From Tuesday
... • “Problems” in this arena break down into three obvious categories – What is the molarity of a solution prepared…. – How many _____ of solute are present in a…. – What volume of solution would contain… ...
... • “Problems” in this arena break down into three obvious categories – What is the molarity of a solution prepared…. – How many _____ of solute are present in a…. – What volume of solution would contain… ...
Topic - Structure and Function
... HS-LS1-6. Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for how carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen from sugar molecules may combine with other elements to form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using evidence from models and simulation ...
... HS-LS1-6. Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for how carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen from sugar molecules may combine with other elements to form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using evidence from models and simulation ...
Cellular Transport Notes
... A: Diffusion Q: Is sugar a solute or solvent? A: Solute Q: What are 3 types of osmotic solutions? A: Isotonic, Hypotonic, Hypertonic Q: If a cell is placed in a strong salt solution, explain what will happen to the cell? A: It will shrink due to the lack of water outside the cell. ...
... A: Diffusion Q: Is sugar a solute or solvent? A: Solute Q: What are 3 types of osmotic solutions? A: Isotonic, Hypotonic, Hypertonic Q: If a cell is placed in a strong salt solution, explain what will happen to the cell? A: It will shrink due to the lack of water outside the cell. ...
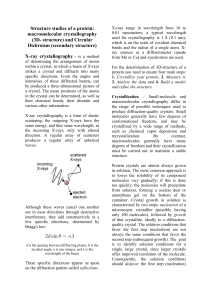
Structure studies of a protein: macromolecular crystallography (3D
... used for crystallography is 1 Å (0.1 nm), which is on the scale of covalent chemical bonds and the radius of a single atom. Xray sources as a diffractometer (anode from Mo or Cu) and synchrotron are used. For the determination of 3D-structure of a protein you need to ensure four main steps: 1. Cryst ...
... used for crystallography is 1 Å (0.1 nm), which is on the scale of covalent chemical bonds and the radius of a single atom. Xray sources as a diffractometer (anode from Mo or Cu) and synchrotron are used. For the determination of 3D-structure of a protein you need to ensure four main steps: 1. Cryst ...
Measurements/Unit Cancellation/Significant Figures 1. When
... Hydrated ion: An ion in which a specific number of water molecules is associated with each formula unit. Hydration: Solvation in water. Limiting reactant: The reactant that is consumed when a reaction occurs and therefore the one that determines the maximum amount of product that can form. Molarity ...
... Hydrated ion: An ion in which a specific number of water molecules is associated with each formula unit. Hydration: Solvation in water. Limiting reactant: The reactant that is consumed when a reaction occurs and therefore the one that determines the maximum amount of product that can form. Molarity ...
The Membrane: Overview
... be compatible with and based upon the existing body of evidence. link an effect to a variable. state the expected effect. be testable. have the potential to be refuted. ...
... be compatible with and based upon the existing body of evidence. link an effect to a variable. state the expected effect. be testable. have the potential to be refuted. ...
Balance this equation:
... The diagram shows iron oxide, Fe2O3, and carbon monoxide, CO reacting to form iron and carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the correct full balanced chemical equation for the reaction depicted? ...
... The diagram shows iron oxide, Fe2O3, and carbon monoxide, CO reacting to form iron and carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the correct full balanced chemical equation for the reaction depicted? ...
Image Tutorial: Surface Properties
... window using File... Save Image with default settings. There is a limit to how thick lines such as silhouette edges, wire, and mesh can be drawn while rendering an image. If supersampling is done, the image is initially drawn at a larger size than requested (3x3 by default) and then sampled back dow ...
... window using File... Save Image with default settings. There is a limit to how thick lines such as silhouette edges, wire, and mesh can be drawn while rendering an image. If supersampling is done, the image is initially drawn at a larger size than requested (3x3 by default) and then sampled back dow ...
Surface and Protein Interactions
... Andrade argued that the free energy of a polymer-water interface is what governs protein adsorption – so as the solid looks more and more like water there is an increase in biocompatibility. Examples are hydrogels and PEOmodified surfaces have reduced coagulation effects. (New Materials: Hydrogels) ...
... Andrade argued that the free energy of a polymer-water interface is what governs protein adsorption – so as the solid looks more and more like water there is an increase in biocompatibility. Examples are hydrogels and PEOmodified surfaces have reduced coagulation effects. (New Materials: Hydrogels) ...
4 ways to penetrate the Cell Membrane
... Signal sequences on the N-terminal represent a string of leucine-rich hydrophobic amino acids that allow the peptide to dock with the receptor The signal peptide is removed after the peptide has penetrated the membrane ...
... Signal sequences on the N-terminal represent a string of leucine-rich hydrophobic amino acids that allow the peptide to dock with the receptor The signal peptide is removed after the peptide has penetrated the membrane ...
AR Chemistry Notes: Solutions
... Most chemical reactions release too much energy when pure samples are mixed together (explosions). To control chemical reactions, most chemicals are dissolved in water to reduce the explosiveness of the reaction. Solutions: two or more materials that are evenly mixed at the molecular level (homogene ...
... Most chemical reactions release too much energy when pure samples are mixed together (explosions). To control chemical reactions, most chemicals are dissolved in water to reduce the explosiveness of the reaction. Solutions: two or more materials that are evenly mixed at the molecular level (homogene ...
2015 Blue Waters book
... requires for solidly based descriptions. Very fortunately, computational modeling can play a significant role in hybrid method structure analysis. First, the accuracy of computational modeling has drastically increased, such that results from computational studies today often exhibit astounding agre ...
... requires for solidly based descriptions. Very fortunately, computational modeling can play a significant role in hybrid method structure analysis. First, the accuracy of computational modeling has drastically increased, such that results from computational studies today often exhibit astounding agre ...
Molecular Representations - West Chester University of
... – All information needed to define 3D shape already present in “sequence” of amino acids – “3° structure is defined by 1° structure…” – How……? ...
... – All information needed to define 3D shape already present in “sequence” of amino acids – “3° structure is defined by 1° structure…” – How……? ...
Seminar L11- Laboratorija za molekularno biologijo in
... technology to study biomolecule interactions. The term Microscale Thermophoresis refers to the directed movement of molecules in optically generated microscopic temperature gradients. This thermophoretic movement is determined by the entropy of the hydration shell around the molecules. Microscale Th ...
... technology to study biomolecule interactions. The term Microscale Thermophoresis refers to the directed movement of molecules in optically generated microscopic temperature gradients. This thermophoretic movement is determined by the entropy of the hydration shell around the molecules. Microscale Th ...
protein folding
... each other. Conversely, similarly charged side chains repel each other. In addition, interactions involving hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds all exert an influence on the folding process. This process of trial and error tests many, but not all, possible configurations, s ...
... each other. Conversely, similarly charged side chains repel each other. In addition, interactions involving hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds all exert an influence on the folding process. This process of trial and error tests many, but not all, possible configurations, s ...
Protein PPT Editted
... fat to form lipoproteins, transport of iron and other nutrients and oxygen in the blood Provides energy as a last resort if the body can’t get energy from carbs and fat or if there is too much protein in the diet Protein provides 4 calories per gram ...
... fat to form lipoproteins, transport of iron and other nutrients and oxygen in the blood Provides energy as a last resort if the body can’t get energy from carbs and fat or if there is too much protein in the diet Protein provides 4 calories per gram ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... 79. A 1.365 g sample of sodium carbonate was added to 25.0 mL of a 1.00 M hydrochloric acid solution in a calorimeter, and the solution’s temperature increased from 21.2ºC to 32.6ºC. If the solution had a mass of 26.834 g and a heat capacity of 4.184 J/gCº, calculate the heat of reaction in kilojoul ...
... 79. A 1.365 g sample of sodium carbonate was added to 25.0 mL of a 1.00 M hydrochloric acid solution in a calorimeter, and the solution’s temperature increased from 21.2ºC to 32.6ºC. If the solution had a mass of 26.834 g and a heat capacity of 4.184 J/gCº, calculate the heat of reaction in kilojoul ...
Journal of Chromatography
... concepts proposed by Bene and Pople 3o. Accordingly, hydrophilic solutes are “structure breakers” and interact more strongly with water than the water molecules with each other. They are readily soluble and give rise to hydration layers that show structural features different from those of the bulk ...
... concepts proposed by Bene and Pople 3o. Accordingly, hydrophilic solutes are “structure breakers” and interact more strongly with water than the water molecules with each other. They are readily soluble and give rise to hydration layers that show structural features different from those of the bulk ...
Sample abstract - Molecular Biophysics Unit
... We have studied a range of molecular complexes including free Xpot protein and intermediate state complexes bound either to ...
... We have studied a range of molecular complexes including free Xpot protein and intermediate state complexes bound either to ...
+ Cl
... In an ionic pair, the cation and anion are close to each other, and few or no solvent molecules are between them. Therefore, HCl does not ionize and NaCl does not dissociate completely in ...
... In an ionic pair, the cation and anion are close to each other, and few or no solvent molecules are between them. Therefore, HCl does not ionize and NaCl does not dissociate completely in ...
introduction - Molecular Creation Home Page
... as well.7,11 Thus, as proteins form, most peptides with hydrocarbon side-chains are left inside forming the anyhdrous core while small water-binding peptides, like glycine, serine and aspartame, are left outside increasing stability and solubility. However, some hydration-ordering regions remain on ...
... as well.7,11 Thus, as proteins form, most peptides with hydrocarbon side-chains are left inside forming the anyhdrous core while small water-binding peptides, like glycine, serine and aspartame, are left outside increasing stability and solubility. However, some hydration-ordering regions remain on ...
Document
... Volume-amount of space an object occupies Mass-amount of matter an object has Weight-force produced by gravity on an object ...
... Volume-amount of space an object occupies Mass-amount of matter an object has Weight-force produced by gravity on an object ...
An anabolic pathway requires energy and builds
... Catabolic pathways involve the degradation of complex molecules into simpler ones. Molecular energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules is released in catabolic pathways and harvested in such a way that it can be used to produce ATP. Other energystoring molecules, such as fats, are also broken ...
... Catabolic pathways involve the degradation of complex molecules into simpler ones. Molecular energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules is released in catabolic pathways and harvested in such a way that it can be used to produce ATP. Other energystoring molecules, such as fats, are also broken ...
cloudfront.net
... a. How many valence electrons does it have? ______ Circle the valence electron(s). b. How many protons does it have? ______ Concept 2.3 The formation and function of molecules depend on chemical bonding between atoms 13. Define molecule. 14. What type of bond is seen in O2? Explain what this means. ...
... a. How many valence electrons does it have? ______ Circle the valence electron(s). b. How many protons does it have? ______ Concept 2.3 The formation and function of molecules depend on chemical bonding between atoms 13. Define molecule. 14. What type of bond is seen in O2? Explain what this means. ...
Structure studies of a protein: macromolecular crystallography (3D
... molecules is prepared, and a wide variety of crystallization solutions are tested. Hundreds, even thousands, of solution ...
... molecules is prepared, and a wide variety of crystallization solutions are tested. Hundreds, even thousands, of solution ...