Deoxyribonucleic acid
... •Whatever substances are not assimilated into the bloodstream through the small intestine move into the large intestine. Within the large intestine, waste material is processed into stool (feces), and water and certain chemicals are absorbed into the bloodstream to preserve the body's fluid ...
... •Whatever substances are not assimilated into the bloodstream through the small intestine move into the large intestine. Within the large intestine, waste material is processed into stool (feces), and water and certain chemicals are absorbed into the bloodstream to preserve the body's fluid ...
Anorexia Nervosa Anorexia Nervosa
... -Bulk storage of swallowed bolus -Mechanical muscular churning of the bolus (peristalsis) -HCl (pH 1.5-2.0) denaturates proteins, deactivates foreign enzymes, breaks down plant cell walls and animal connective tissue, activates pepsin from pepsinogen -Pepsin breaks down proteins by attacking peptide ...
... -Bulk storage of swallowed bolus -Mechanical muscular churning of the bolus (peristalsis) -HCl (pH 1.5-2.0) denaturates proteins, deactivates foreign enzymes, breaks down plant cell walls and animal connective tissue, activates pepsin from pepsinogen -Pepsin breaks down proteins by attacking peptide ...
Residents Reminded Of good Digestive Health
... One in three people will suffer with a digestive disorder at some point in their lifetime. The most common digestive complaints are indigestion and heartburn. Digestive health covers a wide range of conditions including irritable bowel syndrome, coeliac disease, Crohns disease and stomach ulcers. As ...
... One in three people will suffer with a digestive disorder at some point in their lifetime. The most common digestive complaints are indigestion and heartburn. Digestive health covers a wide range of conditions including irritable bowel syndrome, coeliac disease, Crohns disease and stomach ulcers. As ...
general arrangement of the abdominal viscera
... 4-Large Intestine The large intestine extends from the ileum to the anus. It is divided into: ...
... 4-Large Intestine The large intestine extends from the ileum to the anus. It is divided into: ...
GI Digest - Douglas Labs
... acids, which are efficiently absorbed in the upper small intestine. Protein digestion is initiated in the stomach by pepsin and hydrochloric acid, which denature and break large proteins down to smaller polypeptides. In the small intestine, proteases break down these polypeptides into free amino aci ...
... acids, which are efficiently absorbed in the upper small intestine. Protein digestion is initiated in the stomach by pepsin and hydrochloric acid, which denature and break large proteins down to smaller polypeptides. In the small intestine, proteases break down these polypeptides into free amino aci ...
File
... a. Epidermis – exterior layer; contain pigment b. Muscle fibers – run in all directions c. Parenchyma – cells that fill space (no function) d. Eyespots – light sensitive, 2 ocelli e. Cilia – ventral surface, movement ...
... a. Epidermis – exterior layer; contain pigment b. Muscle fibers – run in all directions c. Parenchyma – cells that fill space (no function) d. Eyespots – light sensitive, 2 ocelli e. Cilia – ventral surface, movement ...
Spec for students digestion and metabolism
... Digestive enzymes convert food into small soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Carbohydrases break down carbohydrates to simple sugars. Amylase is a carbohydrase which breaks down starch. Proteases break down proteins to amino acids. Lipases break down lipids (fats) to glycer ...
... Digestive enzymes convert food into small soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Carbohydrases break down carbohydrates to simple sugars. Amylase is a carbohydrase which breaks down starch. Proteases break down proteins to amino acids. Lipases break down lipids (fats) to glycer ...
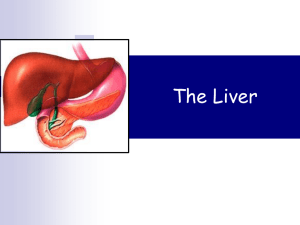
IB 3 Liver - susanpittinaro
... Stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion When muscular wall of gallbladder contracts, bile is expelled into the bile duct ...
... Stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion When muscular wall of gallbladder contracts, bile is expelled into the bile duct ...
How are photosynthesis and respiration related to
... How are photosynthesis and respiration related to each other? Differentiate between C3 and C4 plants. Show with the help of pathway cyclic and non- cyclic Photophosphorylation. Show Hatch and Slack pathway with the help of diagram Show the schematic representation of glycolysis. Discuss ...
... How are photosynthesis and respiration related to each other? Differentiate between C3 and C4 plants. Show with the help of pathway cyclic and non- cyclic Photophosphorylation. Show Hatch and Slack pathway with the help of diagram Show the schematic representation of glycolysis. Discuss ...
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms)
... epidermis (=hypodermis) usually syncytial and secreting a flexible cuticle three true tissue layers; mesoderm forms longitudinal muscle layer lining the body wall no muscle tissue associated with intestine gastrodermal cells line intestine Body Organization: round, nonsegmented, tubular body taperin ...
... epidermis (=hypodermis) usually syncytial and secreting a flexible cuticle three true tissue layers; mesoderm forms longitudinal muscle layer lining the body wall no muscle tissue associated with intestine gastrodermal cells line intestine Body Organization: round, nonsegmented, tubular body taperin ...
Unit 3 - Concord Carlisle High School
... 2. Which organic macromolecule are enzymes made out of? What does it mean to be a catalyst? 3. What is an active site? What is a substrate? Why is it important that the enzyme folds properly? What happens for a chemical reaction if the enzyme does not fold properly? 4. Explain how an enzyme works to ...
... 2. Which organic macromolecule are enzymes made out of? What does it mean to be a catalyst? 3. What is an active site? What is a substrate? Why is it important that the enzyme folds properly? What happens for a chemical reaction if the enzyme does not fold properly? 4. Explain how an enzyme works to ...
Mollusks
... _____________________: filter feeders, burrow in sand & use cilia to beat water through incurrent siphon (gill-like structure) and push food to stomach Gastropods & Cephalopods are predators Nervous system _____________________ nervous system Brain & associate nerves Most have paired eyes Range fro ...
... _____________________: filter feeders, burrow in sand & use cilia to beat water through incurrent siphon (gill-like structure) and push food to stomach Gastropods & Cephalopods are predators Nervous system _____________________ nervous system Brain & associate nerves Most have paired eyes Range fro ...
Chapter 26-Part 2-Digestive System
... Inner circular layer Muscularis Outer longitudinal layer Serosa (b) Section of small intestine ...
... Inner circular layer Muscularis Outer longitudinal layer Serosa (b) Section of small intestine ...
Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids
... the food it is coming from base of salivary gland ) Stomach: Gastric lipase (gastric mucosa): +They act only on short and medium length fatty acids (<12 carbon fatty acid chains, e.g. milk). ...
... the food it is coming from base of salivary gland ) Stomach: Gastric lipase (gastric mucosa): +They act only on short and medium length fatty acids (<12 carbon fatty acid chains, e.g. milk). ...
introduction to - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... Food passes from the mouth and pharynx through the esophagus to the stomach, where it mixes with gastric secretions. Digestion mostly occurs in the stomach and duodenum. Peristalsis, a series of ring-like contraction waves, begins around the middle of the stomach and moves slowly toward the pylorus. ...
... Food passes from the mouth and pharynx through the esophagus to the stomach, where it mixes with gastric secretions. Digestion mostly occurs in the stomach and duodenum. Peristalsis, a series of ring-like contraction waves, begins around the middle of the stomach and moves slowly toward the pylorus. ...
1 NOTES: Respiratory System, Chapter 22 and Digestive System
... • Chambers of pharynx, oral, nasal, and sinus cavities amplify and enhance sound quality • Sound is “shaped” into language by muscles of the pharynx, tongue, soft palate, and lips 30 Larynx • Vocal folds may act as a sphincter to prevent air passage • Example: Valsalva’s maneuver • Glottis closes to ...
... • Chambers of pharynx, oral, nasal, and sinus cavities amplify and enhance sound quality • Sound is “shaped” into language by muscles of the pharynx, tongue, soft palate, and lips 30 Larynx • Vocal folds may act as a sphincter to prevent air passage • Example: Valsalva’s maneuver • Glottis closes to ...
MOLLUSK VOCAB ONLY
... Referring to an organisms that attaches to a surface and does not sessile move_______________ On a clam, the tube through which water enters and leaves the mantle siphon cavity _________________ ganglion A mass of nerve cells ________________ ...
... Referring to an organisms that attaches to a surface and does not sessile move_______________ On a clam, the tube through which water enters and leaves the mantle siphon cavity _________________ ganglion A mass of nerve cells ________________ ...
MOLLUSK VOCAB ONLY
... Referring to an organisms that attaches to a surface and does not sessile move_______________ On a clam, the tube through which water enters and leaves the mantle siphon cavity _________________ ganglion A mass of nerve cells ________________ ...
... Referring to an organisms that attaches to a surface and does not sessile move_______________ On a clam, the tube through which water enters and leaves the mantle siphon cavity _________________ ganglion A mass of nerve cells ________________ ...
34-1 Phylum Platyhelminthes
... Digestive tract with 2 openings Anterior – mouth Posterior – anus One directional movement ...
... Digestive tract with 2 openings Anterior – mouth Posterior – anus One directional movement ...
Esophagus and stomach
... Stomach • The stomach is the most dilated part of the gastrointestinal tract and has a J-like shape. • Positioned between the abdominal esophagus and the small intestine, the stomach is in the epigastric, umbilical, and left hypochondrium regions of the abdomen. • It stores food (in the adult it ha ...
... Stomach • The stomach is the most dilated part of the gastrointestinal tract and has a J-like shape. • Positioned between the abdominal esophagus and the small intestine, the stomach is in the epigastric, umbilical, and left hypochondrium regions of the abdomen. • It stores food (in the adult it ha ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.