Chapter 10 ROCKS
... • Form from cemented together rock fragments, organic material, or from minerals that precipitate out of water. • May have layered structure from deposition of various kinds of sediment ...
... • Form from cemented together rock fragments, organic material, or from minerals that precipitate out of water. • May have layered structure from deposition of various kinds of sediment ...
Chapter 3 – Rocks
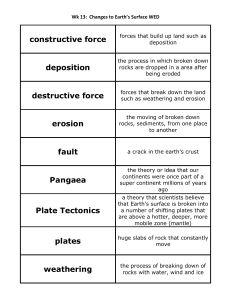
... Erosion - transportation of material. Deposition - When an agent of erosion (water, wind, ice, or gravity) lose energy and sediments drop back to the ground ...
... Erosion - transportation of material. Deposition - When an agent of erosion (water, wind, ice, or gravity) lose energy and sediments drop back to the ground ...
Introduction to Structural Geology
... -highly deformed and display more than 1 generation of folds -contacts between gneissic and greenstone are complex -sedimentary rock types fall into one of two categories: *immature volcanogenic sediments *quartzite-carbonate-iron-assemblages -Similar sedimentary and tectonic conditions occurred glo ...
... -highly deformed and display more than 1 generation of folds -contacts between gneissic and greenstone are complex -sedimentary rock types fall into one of two categories: *immature volcanogenic sediments *quartzite-carbonate-iron-assemblages -Similar sedimentary and tectonic conditions occurred glo ...
PLATE MOVEMENT AND CONTINENTAL GROWTH
... – AGE OF ROCKS IN OCEAN BASINS – FOSSILS – LAND AREAS – TROPICAL AND POLAR REVERSES ...
... – AGE OF ROCKS IN OCEAN BASINS – FOSSILS – LAND AREAS – TROPICAL AND POLAR REVERSES ...
Appalachian Mountain Building
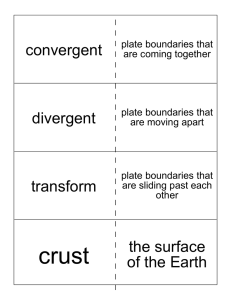
... Orogeny is the process that for all mountain ranges. Orogeny results in broad, linear regions of deformation known as orogenic belts. Most orogenic belts are associated with plate boundaries. The greatest variety and the tallest of these belts Are found at convergent Boundaries. ...
... Orogeny is the process that for all mountain ranges. Orogeny results in broad, linear regions of deformation known as orogenic belts. Most orogenic belts are associated with plate boundaries. The greatest variety and the tallest of these belts Are found at convergent Boundaries. ...
Science Review: Land Formations (Rocks, Minerals, Soil, etc
... Are classified according to the way they form: 1. Igneous: formed from melted rock: magma/lava that has cooled 2. Metamorphic: squeezed and heated to high temperatures, when it cools and hardens it becomes metamorphic rock 3. Sedimentary: layers of clay, sand, mud, rock are squeezed together and sol ...
... Are classified according to the way they form: 1. Igneous: formed from melted rock: magma/lava that has cooled 2. Metamorphic: squeezed and heated to high temperatures, when it cools and hardens it becomes metamorphic rock 3. Sedimentary: layers of clay, sand, mud, rock are squeezed together and sol ...
Normal Faults
... the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks. Occurs along normal faults ...
... the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks. Occurs along normal faults ...
Topic/Objective: ______ _____ Full Name: __________ Class: __
... Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphic means to change Sources of Metamorphic rocks: 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Pre-existing Metamorphic rocks These rocks become metamorphic rocks when they are _changed_. Classification: 1. Formation____ conditions (where they form) 2. Texture______ 3. Parent Rock __ (what ...
... Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphic means to change Sources of Metamorphic rocks: 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Pre-existing Metamorphic rocks These rocks become metamorphic rocks when they are _changed_. Classification: 1. Formation____ conditions (where they form) 2. Texture______ 3. Parent Rock __ (what ...
Name Earth Revealed : Metamorphic Rocks 1. The process of
... 4. Directed pressure and stress, such as compression, can form a metamorphic texture known as _____________________. ...
... 4. Directed pressure and stress, such as compression, can form a metamorphic texture known as _____________________. ...
Geller PPT Slides
... “Rocks formed from particles or dissolved materials from previously existing rocks.” See Table 19.2 in textbook ...
... “Rocks formed from particles or dissolved materials from previously existing rocks.” See Table 19.2 in textbook ...
Petrology and geochemistry of the metamorphic rocks in the SW
... contact metamorphism. Regional metamorphic rocks are composed of slate, phyllite and micaschists and locted in green-schist facies and contact metamorphic rocks are composed of spotted schist and hornfels respectively. Mineralogically, these rocks are composed of quartz, chlorite, muscovite, biotite ...
... contact metamorphism. Regional metamorphic rocks are composed of slate, phyllite and micaschists and locted in green-schist facies and contact metamorphic rocks are composed of spotted schist and hornfels respectively. Mineralogically, these rocks are composed of quartz, chlorite, muscovite, biotite ...
Fortune Teller
... 1. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at the boundary of plates (faults). 2. Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks chemically and physically. 3. Erosion causes weathered rocks and soil to be washed away. 4. Sedimentary – layers of sediment cemented together Igneous – melting and ...
... 1. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at the boundary of plates (faults). 2. Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks chemically and physically. 3. Erosion causes weathered rocks and soil to be washed away. 4. Sedimentary – layers of sediment cemented together Igneous – melting and ...
Rocks and Minerals Study Guide
... What does foliated mean? What are vesicles, and what type of rock has them? Explain how granite would be turned to sanstone. What causes the uplift, folding and faulting that moves rocks through the rock cycle? What is the texture of slate? What two terms are used to describe the texture of metamorp ...
... What does foliated mean? What are vesicles, and what type of rock has them? Explain how granite would be turned to sanstone. What causes the uplift, folding and faulting that moves rocks through the rock cycle? What is the texture of slate? What two terms are used to describe the texture of metamorp ...
Sedimentary Rocks There are a lot of processes that cause rocks to
... place to place. Sediment may get transported thousands of miles by one of the world's major rivers, or it may just go from the top of the hill to the bottom during a landslide New sediment acts like a blanket for old sediment-sediments get buried by other sediments Sediment can include minerals, sma ...
... place to place. Sediment may get transported thousands of miles by one of the world's major rivers, or it may just go from the top of the hill to the bottom during a landslide New sediment acts like a blanket for old sediment-sediments get buried by other sediments Sediment can include minerals, sma ...
The Sevier Orogeny The Sevier orogeny took place at about the
... and uplift. The Laramide orogeny in its various manifestations involves deeply penetrating, steeply dipping reverse faults that deform and fault crystalline basement rocks. The Sevier orogeny was a more ‘thin-skinned’ deformation event. It is characterized by shallow thrust faults affecting only Pal ...
... and uplift. The Laramide orogeny in its various manifestations involves deeply penetrating, steeply dipping reverse faults that deform and fault crystalline basement rocks. The Sevier orogeny was a more ‘thin-skinned’ deformation event. It is characterized by shallow thrust faults affecting only Pal ...
California Geologic History
... The distribution of rocks of these ages suggests that the west coast of the North American Continent was well to the east of all but the southern end of what is now California. ...
... The distribution of rocks of these ages suggests that the west coast of the North American Continent was well to the east of all but the southern end of what is now California. ...
Unit 3 Geochemical Cycles in the Earth`s System
... Form within cooling ________ Form from _________metamorphism _______ – mineral solutions in cracks ________ – large number of veins ______ deposits – concentrated at bottom of stream beds due to water mv’t ...
... Form within cooling ________ Form from _________metamorphism _______ – mineral solutions in cracks ________ – large number of veins ______ deposits – concentrated at bottom of stream beds due to water mv’t ...
Twentieth lecture - 23 October, 2013
... Very active - initially molten, then skinned over with a thin surface layer, continually broken by volcanic activity. ...
... Very active - initially molten, then skinned over with a thin surface layer, continually broken by volcanic activity. ...
Science Practice set 4
... 1. Rocks are classified into the three major groups (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) by A. their color B. their size C. their formation d. the types of minerals in them 2. Igneous rocks are formed when ___________ cools. A. magma B. sediment C. water D. stone 3. How do sedimentary rocks form? ...
... 1. Rocks are classified into the three major groups (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) by A. their color B. their size C. their formation d. the types of minerals in them 2. Igneous rocks are formed when ___________ cools. A. magma B. sediment C. water D. stone 3. How do sedimentary rocks form? ...
PreparationForMidTerm
... marker beds (a volcanic ash bed covering a very large area is an example) global extinction events (the disappearance of many species worldwide) biozones (practice questions were handed out) correlation using planktonic species (more widespread than benthic species) transgression/regression: rise/dr ...
... marker beds (a volcanic ash bed covering a very large area is an example) global extinction events (the disappearance of many species worldwide) biozones (practice questions were handed out) correlation using planktonic species (more widespread than benthic species) transgression/regression: rise/dr ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.