Earthquakes
... 2. How can magma rise up on the ocean floor? 3. What happens to rock to form folded mountain ranges? 4. Explain how Earthquakes occur. 5. How can new ocean floor be created? 6. How do mountain ranges form? 7. Why is density important at subduction zones? ...
... 2. How can magma rise up on the ocean floor? 3. What happens to rock to form folded mountain ranges? 4. Explain how Earthquakes occur. 5. How can new ocean floor be created? 6. How do mountain ranges form? 7. Why is density important at subduction zones? ...
Full-Text - Journal of Tethys
... rocks were significantly different from the geochemistry of rocks obtained using the third model. In the values of La/Sm (n) and ratios of Nb/Th, given in the form of diagrams in Figure 8b, the geochemical differences are wellillustrated. Geochemical show the similarities beetwen Sahand samples and ...
... rocks were significantly different from the geochemistry of rocks obtained using the third model. In the values of La/Sm (n) and ratios of Nb/Th, given in the form of diagrams in Figure 8b, the geochemical differences are wellillustrated. Geochemical show the similarities beetwen Sahand samples and ...
Chapter 2: The need for Earth Heritage Conservation
... the natural environment. Rocks, minerals, fossils, soils and landforms are an integral part of our natural world. The distribution of habitats, plants and animals depends not only upon climate, but also upon the geology and landscape. As well as being a fundamental part of the natural world, geology ...
... the natural environment. Rocks, minerals, fossils, soils and landforms are an integral part of our natural world. The distribution of habitats, plants and animals depends not only upon climate, but also upon the geology and landscape. As well as being a fundamental part of the natural world, geology ...
- Frost Middle School
... • There is more pressure than the mantle but less pressure than the inner core ...
... • There is more pressure than the mantle but less pressure than the inner core ...
SUBDUCTION-RELATED VOLCANISM
... Petrogenesis – The Importance of Water Water plays a very significant role in the generation of magmas in subduction-zone environments – from magma generation to eruption. By the time the ocean crust begins to subduct, mafic minerals in it have become hydrated, where olivine and pyroxene may have tu ...
... Petrogenesis – The Importance of Water Water plays a very significant role in the generation of magmas in subduction-zone environments – from magma generation to eruption. By the time the ocean crust begins to subduct, mafic minerals in it have become hydrated, where olivine and pyroxene may have tu ...
theory of continental drift
... Just as maps of the oceans and coastlines initiated the idea of continental drift, maps of the ocean floor propelled science into the investigation of seafloor spreading. Charts and studies of the mid ocean ridge system, trenches, seamounts, and continental shelves— have been examined and catalogued ...
... Just as maps of the oceans and coastlines initiated the idea of continental drift, maps of the ocean floor propelled science into the investigation of seafloor spreading. Charts and studies of the mid ocean ridge system, trenches, seamounts, and continental shelves— have been examined and catalogued ...
The Lizard
... north of the Lizard Complex from around the Carmenellis granite and are probably part of the heavy mineral assemblage left by the erosion of Tertiary gravel deposits. Trace nickel sulphides have also been discovered in certain Lizard rocks. Ilmenite occurs in abundance and vanadiferous magnetite has ...
... north of the Lizard Complex from around the Carmenellis granite and are probably part of the heavy mineral assemblage left by the erosion of Tertiary gravel deposits. Trace nickel sulphides have also been discovered in certain Lizard rocks. Ilmenite occurs in abundance and vanadiferous magnetite has ...
Earth`s Interior
... • Made of granite – Rock that has larger crystals than basalt, not as dense ...
... • Made of granite – Rock that has larger crystals than basalt, not as dense ...
Science 7 Unit 5 Planet Earth This book belongs to: Topic 1
... The geological time scale is a division of Earth’s history into smaller units based on the appearances of different life forms. (see Figure 5.87, p. 426) The largest divisions are called eons, which are divided into eras and then further divided into periods. Rodinia (Figure 5.85) was the first supe ...
... The geological time scale is a division of Earth’s history into smaller units based on the appearances of different life forms. (see Figure 5.87, p. 426) The largest divisions are called eons, which are divided into eras and then further divided into periods. Rodinia (Figure 5.85) was the first supe ...
SOL Review 1
... Plate Tectonics Continental Drift: Developed by Alfred Wegener. He stated that the there was once one super continent (Pangaea) that split apart, then drifted to the current locations. Proof: rock clues, fossil clues, climate, puzzle-like fit. Problem: could not explain motion of continents ...
... Plate Tectonics Continental Drift: Developed by Alfred Wegener. He stated that the there was once one super continent (Pangaea) that split apart, then drifted to the current locations. Proof: rock clues, fossil clues, climate, puzzle-like fit. Problem: could not explain motion of continents ...
ES SOL Review pg 1
... Plate Tectonics Continental Drift: Developed by Alfred Wegener. He stated that the there was once one super continent (Pangaea) that split apart, then drifted to the current locations. Proof: rock clues, fossil clues, climate, puzzle-like fit. Problem: could not explain motion of continents ...
... Plate Tectonics Continental Drift: Developed by Alfred Wegener. He stated that the there was once one super continent (Pangaea) that split apart, then drifted to the current locations. Proof: rock clues, fossil clues, climate, puzzle-like fit. Problem: could not explain motion of continents ...
Planet Earth - MSU Billings
... Earth’s Outermost Layers • The most dynamic portion of the Earth – Atmosphere • Thin gaseous envelope surrounding Earth – Hydrosphere • Water layer dominated by the oceans – Biosphere • All living things on the planet – Lithosphere • Rocky outer shell ...
... Earth’s Outermost Layers • The most dynamic portion of the Earth – Atmosphere • Thin gaseous envelope surrounding Earth – Hydrosphere • Water layer dominated by the oceans – Biosphere • All living things on the planet – Lithosphere • Rocky outer shell ...
The Isotopic Datings by U-Pb in Zircons of Granitoides of Gashi
... the granitic massif of Fierza are dated by U-Pb method in zircons. The isotopic dating is realized in the Istem, CC 066 Laboratory of the Montpellie II University, France. Based on these data we conclude that there are two kinds of granitoide rocks. Juniku granites is dated 329.6±2.1 Ma (Carbon, Mis ...
... the granitic massif of Fierza are dated by U-Pb method in zircons. The isotopic dating is realized in the Istem, CC 066 Laboratory of the Montpellie II University, France. Based on these data we conclude that there are two kinds of granitoide rocks. Juniku granites is dated 329.6±2.1 Ma (Carbon, Mis ...
File
... Earth keeps the core solid, while the mantle is further away which makes it soft & free flowing. The mantle then rises to the top where it cools and becomes the crust. ...
... Earth keeps the core solid, while the mantle is further away which makes it soft & free flowing. The mantle then rises to the top where it cools and becomes the crust. ...
classifying rocks
... Sedimentary rocks have characteristics unique to how they form. Forces on Earth’s surface can break down rocks. This process is called weathering. Rocks can be broken down through physical weathering or chemical weathering. Physical weathering breaks down rocks into smaller pieces through physical p ...
... Sedimentary rocks have characteristics unique to how they form. Forces on Earth’s surface can break down rocks. This process is called weathering. Rocks can be broken down through physical weathering or chemical weathering. Physical weathering breaks down rocks into smaller pieces through physical p ...
The Structure of Earth - Mrs. wolfe`s 6th grade science classroom
... times a single landmass that broke apart and eventually moved into the positions they are in today. ...
... times a single landmass that broke apart and eventually moved into the positions they are in today. ...
ch 15 ppt - Walton High School
... • Any rock type can turn into any other rock type through the rock cycle – Rocks change due to chemical or physical conditions that change over time – Slowest of earth’s cyclic processes ...
... • Any rock type can turn into any other rock type through the rock cycle – Rocks change due to chemical or physical conditions that change over time – Slowest of earth’s cyclic processes ...
Presentation
... Tracing made by a seismograph can be used to tell how far away an earthquake’s epicenter is from the station that recorded it: •Need distance from 3 different stations in order to determine location •Point where all 3 circles meet is location of epicenter ...
... Tracing made by a seismograph can be used to tell how far away an earthquake’s epicenter is from the station that recorded it: •Need distance from 3 different stations in order to determine location •Point where all 3 circles meet is location of epicenter ...
Earth`s Crust - Southern Local Schools
... Igneous rocks, also called volcanic rocks, are formed from melted rock that has cooled and solidified. When rocks are buried deep within the Earth, they melt because of the high pressure and temperature; the molten rock (called magma) can then flow upward or even be erupted from a volcano onto the E ...
... Igneous rocks, also called volcanic rocks, are formed from melted rock that has cooled and solidified. When rocks are buried deep within the Earth, they melt because of the high pressure and temperature; the molten rock (called magma) can then flow upward or even be erupted from a volcano onto the E ...
C1 Revision Checklist - Set 1 only
... g) The number of protons in an atom of an element is its atomic number. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom is its mass number. h) Electrons occupy particular energy levels or shells and be able to represent the electronic structure of the first twenty elements of the periodic table in th ...
... g) The number of protons in an atom of an element is its atomic number. The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom is its mass number. h) Electrons occupy particular energy levels or shells and be able to represent the electronic structure of the first twenty elements of the periodic table in th ...
guide
... 5. Depth of deepest drill hole (12 km) – Drilling used for scientific study and oil exploration. 6. The Moho – crust/mantle boundary (~35 km [beneath continents]) – Crust is a thin shell; mantle is ~82% of Earth. 7. Base of the lithosphere (~100 km) – The Earth’s plates (lithosphere) are moving at c ...
... 5. Depth of deepest drill hole (12 km) – Drilling used for scientific study and oil exploration. 6. The Moho – crust/mantle boundary (~35 km [beneath continents]) – Crust is a thin shell; mantle is ~82% of Earth. 7. Base of the lithosphere (~100 km) – The Earth’s plates (lithosphere) are moving at c ...
Basic Structure of the Earth
... Layers Defined by Composition Crust • Continental crust - Upper crust composed of granitic rocks - Lower crust is more akin to basalt - Average density is about 2.7 g/cm3 - Up to 4 billion years old ...
... Layers Defined by Composition Crust • Continental crust - Upper crust composed of granitic rocks - Lower crust is more akin to basalt - Average density is about 2.7 g/cm3 - Up to 4 billion years old ...
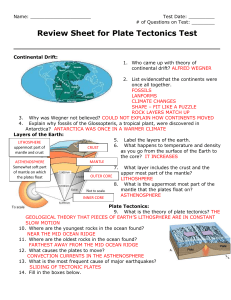
Name - Cedar Hill ISD
... 15. The oceanic plate is SUBDUCTED below the continental plate in a convergent boundary because the oceanic plate is MORE dense then the continental plate. When this happens, the oceanic plate returns to the MANTLE. 16. Why does subduction not occur when two continental plates converge? THEY ARE THE ...
... 15. The oceanic plate is SUBDUCTED below the continental plate in a convergent boundary because the oceanic plate is MORE dense then the continental plate. When this happens, the oceanic plate returns to the MANTLE. 16. Why does subduction not occur when two continental plates converge? THEY ARE THE ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... BONUS FACTS: 2900 km below earth’s surface (7,250 laps around 400 meter track) ...
... BONUS FACTS: 2900 km below earth’s surface (7,250 laps around 400 meter track) ...