We venture into proteins` potential as functional molecules by means
... which is more than the total number of stars, and by utilizing these structures, we create the functional molecules that can be utilized in the fields of medicine, environment and nanotechnology. Generating new functional proteins can be mimicked in vitro (molecular evolutional technique). This meth ...
... which is more than the total number of stars, and by utilizing these structures, we create the functional molecules that can be utilized in the fields of medicine, environment and nanotechnology. Generating new functional proteins can be mimicked in vitro (molecular evolutional technique). This meth ...
Membranes and Transport - Bio-Guru
... Is the “cell” hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic with respect to its environment? ...
... Is the “cell” hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic with respect to its environment? ...
Metal chelate chrom
... • Is useful for concentrating dilute protein solutions • Is compatible with a number of buffers containing high ionic strength or chaotropic components • Generally does not affect the structure of proteins • The use of a non‐charged IMAC column allows solutions to become transiently sterile since al ...
... • Is useful for concentrating dilute protein solutions • Is compatible with a number of buffers containing high ionic strength or chaotropic components • Generally does not affect the structure of proteins • The use of a non‐charged IMAC column allows solutions to become transiently sterile since al ...
Structural Genomics
... The initial stages of folding must be nearly random, but if the entire process was a random search it would require too much time. Consider a 100 residue protein. If each residue is considered to have just 3 possible conformations the total number of conformations of the protein is 3100. Conformatio ...
... The initial stages of folding must be nearly random, but if the entire process was a random search it would require too much time. Consider a 100 residue protein. If each residue is considered to have just 3 possible conformations the total number of conformations of the protein is 3100. Conformatio ...
Appendix
... where C0 is the bulk ion concentration, F is Faraday’s constant, 1 is the Debye length, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature. The calculated surface charge density for the membrane charged for 24 hr was qp = -2.7 mC/m2. ...
... where C0 is the bulk ion concentration, F is Faraday’s constant, 1 is the Debye length, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature. The calculated surface charge density for the membrane charged for 24 hr was qp = -2.7 mC/m2. ...
Proteins - mrsmaineswiki
... 10.Sometimes proteins lose their shape due to various reasons. What is the process called when proteins lose there shape? 11.What can happen to a protein that would lose its shape? a. b. c. 12.You have models of a dipeptide and a tripeptide. If you were assigned a polypeptide to construct, how many ...
... 10.Sometimes proteins lose their shape due to various reasons. What is the process called when proteins lose there shape? 11.What can happen to a protein that would lose its shape? a. b. c. 12.You have models of a dipeptide and a tripeptide. If you were assigned a polypeptide to construct, how many ...
Physical Chemistry Reference: Physical Chemistry Principles and
... Therefore, the molecules of liquid water form a mobile network. The network is not a rigid one, and change in neighbors occurs rapidly because of thermal motions. ...
... Therefore, the molecules of liquid water form a mobile network. The network is not a rigid one, and change in neighbors occurs rapidly because of thermal motions. ...
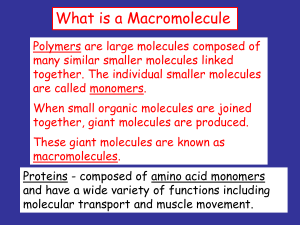
What is a Macromolecule
... • Hemoglobin is a protein found in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) and this is what actually carries the oxygen found in blood • Four oxygen atoms can bond to each hemoglobin (one to each major subunit of hemoglobin) ...
... • Hemoglobin is a protein found in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) and this is what actually carries the oxygen found in blood • Four oxygen atoms can bond to each hemoglobin (one to each major subunit of hemoglobin) ...
chemistry log: solutions
... a). Solution Process-- explain the solute-solvent interactions that cause polar and ionic solutes to dissolve in a polar solvent like water and nonpolar solutes to dissolve in nonpolar solvents like CCl4. Answer question 3 b) What happens to the following colligative properties of a liquid when a no ...
... a). Solution Process-- explain the solute-solvent interactions that cause polar and ionic solutes to dissolve in a polar solvent like water and nonpolar solutes to dissolve in nonpolar solvents like CCl4. Answer question 3 b) What happens to the following colligative properties of a liquid when a no ...
The Structure of Cell Membranes - Biochemical Society Transactions
... inner and mitochondria1 inner membranes. This is not true of bacterial outer membranes, which are probably not real membranes anyway. These former membranes can also serve a different purpose; they can be used to concentrate (hydrophobic) enzymes. This has a special advantage if these enzymes are mo ...
... inner and mitochondria1 inner membranes. This is not true of bacterial outer membranes, which are probably not real membranes anyway. These former membranes can also serve a different purpose; they can be used to concentrate (hydrophobic) enzymes. This has a special advantage if these enzymes are mo ...
EDITORS’CHOICE To Have or Have Not
... the fundamental questions they raise about bonding motifs, as well as their role as models for bulk hydrated electrons of interest in biological electron transfer and photodamage. To render the method computationally tractable, the authors propagate the cluster atoms along a classical trajectory whi ...
... the fundamental questions they raise about bonding motifs, as well as their role as models for bulk hydrated electrons of interest in biological electron transfer and photodamage. To render the method computationally tractable, the authors propagate the cluster atoms along a classical trajectory whi ...
Using Computers to teach Undergraduates about Biological Molecules
... offers a half-way house between the simpler microcomputer-based systems and the comprehensive, normally expensive, commercial modelling packages such as those from Biosym, Chemical Design, Molecular Simulations and Tripos etc. It is particularly useful since it operates in a Windows-type environment ...
... offers a half-way house between the simpler microcomputer-based systems and the comprehensive, normally expensive, commercial modelling packages such as those from Biosym, Chemical Design, Molecular Simulations and Tripos etc. It is particularly useful since it operates in a Windows-type environment ...
Transport in Bacterial Cells
... • Higher potential energy of water • Higher concentration of water molecules that have free energy of movement ...
... • Higher potential energy of water • Higher concentration of water molecules that have free energy of movement ...
TUTORIAL FOR PROTEIN TECHNOLOGY: Ion-exchange
... When two non-polar solutes interact, there is less surface area for the water molecules to bind to the non-polar solutes. The water molecules will move to the area of bulk water, where it is less structured, and therefore more thermodynamically favourable. Certain ions-the ones high in the Hoffmeist ...
... When two non-polar solutes interact, there is less surface area for the water molecules to bind to the non-polar solutes. The water molecules will move to the area of bulk water, where it is less structured, and therefore more thermodynamically favourable. Certain ions-the ones high in the Hoffmeist ...
2. Essential Chemistry
... o Ratio of solute to solvent expressed as a percentage: weight (g)/volume (ml) o Unit seen on IV bags and medicinal solutions 5% dextrose = 5g dextrose / 100 ml of solution 0.9% saline = 0.9g NaCl / 100 ml of solution o Example: o Betadine antiseptic solution contains 10g of povidine-iodine in 1 ...
... o Ratio of solute to solvent expressed as a percentage: weight (g)/volume (ml) o Unit seen on IV bags and medicinal solutions 5% dextrose = 5g dextrose / 100 ml of solution 0.9% saline = 0.9g NaCl / 100 ml of solution o Example: o Betadine antiseptic solution contains 10g of povidine-iodine in 1 ...
Nutrition
... bloodstream; include Vitamin C and all B vitamins – Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in fatty issues; Vitamins A, D, E, and K ...
... bloodstream; include Vitamin C and all B vitamins – Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in fatty issues; Vitamins A, D, E, and K ...
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
... The appearance may change, but you still have the same substance as before – can be reversed and no energy is produced Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a l ...
... The appearance may change, but you still have the same substance as before – can be reversed and no energy is produced Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a l ...
GC-Final-Review-2014
... a. A substances resistance to flow b. The substance being dissolved c. Solutions that have solutes that settle out, more than one phase d. Substances that can interfere with H bonds, i.e. soap e. Temp at which a liquid turns to a vapor/gas f. A substance that contain reflective particles that displa ...
... a. A substances resistance to flow b. The substance being dissolved c. Solutions that have solutes that settle out, more than one phase d. Substances that can interfere with H bonds, i.e. soap e. Temp at which a liquid turns to a vapor/gas f. A substance that contain reflective particles that displa ...
Topic 6
... state!) can be considered a function of the nuclear coordinates only. (2) Transferability – enables a set of parameters developed and tested on a relatively small dataset to be applied to a much wider range of chemical problems. ...
... state!) can be considered a function of the nuclear coordinates only. (2) Transferability – enables a set of parameters developed and tested on a relatively small dataset to be applied to a much wider range of chemical problems. ...
Cell Transport
... *Because the cell needs isolated areas of the cell with different pH for particular functions; ex) lysosomes – have proton pumps to maintain a pH=5 *Because the cell only uses one ATP to pump a proton out, and that proton can be used in co-transport Co-transport – process cells use to bring large mo ...
... *Because the cell needs isolated areas of the cell with different pH for particular functions; ex) lysosomes – have proton pumps to maintain a pH=5 *Because the cell only uses one ATP to pump a proton out, and that proton can be used in co-transport Co-transport – process cells use to bring large mo ...
Carbohydrates - MCAT Cooperative
... It increases the molecular weight of the molecules, causing them to move through the column faster. It decreases the strength of the charge interactions between the molecules and the stationery phase. It increases the charge differences between the negatively and positively charged molecules. It fil ...
... It increases the molecular weight of the molecules, causing them to move through the column faster. It decreases the strength of the charge interactions between the molecules and the stationery phase. It increases the charge differences between the negatively and positively charged molecules. It fil ...
Understanding Polarity
... A. Are made up of single sheets of lipids (monolayers) B. Are completely nonpolar and therefore do not dissolve in water C. Have a polar head domain that is not soluble in water D. Have a polar hydrocarbon tail domain that is not soluble in water E. Formed when lipid bilayers formed vesicles by rema ...
... A. Are made up of single sheets of lipids (monolayers) B. Are completely nonpolar and therefore do not dissolve in water C. Have a polar head domain that is not soluble in water D. Have a polar hydrocarbon tail domain that is not soluble in water E. Formed when lipid bilayers formed vesicles by rema ...
Phospholipids make up cell membranes
... 2. Water molecules “stick” temporarily to any dissolved solute molecules. As a result, water molecules spend more time and accumulate on the side of the membrane with the higher concentration of dissolved ...
... 2. Water molecules “stick” temporarily to any dissolved solute molecules. As a result, water molecules spend more time and accumulate on the side of the membrane with the higher concentration of dissolved ...
Nanoparticle drug vectors in a bloodstream, theoretical study of
... Nanoparticle drug vectors in a bloodstream, theoretical study of competition between carbon nanotubes and testosterone for interactions with serum albumin dr inż. Sebastian Kraszewski ...
... Nanoparticle drug vectors in a bloodstream, theoretical study of competition between carbon nanotubes and testosterone for interactions with serum albumin dr inż. Sebastian Kraszewski ...