Attachment 2
... i. Exploration and Application of Knowledge: Water contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The oxygen is very electronegative and therefore has a partial positive charge. b. This polarity affects the way the molecule interacts with other molecules, such as water. The hydrogen in water has a ...
... i. Exploration and Application of Knowledge: Water contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The oxygen is very electronegative and therefore has a partial positive charge. b. This polarity affects the way the molecule interacts with other molecules, such as water. The hydrogen in water has a ...
Activation energy
... • Molecules contain heat energy that causes them to vibrate and wander randomly. ...
... • Molecules contain heat energy that causes them to vibrate and wander randomly. ...
Bond
... molecules. Students will then predict the shapes of the molecules and use their prior knowledge of bond polarity to predict the polarity of the molecule. INTRODUCTION Covalent Bonds A group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is called a molecule. The properties of a molecule, including its rol ...
... molecules. Students will then predict the shapes of the molecules and use their prior knowledge of bond polarity to predict the polarity of the molecule. INTRODUCTION Covalent Bonds A group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is called a molecule. The properties of a molecule, including its rol ...
DEXTROSE CERTIFIED MALTOSE
... Dextrose is used as a source of energy to cultivate microorganisms and for fermentation studies. Dextrose is incorporated into many culture media formulae, such as those employed in the selective isolation of enterobacteriaceae. In liquid culture media, Dextrose is generally used in a 0.5% concentra ...
... Dextrose is used as a source of energy to cultivate microorganisms and for fermentation studies. Dextrose is incorporated into many culture media formulae, such as those employed in the selective isolation of enterobacteriaceae. In liquid culture media, Dextrose is generally used in a 0.5% concentra ...
6. 3-D structure of proteins
... 3-D Structure of Proteins • Primary Structure – basic amino acid sequence • Secondary Structure – refers to the local conformation of some part of the polypeptide [α helix; β conformations] • Teritiary Structure - is the overall three-dimensional arrangement of all atoms in a protein. • Quaternary ...
... 3-D Structure of Proteins • Primary Structure – basic amino acid sequence • Secondary Structure – refers to the local conformation of some part of the polypeptide [α helix; β conformations] • Teritiary Structure - is the overall three-dimensional arrangement of all atoms in a protein. • Quaternary ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... 46. (6 pts) When 0.560 g of Na(s) reacts with excess F2(g) to form NaF(s), 13.8 kJ of heat is evolved at standard-state conditions. What is the standard enthalpy of formation (ΔH°f) of NaF(s)? Note that the units of ΔH°f are in kJ/mole and the heat evolved in the reaction is given in kJ. ...
... 46. (6 pts) When 0.560 g of Na(s) reacts with excess F2(g) to form NaF(s), 13.8 kJ of heat is evolved at standard-state conditions. What is the standard enthalpy of formation (ΔH°f) of NaF(s)? Note that the units of ΔH°f are in kJ/mole and the heat evolved in the reaction is given in kJ. ...
Chem 4B Final Exam Review Sheet Systematic error
... folded very tightly to fit inside. Urea can have multiple H bonds with amino acids It disrupts alpha helices and beta sheets in a protein. It also affects interactions between side chains, between water and a side chain. But it’s not an acid/base; it is not ionic. ...
... folded very tightly to fit inside. Urea can have multiple H bonds with amino acids It disrupts alpha helices and beta sheets in a protein. It also affects interactions between side chains, between water and a side chain. But it’s not an acid/base; it is not ionic. ...
Biology\Ch 2 Chemistry
... isotopes, compounds, chemical formula, chemical equation, ions, ionic bonds, covalent bonds, molecules, structural formula, polarity, cohesion, adhesion, mixture, solution, isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic, solute, solvent, concentration, suspension, colloid, hydronium ion, acid, hydroxide ion, base, ...
... isotopes, compounds, chemical formula, chemical equation, ions, ionic bonds, covalent bonds, molecules, structural formula, polarity, cohesion, adhesion, mixture, solution, isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic, solute, solvent, concentration, suspension, colloid, hydronium ion, acid, hydroxide ion, base, ...
Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... Solution and concentration When a substance is dissolved in a liquid (ex. water), a solution is formed. The substance that is dissolved is the solute and the liquid in which the dissolution occurred is the solvent. Concentration: The measure of dissolution of a particular solute in a given volume o ...
... Solution and concentration When a substance is dissolved in a liquid (ex. water), a solution is formed. The substance that is dissolved is the solute and the liquid in which the dissolution occurred is the solvent. Concentration: The measure of dissolution of a particular solute in a given volume o ...
Chapter 2 Atoms Subatomic particles of atoms
... Building blocks from large to small • Matter is anything that has weight and takes up space ...
... Building blocks from large to small • Matter is anything that has weight and takes up space ...
Matter Notes X Law of Definite Proportions – or Constant
... Law of Definite Proportions – or Constant Composition elemental composition of a pure substance is always the same, ex. Water (Proust) X Law of Multiple Proportions – (Dalton) If two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one that combine with a given mass of the other, are in the ratio ...
... Law of Definite Proportions – or Constant Composition elemental composition of a pure substance is always the same, ex. Water (Proust) X Law of Multiple Proportions – (Dalton) If two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one that combine with a given mass of the other, are in the ratio ...
Organic Molecules Study Guide: Substance Basic Structure
... Which organic molecule is known for insulation? _______lipids__________ Which organic molecule is found in cellular membranes? ________lipids________ Which organic molecule helps with protein synthesis and carries genetic information? __Nucleic ...
... Which organic molecule is known for insulation? _______lipids__________ Which organic molecule is found in cellular membranes? ________lipids________ Which organic molecule helps with protein synthesis and carries genetic information? __Nucleic ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... 3. ATOM SMALLEST unit of an ELEMENT and maintain the PROPERTIES of that element 4. MOLECULE SMALLEST unit of a COMPOUND; maintaining PROPERTIES of the compound 5. ELEMENT matter that is composed of one kind of ATOM (e.g. sulfur [S]; carbon [C]) a. each ELEMENT has its own CHARACTERISTIC chemic ...
... 3. ATOM SMALLEST unit of an ELEMENT and maintain the PROPERTIES of that element 4. MOLECULE SMALLEST unit of a COMPOUND; maintaining PROPERTIES of the compound 5. ELEMENT matter that is composed of one kind of ATOM (e.g. sulfur [S]; carbon [C]) a. each ELEMENT has its own CHARACTERISTIC chemic ...
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
... A detector is needed to see the separated compound bands as they elute from the HPLC column [most compounds have no color, so we can’t see them with our eyes]. The mobile phase exits the detector and can be sent to waste, or collected. When the mobile phase contains a separated compound band, HPLC p ...
... A detector is needed to see the separated compound bands as they elute from the HPLC column [most compounds have no color, so we can’t see them with our eyes]. The mobile phase exits the detector and can be sent to waste, or collected. When the mobile phase contains a separated compound band, HPLC p ...
ic199p5a
... 8) and another, the zinc blende structure (C.N. = 4). Choose the most likely salts (2) from this list to have these two other structures and briefly explain the reason for your choice (assume that the anion is bigger than the cation in each case). Ans.: BeSe is most likely to have the zinc blende st ...
... 8) and another, the zinc blende structure (C.N. = 4). Choose the most likely salts (2) from this list to have these two other structures and briefly explain the reason for your choice (assume that the anion is bigger than the cation in each case). Ans.: BeSe is most likely to have the zinc blende st ...
CH 460 Dr. Muccio What are the 4 levels of protein structure and
... What are the 4 levels of protein structure and describe each. Do proteins with similar structures usually have similar functions? Primary - amino acid sequence Secondary – helices, sheets, turns, loops Tertiary – 3d folding Quaternary – organization of 3d subunits Yes usually (not always), similar s ...
... What are the 4 levels of protein structure and describe each. Do proteins with similar structures usually have similar functions? Primary - amino acid sequence Secondary – helices, sheets, turns, loops Tertiary – 3d folding Quaternary – organization of 3d subunits Yes usually (not always), similar s ...
Mixing Ideal Mixtures Ideal Mixtures Colligative Properties Van t`Hoff
... • Problem: The Henry's law constant K for CO2 dissolved in water is K = 1.6 × 103 atm at 300K (for use with Pgas [atm] = K [atm] xaq, where xaq is the molar fraction of the solute). If the partial pressure of CO2 in air is 0.038 atm under STP, estimate the concentration, in mol/L, of dissolved CO2 i ...
... • Problem: The Henry's law constant K for CO2 dissolved in water is K = 1.6 × 103 atm at 300K (for use with Pgas [atm] = K [atm] xaq, where xaq is the molar fraction of the solute). If the partial pressure of CO2 in air is 0.038 atm under STP, estimate the concentration, in mol/L, of dissolved CO2 i ...
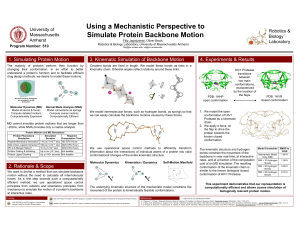
Using a Mechanistic Perspective to Simulate Protein Backbone Motion
... conformation of the kinematic chain is similar to the known biological closed conformation of HIV1 Protease. ...
... conformation of the kinematic chain is similar to the known biological closed conformation of HIV1 Protease. ...
Peptide Bonds
... ---polar hydrophilic groups are aimed outwards towards water, whereas non-polar “greasy” hydrophobic hydrocarbon portions cluster inside the molecule, so protecting them from the hostile aqueous environment ----- Soluble Proteins ...
... ---polar hydrophilic groups are aimed outwards towards water, whereas non-polar “greasy” hydrophobic hydrocarbon portions cluster inside the molecule, so protecting them from the hostile aqueous environment ----- Soluble Proteins ...
FlexWeb
... 3. Many biochemical process are regulated by protein switching from one shape to another shape. ...
... 3. Many biochemical process are regulated by protein switching from one shape to another shape. ...