Chapter_3_Notes_Pearson_Abreu - Mater Academy Lakes High
... 5. Coal forms from the remains of swamp plants buried in water 5. Limestone forms in the ocean, where many living things, such as coral, clams, and oysters, have hard shells or skeletons made of the mineral calcite. When these animals die, their shells pile up thickly on the floor. Millions of years ...
... 5. Coal forms from the remains of swamp plants buried in water 5. Limestone forms in the ocean, where many living things, such as coral, clams, and oysters, have hard shells or skeletons made of the mineral calcite. When these animals die, their shells pile up thickly on the floor. Millions of years ...
What is “magnetic reversal?”
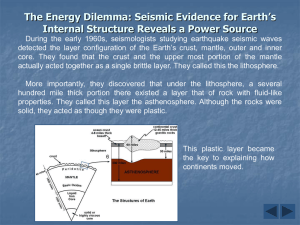
... During the early 1960s, seismologists studying earthquake seismic waves detected the layer configuration of the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer and inner core. They found that the crust and the upper most portion of the mantle actually acted together as a single brittle layer. They called this the lith ...
... During the early 1960s, seismologists studying earthquake seismic waves detected the layer configuration of the Earth’s crust, mantle, outer and inner core. They found that the crust and the upper most portion of the mantle actually acted together as a single brittle layer. They called this the lith ...
Science Chapter Two Landforms and Constructive/Destructive
... minimize damage that they do which will help to improve lives ...
... minimize damage that they do which will help to improve lives ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Minerals
... fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) metallic minerals (such as aluminum, iron, and copper) nonmetallic minerals (such as sand, gravel, & limestone) As they take so long to produce, these components of the earth’s natural capital are classified as nonrenewable mineral resources. ...
... fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) metallic minerals (such as aluminum, iron, and copper) nonmetallic minerals (such as sand, gravel, & limestone) As they take so long to produce, these components of the earth’s natural capital are classified as nonrenewable mineral resources. ...
Study Guide: Academic Standard 8-3 Earth`s Structure and Processes
... Igneous: Forms when molten rock cools and hardens. If cooling takes place slowly beneath Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is called intrusive and the mineral crystals that form are large. If cooling takes place rapidly on Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is extrusive and the mineral crystals are s ...
... Igneous: Forms when molten rock cools and hardens. If cooling takes place slowly beneath Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is called intrusive and the mineral crystals that form are large. If cooling takes place rapidly on Earth’s surface, the igneous rock is extrusive and the mineral crystals are s ...
Crust - Mrs. Bock
... are caused by the very hot material at the deepest part of the mantle rising, then cooling and sinking again --repeating this cycle over and over. ...
... are caused by the very hot material at the deepest part of the mantle rising, then cooling and sinking again --repeating this cycle over and over. ...
Oceanography 101 Linda Khandro, MAT Homework 2: Opening the
... The rocks just off the west coast of Spain formed during the Early Cretaceous. At that time, when Spain broke away from the Grand Banks, seafloor basalt would have begun to flow into the space between them. ...
... The rocks just off the west coast of Spain formed during the Early Cretaceous. At that time, when Spain broke away from the Grand Banks, seafloor basalt would have begun to flow into the space between them. ...
Rock Jeopardy
... Then, click “To Game Board” and continue the game until all categories are finished. ...
... Then, click “To Game Board” and continue the game until all categories are finished. ...
ROCKING AND ROLLING By Philip Steele DOWN UNDER Our
... look just like a jigsaw puzzle made up of lots of big pieces. The pieces are called plates, and there are about 20 of them. They float on the lower part of the earth’s mantle, moving very, very slowly – between 1 and 8 inches per year. Sometimes the plates move apart and gooey magma rises up from th ...
... look just like a jigsaw puzzle made up of lots of big pieces. The pieces are called plates, and there are about 20 of them. They float on the lower part of the earth’s mantle, moving very, very slowly – between 1 and 8 inches per year. Sometimes the plates move apart and gooey magma rises up from th ...
Sea-floor Spreading
... which the ocean floor is pulled outwards when two plates move apart. As the plates move apart, the rocks break and form a crack between the plates. Magma rises through the cracks and seeps out onto the ocean floor. ...
... which the ocean floor is pulled outwards when two plates move apart. As the plates move apart, the rocks break and form a crack between the plates. Magma rises through the cracks and seeps out onto the ocean floor. ...
Chapter 7-Study Questions
... a. United States b. Atlantic Ocean c. Mediterranean Sea d. Indian Ocean e. Pacific Ocean ___9. Volcanoes located within the ocean extrude lavas that are primarily of ____ composition. a. rhyolithic b. granitic c. andesitic d. basaltic e. gabbroic ___10. Subduction zone volcanism in the ocean produce ...
... a. United States b. Atlantic Ocean c. Mediterranean Sea d. Indian Ocean e. Pacific Ocean ___9. Volcanoes located within the ocean extrude lavas that are primarily of ____ composition. a. rhyolithic b. granitic c. andesitic d. basaltic e. gabbroic ___10. Subduction zone volcanism in the ocean produce ...
Morphology (-Plate Tectonics)
... 5. Sea floor aging shows that the seafloor closer to the continents is older, younger at the mid ocean ridges where plates separate
6. Alternating polarity bands in minerals found at areas of spreading seafloor
a.
Earth occasionally switches its poles (est. 200,000 years)
b ...
... 5. Sea floor aging shows that the seafloor closer to the continents is older, younger at the mid ocean ridges where plates separate
Lecture 10 Plate Tectonics i
... from deep in the mantle. As plates move over them, new volcanic Seamounts are formed. Any that stick up above the ocean’s surface as islands are eroded away, and as they move away from the Hot Spot, they cool, contract, and are submerged. They are ...
... from deep in the mantle. As plates move over them, new volcanic Seamounts are formed. Any that stick up above the ocean’s surface as islands are eroded away, and as they move away from the Hot Spot, they cool, contract, and are submerged. They are ...
geography - KCPE-KCSE
... Dynamic/kinetic (due to pressure changes) Thermal/contact metamorphism (due to intense heat) Thermal dynamic/region (combination of heat and pressure) Metasomatism (due to hot and molten rocks) ...
... Dynamic/kinetic (due to pressure changes) Thermal/contact metamorphism (due to intense heat) Thermal dynamic/region (combination of heat and pressure) Metasomatism (due to hot and molten rocks) ...
Oceanography Notes - Intro (Day 1-3)
... B. __________ BYA Collisions of Dust & gravity formed early Sun & proto-planets (Earth 1000 times larger than today), 4 inner planets (Mercury ,Venus ,Earth ,Mars) lost most of the lighter gases (Hydrogen, Helium, etc.) leaving the “rocky” planets C. __________– __________BYA Early Earth Formati ...
... B. __________ BYA Collisions of Dust & gravity formed early Sun & proto-planets (Earth 1000 times larger than today), 4 inner planets (Mercury ,Venus ,Earth ,Mars) lost most of the lighter gases (Hydrogen, Helium, etc.) leaving the “rocky” planets C. __________– __________BYA Early Earth Formati ...
Q. What is the concept of plate tectonics theory?
... - It is a scientific theory which describes the large scale motion of Earth’s lithosphere. The theory builds on the older concepts of continental drift developed by Alfred Wegner and seafloor spreading. Where the plates are relatively moving towards each others and changing their sizes and shapes. T ...
... - It is a scientific theory which describes the large scale motion of Earth’s lithosphere. The theory builds on the older concepts of continental drift developed by Alfred Wegner and seafloor spreading. Where the plates are relatively moving towards each others and changing their sizes and shapes. T ...
Birth of the Universe
... - alternating layers of lava, ash and pyroclastics - explosive (due to high magma viscosity and gas content ...
... - alternating layers of lava, ash and pyroclastics - explosive (due to high magma viscosity and gas content ...
Lesson 3.3 - Earth`s Spheres
... All the water found on planet Earth 97.5% of it is salt, the rest is fresh, but only 0.5% is unfrozen Water cycles through all spheres of Earth ...
... All the water found on planet Earth 97.5% of it is salt, the rest is fresh, but only 0.5% is unfrozen Water cycles through all spheres of Earth ...
Earth`s Layers Vocabulary
... PHYSICAL (how it behaves) Lithosphere: (rocky sphere) The layer of Earth made up of the crust and rigid rock of the upper mantle, averaging about 40 kilometers thick and broken into tectonic plates. Asthenosphere: (weak sphere) The layer in Earth’s upper mantle and directly under the lithosphere in ...
... PHYSICAL (how it behaves) Lithosphere: (rocky sphere) The layer of Earth made up of the crust and rigid rock of the upper mantle, averaging about 40 kilometers thick and broken into tectonic plates. Asthenosphere: (weak sphere) The layer in Earth’s upper mantle and directly under the lithosphere in ...
No Slide Title
... dozen rigid plates that are moving with several smaller plates. The plates contain areas of light continental rock (felsic) as well as dense oceanic bottoms(mafic) ...
... dozen rigid plates that are moving with several smaller plates. The plates contain areas of light continental rock (felsic) as well as dense oceanic bottoms(mafic) ...
Plate Tectonic Learning Target Sheet
... What are the 3 types of earthquakes the Pacific Northwest could experience? How and where do they occur? ...
... What are the 3 types of earthquakes the Pacific Northwest could experience? How and where do they occur? ...
Objectives for Geology Exam
... Objectives for Geology Exam (Pages numbers refer to The blue Earth Science Text) 1. Be able to explain all characteristics and facts associated with minerals. (notes and chapter 9) 2. Be able to group minerals based on their chemical formula (notes and chapter 9) 3. Be able to explain the characteri ...
... Objectives for Geology Exam (Pages numbers refer to The blue Earth Science Text) 1. Be able to explain all characteristics and facts associated with minerals. (notes and chapter 9) 2. Be able to group minerals based on their chemical formula (notes and chapter 9) 3. Be able to explain the characteri ...