Researchers find oldest rocks on Earth
... Canadian bedrock more than four billion years old but also for their chemical composition, which resembles that of volcanic rocks in geologic may be the oldest known section of the Earth's settings where tectonic plates are crashing early crust. Scientists at the Carnegie Institution together. "This ...
... Canadian bedrock more than four billion years old but also for their chemical composition, which resembles that of volcanic rocks in geologic may be the oldest known section of the Earth's settings where tectonic plates are crashing early crust. Scientists at the Carnegie Institution together. "This ...
REGIONAL GEOLOGY AND MINERALIZATION
... the Banket Group, comprise the basal portion of the series. The Tarkwaian Series is largely confined to elongate north northeast trending basins, believed to represent intra-cratonic rifts. The margins of these basins commonly coincide with major (frequently mineralized) structures representing the ...
... the Banket Group, comprise the basal portion of the series. The Tarkwaian Series is largely confined to elongate north northeast trending basins, believed to represent intra-cratonic rifts. The margins of these basins commonly coincide with major (frequently mineralized) structures representing the ...
MOUNTAINS and METAMO..
... 13) The deepest earthquakes occur at what type of lithospheric boundary? 13_________________ 14) The magnitude of an earthquake is stated by what is called the _______ scale. 14_________________ 15) The boundary between the crust and the mantle: 15______________ 16) In some mountain systems the faul ...
... 13) The deepest earthquakes occur at what type of lithospheric boundary? 13_________________ 14) The magnitude of an earthquake is stated by what is called the _______ scale. 14_________________ 15) The boundary between the crust and the mantle: 15______________ 16) In some mountain systems the faul ...
Homework 05c
... Arcs (Aleutians, Japan, Philippines, Solomons, Lesser Antilles) are examples of volcanoes formed above a) mid-ocean ridges b) plumes c) subduction zones 16) Transform Faults may be recognized in aerial photographs by a) flatirons b) offset streams 17) Sediments are originally horizontal beds, with f ...
... Arcs (Aleutians, Japan, Philippines, Solomons, Lesser Antilles) are examples of volcanoes formed above a) mid-ocean ridges b) plumes c) subduction zones 16) Transform Faults may be recognized in aerial photographs by a) flatirons b) offset streams 17) Sediments are originally horizontal beds, with f ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... sedimentary rocks in what are now the southern Coast Ranges and western Transverse Ranges. ...
... sedimentary rocks in what are now the southern Coast Ranges and western Transverse Ranges. ...
Instructor Copy
... How can rocks be identified? Rocks may show ripple marks, mudcracks, raindrops and fossils. Can often see sand, pebbles, or stones in the rock. ...
... How can rocks be identified? Rocks may show ripple marks, mudcracks, raindrops and fossils. Can often see sand, pebbles, or stones in the rock. ...
MESOZOIC ERA IN CALIFORNIA
... a. By the end of Mesozoic (about 63 m.y) all elements of Mts. and Great Valley were established b. Limited mountain building in late Triassic to middle Jurassic time c. Major mountain building period occurred near close of Jurassic *best known in Sierra Nevada--so it is called the Nevadan Orogeny d. ...
... a. By the end of Mesozoic (about 63 m.y) all elements of Mts. and Great Valley were established b. Limited mountain building in late Triassic to middle Jurassic time c. Major mountain building period occurred near close of Jurassic *best known in Sierra Nevada--so it is called the Nevadan Orogeny d. ...
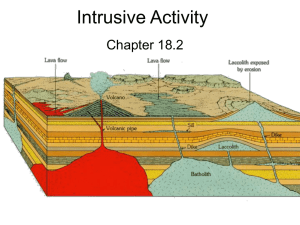
Intrusive Activity
... B. Magma can also cause blocks of rock to break off and sink into the magma, where the rocks may eventually melt. C. Magma can melt the rock into which it intrudes. ...
... B. Magma can also cause blocks of rock to break off and sink into the magma, where the rocks may eventually melt. C. Magma can melt the rock into which it intrudes. ...
Science Chapter 4 Study Guide Vocabulary
... planets—large bodies of rock or gas that revolve around the sun minerals--the basic building block of rocks (example-sulfur, salt) conservation—to use resources wisely (example—turn off lights) Sedimentary Rocks—rocks made of sand or sediment and is pressed into layers. This would be a good place to ...
... planets—large bodies of rock or gas that revolve around the sun minerals--the basic building block of rocks (example-sulfur, salt) conservation—to use resources wisely (example—turn off lights) Sedimentary Rocks—rocks made of sand or sediment and is pressed into layers. This would be a good place to ...
unit 8: Metamorphic Rocks
... change due to pressure or heat in the earth. Marble is an example of a metamorphic rock. Limestone changes under heat and pressure, transforming into a new kind of rock, marble. Metamorphism means "change" in rocks. Heat, pressure, and fluids that contain chemicals can convert mineral composition in ...
... change due to pressure or heat in the earth. Marble is an example of a metamorphic rock. Limestone changes under heat and pressure, transforming into a new kind of rock, marble. Metamorphism means "change" in rocks. Heat, pressure, and fluids that contain chemicals can convert mineral composition in ...
review list 2013
... P or S travel time (using epicenter distance and ESRT p.11) Epicenter distance (using S minus P arrival times and ESRT p.11) Origin time (Arrival time minus travel time) The area between two plates colliding is where regional metamorphism occurs, with heat and pressure. Contact metamorphism ...
... P or S travel time (using epicenter distance and ESRT p.11) Epicenter distance (using S minus P arrival times and ESRT p.11) Origin time (Arrival time minus travel time) The area between two plates colliding is where regional metamorphism occurs, with heat and pressure. Contact metamorphism ...
The Rock Cycle - Geevor Tin Mine
... within the Earth’s crust. Rocks that solidify from magma are called igneous and are broadly divided into extrusive rocks that are formed when the molten magma erupts from the surface as volcanoes or intrusive rocks that form when the magma cools and solidifies beneath the surface. Granite is an igne ...
... within the Earth’s crust. Rocks that solidify from magma are called igneous and are broadly divided into extrusive rocks that are formed when the molten magma erupts from the surface as volcanoes or intrusive rocks that form when the magma cools and solidifies beneath the surface. Granite is an igne ...
Earth Science 2007-2008 Final Study Guide
... All mountains are formed by a process called orogeny. Crust getting uplifted can cause Uplifted Mountains If large pieces of crust are tilted or dropped between normal faults it forms Fault block mountains Rocks made at ocean ridges include pillow basalts. ...
... All mountains are formed by a process called orogeny. Crust getting uplifted can cause Uplifted Mountains If large pieces of crust are tilted or dropped between normal faults it forms Fault block mountains Rocks made at ocean ridges include pillow basalts. ...
Date: Block
... C. Compression: the type of stress that occurs when an object is squeezed, such as when two tectonic plates collide. It occurs at a convergent boundary. D. Tension: stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object. They occur at divergent boundaries such as mid-ocean ridges. II. Folding A. De ...
... C. Compression: the type of stress that occurs when an object is squeezed, such as when two tectonic plates collide. It occurs at a convergent boundary. D. Tension: stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object. They occur at divergent boundaries such as mid-ocean ridges. II. Folding A. De ...
under pressure
... UNDER PRESSURE Metamorphism is classed as low, medium, or high grade, depending on how extreme the conditions are that produce the rock. Low-grade metamorphosed rocks are often fine-grained, while high-grade metamorphosed rocks are coarse-grained. The graph shown here is often used by geologists to ...
... UNDER PRESSURE Metamorphism is classed as low, medium, or high grade, depending on how extreme the conditions are that produce the rock. Low-grade metamorphosed rocks are often fine-grained, while high-grade metamorphosed rocks are coarse-grained. The graph shown here is often used by geologists to ...
Rock Types - Volcanoes Alive!
... igneous rocks, on the other hand, are formed when magma reaches the surface of Earth and cools quickly. Mineral crystals cannot grow very large during this rapid cooling, so the rocks are fine grained. Texture can vary. Examples are pumice and obsidian. Igneous rocks are the most common rocks found ...
... igneous rocks, on the other hand, are formed when magma reaches the surface of Earth and cools quickly. Mineral crystals cannot grow very large during this rapid cooling, so the rocks are fine grained. Texture can vary. Examples are pumice and obsidian. Igneous rocks are the most common rocks found ...
Plate Tectonic/Rock Cycle Crossward Puzzle
... 1. interactions among earth's water, air, and land that can cause rocks to change from one type to another 3. forms when magma cools and hardens underneath earth's surface or as a result from a volcanic eruption 4. a theory that proposes earth's outer shell consists of individual plates that interac ...
... 1. interactions among earth's water, air, and land that can cause rocks to change from one type to another 3. forms when magma cools and hardens underneath earth's surface or as a result from a volcanic eruption 4. a theory that proposes earth's outer shell consists of individual plates that interac ...
Earth`s Composition Tectonic Plates Virginia Geology Rock Cycle
... - transform boundaries’ features: strike-slip faults – San Andreas Fault ...
... - transform boundaries’ features: strike-slip faults – San Andreas Fault ...
Geology Review Sheet
... 2. Explain the steps of the rock cycle, how each type of rock forms, and the processes that form different types of rocks. Be able to describe how one rock transforms into another. 3. Explain the relationships between the type of plate boundary and the likely depth, magnitude, and intensity of an ea ...
... 2. Explain the steps of the rock cycle, how each type of rock forms, and the processes that form different types of rocks. Be able to describe how one rock transforms into another. 3. Explain the relationships between the type of plate boundary and the likely depth, magnitude, and intensity of an ea ...
Practice20m
... 11) The Earth’s hotter Archean surface temperatures are indicated by the presence of: a) komatiite rocks. b) basalt rocks. c) andesite rocks. d) granite rocks. 12) Archean rocks are commonly exposed: a) on the continental margins. b) in the shield areas of the continental interiors. c) on the ocean ...
... 11) The Earth’s hotter Archean surface temperatures are indicated by the presence of: a) komatiite rocks. b) basalt rocks. c) andesite rocks. d) granite rocks. 12) Archean rocks are commonly exposed: a) on the continental margins. b) in the shield areas of the continental interiors. c) on the ocean ...
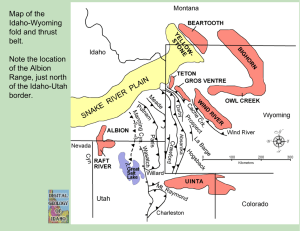
Albions
... View from near Albion, looking south at Big Bertha Dome of the northern Albion Range. Mt. Harrison is on the right. The Pomerelle ski area is in the valley in the middle-ground. The prominent dome is the surface of the Proterozoic Elba quartzite which is folded into a turtleback-shaped anticline as ...
... View from near Albion, looking south at Big Bertha Dome of the northern Albion Range. Mt. Harrison is on the right. The Pomerelle ski area is in the valley in the middle-ground. The prominent dome is the surface of the Proterozoic Elba quartzite which is folded into a turtleback-shaped anticline as ...
Name: Chapter 7 Review Guide Directions: Please answer all
... 3. What are two common and useful metamorphic rocks? What is the most common intrusive rock? Give two examples of useful igneous rocks. ...
... 3. What are two common and useful metamorphic rocks? What is the most common intrusive rock? Give two examples of useful igneous rocks. ...
George Cuvier (1769 – 1832) Introduced the concept of
... Neptunism: rocks form from crystallization in the early earth’s oceans James Hutton (1726 – 1797) “present is the key to the past” – Uniformitariansim Uniformitariansim: geologic process creates and destroys rock. Studied rock exposures, showed how rocks could form by slow geologic process Recognize ...
... Neptunism: rocks form from crystallization in the early earth’s oceans James Hutton (1726 – 1797) “present is the key to the past” – Uniformitariansim Uniformitariansim: geologic process creates and destroys rock. Studied rock exposures, showed how rocks could form by slow geologic process Recognize ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.