03_Worked_Examples
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
... (c) The reactants box contains four O2 and eight NO. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each two NO, as required by the balanced equation. The products box contains eight NO 2, which means the number of NO2 product molecules equals the number of NO reactant molecules, as the balanced equation r ...
Thermochemistry Exam Review Questions
... 11. A student found that orange IV indicator turned yellow and methyl orange turned red in samples of an unknown solution. What is the pH for the unknown solution likely to be? A. 1.2 B. 3.0 C. 5.3 D. 9.0 12. What is the name of the ion when a positively charged proton combines with a water molecul ...
... 11. A student found that orange IV indicator turned yellow and methyl orange turned red in samples of an unknown solution. What is the pH for the unknown solution likely to be? A. 1.2 B. 3.0 C. 5.3 D. 9.0 12. What is the name of the ion when a positively charged proton combines with a water molecul ...
- Angelo State University
... The Molar Mass of a Compound • The molar mass of a compound is obtained by adding together the atomic masses of all of the atoms in the molecule or formula unit. This number is either the mass of the compound in units of amu, or the mass of one mole of the compound in grams. – For molecular compound ...
... The Molar Mass of a Compound • The molar mass of a compound is obtained by adding together the atomic masses of all of the atoms in the molecule or formula unit. This number is either the mass of the compound in units of amu, or the mass of one mole of the compound in grams. – For molecular compound ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when methanol,CH3OH(l), is burned in air. When any compound containing C, H, and O is combusted, it reacts with the O2(g) in air to produce CO2(g) and H2O(g). Thus, the unbalanced equation is CH3OH(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) The C atoms are ...
... Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when methanol,CH3OH(l), is burned in air. When any compound containing C, H, and O is combusted, it reacts with the O2(g) in air to produce CO2(g) and H2O(g). Thus, the unbalanced equation is CH3OH(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) The C atoms are ...
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... 89. One way of obtaining pure sodium carbonate is through the decomposition of the mineral trona, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O(s) → 5Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) When 1.00 metric ton (1 × 103 kg) of trona is decomposed, 0.74 metric ton of Na2CO3 is recovered. What is the percent yield ...
... 89. One way of obtaining pure sodium carbonate is through the decomposition of the mineral trona, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O(s) → 5Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) When 1.00 metric ton (1 × 103 kg) of trona is decomposed, 0.74 metric ton of Na2CO3 is recovered. What is the percent yield ...
Chem 2A Final Review
... ans. Ba(OH)2 (aq) , BaSO4 (s) , BaS (s) , Ba(NO3)2 (aq) 40. Ans. (0.220 g NaCl/100 mL solution) 65.0 mL solution = 0.143 g NaCl 41. Ans. 12.1 g NaCl /(12.1 g NaCl + 150.1 g water) 100 = 7.57 % 42. M = mol/L, mol = M L, 50.0 mL 1L/1000mL 12.0 M = 0.600 mol HNO3, mol = g/mw, g = mol mw = 0 ...
... ans. Ba(OH)2 (aq) , BaSO4 (s) , BaS (s) , Ba(NO3)2 (aq) 40. Ans. (0.220 g NaCl/100 mL solution) 65.0 mL solution = 0.143 g NaCl 41. Ans. 12.1 g NaCl /(12.1 g NaCl + 150.1 g water) 100 = 7.57 % 42. M = mol/L, mol = M L, 50.0 mL 1L/1000mL 12.0 M = 0.600 mol HNO3, mol = g/mw, g = mol mw = 0 ...
Topic 3 MOLE Avodagro`s number = 6.02 x 1023 things = 1 mole 1
... a) How many grams of O2 are needed to burn 1.50 mole of octane? 1.5 mole octane (25mole O2 /2mole octane) (32 g /mole O2) = 600 g 12. One of the steps in the commercial process for converting ammonia to nitric acid involves the conversion of N H3 to NO: 4NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4NO (g) + 6 H2O (g) In a ...
... a) How many grams of O2 are needed to burn 1.50 mole of octane? 1.5 mole octane (25mole O2 /2mole octane) (32 g /mole O2) = 600 g 12. One of the steps in the commercial process for converting ammonia to nitric acid involves the conversion of N H3 to NO: 4NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4NO (g) + 6 H2O (g) In a ...
1970 - Warren County Schools
... Lattice energy - quantity of energy released in the formation of one mole of an ionic solid from its separated gaseous ions. The energy quantities needed to be determined: sublimation of solid metal ionization of gaseous atomic metal (ionization energy) dissociation of gaseous non-metal ion formatio ...
... Lattice energy - quantity of energy released in the formation of one mole of an ionic solid from its separated gaseous ions. The energy quantities needed to be determined: sublimation of solid metal ionization of gaseous atomic metal (ionization energy) dissociation of gaseous non-metal ion formatio ...
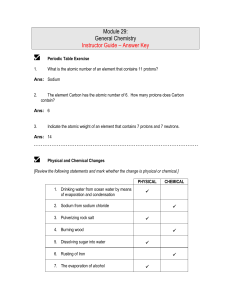
Module 29: General Chemistry Instructor Guide – Answer Key
... area away from sources of heat, moisture and incompatibilities. Always add the caustic to water while stirring; never the reverse. Containers of this material may be hazardous when empty since they retain product residues (dust, solids); observe all warnings and precautions listed for the product. D ...
... area away from sources of heat, moisture and incompatibilities. Always add the caustic to water while stirring; never the reverse. Containers of this material may be hazardous when empty since they retain product residues (dust, solids); observe all warnings and precautions listed for the product. D ...
odd - WWW2
... 14.11 The chemical equation is SiO2(s) + 3 C(s) SiC(s) + 2 CO(g) and with the net increase of two moles of gas, the reaction should be entropy driven. The need for high-temperature synthesis might indicate that there is not only a high activation energy but also the possibility of the reaction being ...
... 14.11 The chemical equation is SiO2(s) + 3 C(s) SiC(s) + 2 CO(g) and with the net increase of two moles of gas, the reaction should be entropy driven. The need for high-temperature synthesis might indicate that there is not only a high activation energy but also the possibility of the reaction being ...
Practice Exam I FR Answers and Explanations
... Cd changes oxidation states from 0 to +2—thus, it is oxidized. Whatever species is oxidized is known as the reducing agent. (c) At a higher temperature, how would the cell potential change? Explain questions such as this with mathematical formulas if at all possible. There are two equations that all ...
... Cd changes oxidation states from 0 to +2—thus, it is oxidized. Whatever species is oxidized is known as the reducing agent. (c) At a higher temperature, how would the cell potential change? Explain questions such as this with mathematical formulas if at all possible. There are two equations that all ...
1970 - 2005 Solids/Liquids/Solutions FRQs
... Lattice energy - quantity of energy released in the formation of one mole of an ionic solid from its separated gaseous ions. The energy quantities needed to be determined: sublimation of solid metal ionization of gaseous atomic metal (ionization energy) dissociation of gaseous non-metal ion formatio ...
... Lattice energy - quantity of energy released in the formation of one mole of an ionic solid from its separated gaseous ions. The energy quantities needed to be determined: sublimation of solid metal ionization of gaseous atomic metal (ionization energy) dissociation of gaseous non-metal ion formatio ...
Primary Structure of Diphtheria Toxin Fragment B
... Polarity indices of CBS (44.0%) and of the N-terminal 22residues segment of CB3 (40 .9%) are close to the mean value of most water-soluble proteins. The difference between the highly hydrophilic N-terminal and the highly hydrophobic middle segments of fragment B is stressed by the fact that both are ...
... Polarity indices of CBS (44.0%) and of the N-terminal 22residues segment of CB3 (40 .9%) are close to the mean value of most water-soluble proteins. The difference between the highly hydrophilic N-terminal and the highly hydrophobic middle segments of fragment B is stressed by the fact that both are ...
Electron configuration
... Camels store the fat tristearin (C57H110O6) in the hump. As well as being a source of energy, the fat is a source of water, because when it is used the reaction 2 C57H110O6(s) + 163 O2(g) 114 CO2(g) + 110 H2O(l) takes place. What mass of water can be made from 1.0 kg of fat? ...
... Camels store the fat tristearin (C57H110O6) in the hump. As well as being a source of energy, the fat is a source of water, because when it is used the reaction 2 C57H110O6(s) + 163 O2(g) 114 CO2(g) + 110 H2O(l) takes place. What mass of water can be made from 1.0 kg of fat? ...
Prior Art - Cabic.com
... of protein P was known in the art. The description explains that the activity of protein P was previously known to result in lowering blood pressure. The inventors assert they have newly produced a stable crystalline form of protein P. Protein P in crystalline form is inactive. The descripti ...
... of protein P was known in the art. The description explains that the activity of protein P was previously known to result in lowering blood pressure. The inventors assert they have newly produced a stable crystalline form of protein P. Protein P in crystalline form is inactive. The descripti ...
Relationship between Hot Spot Residues and Ligand Binding Hot
... a standard set of 16 small probe molecules.32 We used a mask to favor the atoms of the RNase A surface that are within 5 Å of any atom of RNI in the complex (see Materials and Methods). Figure 1b shows that FTMap identified the same three consensus sites found experimentally by MSCS, as well as an ad ...
... a standard set of 16 small probe molecules.32 We used a mask to favor the atoms of the RNase A surface that are within 5 Å of any atom of RNI in the complex (see Materials and Methods). Figure 1b shows that FTMap identified the same three consensus sites found experimentally by MSCS, as well as an ad ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry
... Begin by counting each kind of atom on the two sides of the arrow. There are one Na, one O, and two H on the left side, and one Na, one O, and three H on the right. The Na and O atoms are balanced, but the number of H atoms is not. To increase the number of H atoms on the left, let’s try placing the ...
... Begin by counting each kind of atom on the two sides of the arrow. There are one Na, one O, and two H on the left side, and one Na, one O, and three H on the right. The Na and O atoms are balanced, but the number of H atoms is not. To increase the number of H atoms on the left, let’s try placing the ...
Laboratory Practices from Physical Chemistry
... Using analytical scales, we determine the weight, m1, of empty Dumas flask with stopper. We add ca 1–2 ml of sample to Dumas flask and we place it in the thermostatic bath with temperature Tk. Only the end of the flask neck (1–2 cm) has to project from the bath. During sample evaporation, all air fr ...
... Using analytical scales, we determine the weight, m1, of empty Dumas flask with stopper. We add ca 1–2 ml of sample to Dumas flask and we place it in the thermostatic bath with temperature Tk. Only the end of the flask neck (1–2 cm) has to project from the bath. During sample evaporation, all air fr ...
Part One: Mass and Moles of Substance A. Molecular Mass and
... compound is 34.0 amu, then we could find the true molecular formula: empirical formula is HO (Formula Mass = 17.0 g/mol) convert to formula H2O2 with Molar mass = 34.0 g/mol ...
... compound is 34.0 amu, then we could find the true molecular formula: empirical formula is HO (Formula Mass = 17.0 g/mol) convert to formula H2O2 with Molar mass = 34.0 g/mol ...
Recombinant human insulin-11. Size-exclusion HPLC of
... result of silanol group ionization, are weaken by the eluent pH reduction, but at pH<4 silica begins to dissolve. However nonmodified silica is practically not used for SE HPLC of proteins and peptides because of high sorption of the latter. Hydrogen bonds between the column support surface and prot ...
... result of silanol group ionization, are weaken by the eluent pH reduction, but at pH<4 silica begins to dissolve. However nonmodified silica is practically not used for SE HPLC of proteins and peptides because of high sorption of the latter. Hydrogen bonds between the column support surface and prot ...
Coarse-Grained Modeling of ProteinDynamics
... One of the functional features of proteins is response to a wide range of applied forces. Being subjected to an applied load, proteins play key roles in cytoskeletal organization (Fletcher and Mullins 2010), mechanics (Granzier and Labeit 2004), cellular transport (Serohijos et al. 2006), signaling ...
... One of the functional features of proteins is response to a wide range of applied forces. Being subjected to an applied load, proteins play key roles in cytoskeletal organization (Fletcher and Mullins 2010), mechanics (Granzier and Labeit 2004), cellular transport (Serohijos et al. 2006), signaling ...
Mole
... relationships between the amounts of reactants used and products formed by a chemical reactions; it is based on the law of conservation of mass. ...
... relationships between the amounts of reactants used and products formed by a chemical reactions; it is based on the law of conservation of mass. ...
Chapter 9 - HCC Learning Web
... 50. How many resonance structures are there for the cyclobutene molecule (C4H6; the four carbon atoms are arranged in a ring)? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 50. How many resonance structures are there for the cyclobutene molecule (C4H6; the four carbon atoms are arranged in a ring)? A. B. C. D. E. ...
6 Colloidal dispersion
... 7) Blood plasma substitutes as dextran, PVP & gelatin are hydrophilic colloids used to restore or maintain blood volume. 8) Iron - dextran complex form non-ionic hydrophilic sols used for treatment of anemia. ...
... 7) Blood plasma substitutes as dextran, PVP & gelatin are hydrophilic colloids used to restore or maintain blood volume. 8) Iron - dextran complex form non-ionic hydrophilic sols used for treatment of anemia. ...