Lab
... stage – penetrates the skin of humans (between the toes) – symptoms: most individuals with hookworm infection are asymptomatic • pain in the stomach, pica (or dirt-eating), obstinate constipation followed by diarrhea, palpitations, unsteady pulse, coldness & pallor of the skin and mucous membranes • ...
... stage – penetrates the skin of humans (between the toes) – symptoms: most individuals with hookworm infection are asymptomatic • pain in the stomach, pica (or dirt-eating), obstinate constipation followed by diarrhea, palpitations, unsteady pulse, coldness & pallor of the skin and mucous membranes • ...
An External Channel for Endoscopy
... During endoscopy, a procedure using an endoscope to look inside the gastrointestinal tract, a surgeon may encounter blockages such as blood clots or partially digested food. Limitations of standard endoscope internal channel sizes may prevent these obstacles from being suctioned. This invention, whi ...
... During endoscopy, a procedure using an endoscope to look inside the gastrointestinal tract, a surgeon may encounter blockages such as blood clots or partially digested food. Limitations of standard endoscope internal channel sizes may prevent these obstacles from being suctioned. This invention, whi ...
BIO 110 Test 3 Review (All starred (*) questions are related to
... 28. Describe these three phases. Review the animation on you power point. a. Cephalic b. Gastric c. Intestinal 29. What are the functions of the following stomach secretions? a. Hydrocholiric acid b. Pepsin c. Rennin d. Intrinsic factor 30. What is the exocrine function of the pancreas? 31. What eff ...
... 28. Describe these three phases. Review the animation on you power point. a. Cephalic b. Gastric c. Intestinal 29. What are the functions of the following stomach secretions? a. Hydrocholiric acid b. Pepsin c. Rennin d. Intrinsic factor 30. What is the exocrine function of the pancreas? 31. What eff ...
Slide 1
... Direct continuation of ductus epididymis Coiled part Straightened part 0.5 m in length Ampulla Ejaculatory duct ...
... Direct continuation of ductus epididymis Coiled part Straightened part 0.5 m in length Ampulla Ejaculatory duct ...
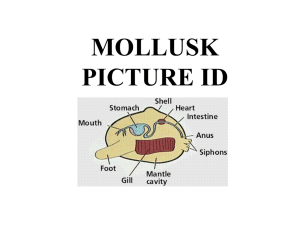
Mollusks PICTURE ID REVIEW
... http://www.discoveryvillage.net/img/oyster.jpg Scallops image : http://www.lib.noaa.gov/japan/aquaculture/exchange/2000tripimages/scallops.jpg ...
... http://www.discoveryvillage.net/img/oyster.jpg Scallops image : http://www.lib.noaa.gov/japan/aquaculture/exchange/2000tripimages/scallops.jpg ...
Removal of materials from the blood
... does not perform a useful role in digestion. Its release in bile is a form of excretion. • In the gut, bilirubin is converted by bacteria to the brown pigment that gives faeces their characteristic colour. ...
... does not perform a useful role in digestion. Its release in bile is a form of excretion. • In the gut, bilirubin is converted by bacteria to the brown pigment that gives faeces their characteristic colour. ...
Virtual Rat Dissection Guide
... one of which is to produce bile which aids in digesting fat. The liver also stores glycogen and transforms wastes into less harmful substances. Rats do not have a gall bladder which is used for storing bile in other animals. There are four parts to the liver, these are known as the lobes. 3. The eso ...
... one of which is to produce bile which aids in digesting fat. The liver also stores glycogen and transforms wastes into less harmful substances. Rats do not have a gall bladder which is used for storing bile in other animals. There are four parts to the liver, these are known as the lobes. 3. The eso ...
28-duodenum & Pancreas
... curves around the head of the pancreas. It lies in the epigastric and umbilical regions. The 1st inch of the first part resembles the stomach in that it is covered on its anterior and posterior surfaces with peritoneum and has the lesser omentum attached to its upper border and the greater omentum a ...
... curves around the head of the pancreas. It lies in the epigastric and umbilical regions. The 1st inch of the first part resembles the stomach in that it is covered on its anterior and posterior surfaces with peritoneum and has the lesser omentum attached to its upper border and the greater omentum a ...
Simple Animals - Veritas Science
... outer cuticle for protection Digestive system has 2 openings: Mouth Anus “Tube-in-Tube Design” - saves time in efficiency - allows more time for digestion - prevents disease Simplest animals to have bilateral symmetry and cephalization Some are free-living (non-parasitic) - Ascaris lumbracoi ...
... outer cuticle for protection Digestive system has 2 openings: Mouth Anus “Tube-in-Tube Design” - saves time in efficiency - allows more time for digestion - prevents disease Simplest animals to have bilateral symmetry and cephalization Some are free-living (non-parasitic) - Ascaris lumbracoi ...
Rat Dissection_2017v2 438KB Apr 04 2017 03:53:11 PM
... is similar to the appendix in humans. It also is the point at which the small intestine becomes the large intestine. The ascending colon - the first main part of the large intestine, which passes upward from the cecum on the right side of the abdomen. The transverse colon - The transverse colon's fu ...
... is similar to the appendix in humans. It also is the point at which the small intestine becomes the large intestine. The ascending colon - the first main part of the large intestine, which passes upward from the cecum on the right side of the abdomen. The transverse colon - The transverse colon's fu ...
Endocrine - Harlan Community Academy
... we feel hungry when we are low on food – why our stomach starts producing stomach acid, our mouths start producing saliva, and our brains seem to only focus on food – and yet feel quickly full as soon as we have eaten. After years of searching, a team of scientists at the University of Washington in ...
... we feel hungry when we are low on food – why our stomach starts producing stomach acid, our mouths start producing saliva, and our brains seem to only focus on food – and yet feel quickly full as soon as we have eaten. After years of searching, a team of scientists at the University of Washington in ...
المحاضرة السادسة عشر Sixteenth lecture
... The coelom of the earthworm is partitioned by septa بفواصل, ...
... The coelom of the earthworm is partitioned by septa بفواصل, ...
phylum nematoda
... intestine, of only a single layer of cells and without any musculature, extends to the muscular rectum and the anus. The “excretory system” will be hard to see and includes an excretory pore that opens near the cervical papilla in the same area as the nerve ring. The “excretory system” consists of r ...
... intestine, of only a single layer of cells and without any musculature, extends to the muscular rectum and the anus. The “excretory system” will be hard to see and includes an excretory pore that opens near the cervical papilla in the same area as the nerve ring. The “excretory system” consists of r ...
The Head and Neck
... Swallowing voluntarily initiated (pharynx) Peristalsis = propulsion Involuntary Alternate waves of contraction and relaxation of muscles in organ walls (e.g. esophagus) Squeezes food from one organ to next Some mixing ...
... Swallowing voluntarily initiated (pharynx) Peristalsis = propulsion Involuntary Alternate waves of contraction and relaxation of muscles in organ walls (e.g. esophagus) Squeezes food from one organ to next Some mixing ...
Flatworms/Roundworms
... no respiratory or circulatory systems: depend on diffusion to transport nutrients. Sense receptors and nerves found at the anterior end Free living or parasitic Found n rivers, lakes, and streams ...
... no respiratory or circulatory systems: depend on diffusion to transport nutrients. Sense receptors and nerves found at the anterior end Free living or parasitic Found n rivers, lakes, and streams ...
Class - Educast
... • Some annelids (e.g. marine sandworms) are dioecious and they release eggs and sperm into the marine environment, where gametes unite to form trochophore larvae ...
... • Some annelids (e.g. marine sandworms) are dioecious and they release eggs and sperm into the marine environment, where gametes unite to form trochophore larvae ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Unit - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... The pig has a digestive system which is classified as monogastric or nonruminant. Humans also have this type of digestive system. They have one stomach (mono=one, gastric=stomach). Locate the entrance to the stomach or esophageal area, the cardiac region which is largest, and the pyloric region wher ...
... The pig has a digestive system which is classified as monogastric or nonruminant. Humans also have this type of digestive system. They have one stomach (mono=one, gastric=stomach). Locate the entrance to the stomach or esophageal area, the cardiac region which is largest, and the pyloric region wher ...
34-1 Phylum Platyhelminthes
... Found in lymphatic system (collects excess fluid from blood vessels) Can cause elephantiasis Swollen limbs, skin hardens & thickens ...
... Found in lymphatic system (collects excess fluid from blood vessels) Can cause elephantiasis Swollen limbs, skin hardens & thickens ...
UNIT 5 Notes #3 – Phylum CNIDARIA - Mr. Lesiuk
... food. Other cells of the endoderm will then absorb the digested nutrients. Indigestible material will then be eliminated out of the mouth. 2) CIRCULATION: There is no true circulatory system. Food/nutrient particles will be passed through the central cavity by body movements and by flagellated cells ...
... food. Other cells of the endoderm will then absorb the digested nutrients. Indigestible material will then be eliminated out of the mouth. 2) CIRCULATION: There is no true circulatory system. Food/nutrient particles will be passed through the central cavity by body movements and by flagellated cells ...
Annelid lab info
... - cs slide (pre and post clitellum) Body Wall: Cuticle, epidermis, circular muscles, longitudinal muscles, setae Excretory: Nephrostome, nephridium bladder and nephridiopore Body cavity: Coelom, dorsal bv, ventral bv, nerve cord (dorsally or ventrally located?), chloragogue cells (Store nitrogen and ...
... - cs slide (pre and post clitellum) Body Wall: Cuticle, epidermis, circular muscles, longitudinal muscles, setae Excretory: Nephrostome, nephridium bladder and nephridiopore Body cavity: Coelom, dorsal bv, ventral bv, nerve cord (dorsally or ventrally located?), chloragogue cells (Store nitrogen and ...
Exam 2
... F. Slow moving water living radial, kind of a throw back G. Flat worm with complete simple nervous and digestive systems H. Both medusan and polyp stages in a radial life style I. The first closed circulatory system and they have a proboscis J. All of us have (can put) a foot and (on a) mantle ...
... F. Slow moving water living radial, kind of a throw back G. Flat worm with complete simple nervous and digestive systems H. Both medusan and polyp stages in a radial life style I. The first closed circulatory system and they have a proboscis J. All of us have (can put) a foot and (on a) mantle ...
JUST VOCAB
... Kind of circulatory system in which open blood is NOT contained in vessels __________________ and flows loose inside the coelom 2 Small teeth on the roof of the frog’s mouth that keep prey from escaping ...
... Kind of circulatory system in which open blood is NOT contained in vessels __________________ and flows loose inside the coelom 2 Small teeth on the roof of the frog’s mouth that keep prey from escaping ...
ABC Anatomy coloring book By: Britney Rac
... The sacrum is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine and at the upper and back part of the pelvic cavity, where it is inserted like a wedge between the ...
... The sacrum is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine and at the upper and back part of the pelvic cavity, where it is inserted like a wedge between the ...
The Head and Neck
... Voluntarily initiated (pharynx) Peristalsis = propulsion Involuntary Alternate waves of contraction and relaxation of muscles in organ walls (e.g. esophagus) Squeezes food from one organ to next Some mixing ...
... Voluntarily initiated (pharynx) Peristalsis = propulsion Involuntary Alternate waves of contraction and relaxation of muscles in organ walls (e.g. esophagus) Squeezes food from one organ to next Some mixing ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.