions in which rocks move along it D. distance that rocks on either side of the fault move ...
Specific Gravity
... Density is one of the most fundamental properties of geological materials, from rocks to water to air. Minerals on Earth have a rather limited range, from about 2.0 g/cm3 for some zeolites to 7.6 g/cm3 for galena (22.6 g/ cm3 for native iridium). Rocks, which are masses of various minerals, have an ...
... Density is one of the most fundamental properties of geological materials, from rocks to water to air. Minerals on Earth have a rather limited range, from about 2.0 g/cm3 for some zeolites to 7.6 g/cm3 for galena (22.6 g/ cm3 for native iridium). Rocks, which are masses of various minerals, have an ...
File
... Earth’s continents move on the surface. We are constantly moving away from Africa/Europe and closer to Asia/Australia! ...
... Earth’s continents move on the surface. We are constantly moving away from Africa/Europe and closer to Asia/Australia! ...
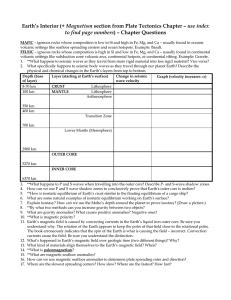
Earth`s Interior (+ Magnetism section from Plate Tectonics Chapter
... MAFIC – igneous rocks whose composition is low in Si and high in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in oceanic volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in contin ...
... MAFIC – igneous rocks whose composition is low in Si and high in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in oceanic volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in contin ...
HISTORY OF THE OCEANS
... • New oceans have been born. • The continents were once united in a single supercontinent called Pangaea that began to break up about 180 million years ago. ...
... • New oceans have been born. • The continents were once united in a single supercontinent called Pangaea that began to break up about 180 million years ago. ...
Chapter 10 * Plate Tectonics
... It has taken millions of years for these continents to drift to their present locations. Some mountains may be the result of two plates colliding. ...
... It has taken millions of years for these continents to drift to their present locations. Some mountains may be the result of two plates colliding. ...
Continental Drift and Sea-Floor Spreading 7.2
... and Africa – It couldn’t swim! 3. Glossopteris – Tropical plant fossil that was found in Antarctica! ...
... and Africa – It couldn’t swim! 3. Glossopteris – Tropical plant fossil that was found in Antarctica! ...
Earth Science, 10th edition Chapter 9: Mountain Building I
... a. Dominant displacement is horizontal and parallel to the trend, or strike b. Transform fault 1. Large strike-slip fault that cuts through the lithosphere 2. Often associated with plate boundaries 3. Joints a. Fractures along which no appreciable displacement has occurred b. Most are formed when ro ...
... a. Dominant displacement is horizontal and parallel to the trend, or strike b. Transform fault 1. Large strike-slip fault that cuts through the lithosphere 2. Often associated with plate boundaries 3. Joints a. Fractures along which no appreciable displacement has occurred b. Most are formed when ro ...