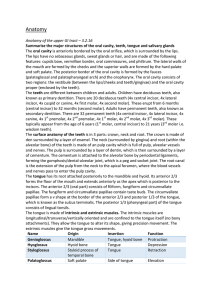
Segmented Worms: Phylum Annelida EX: Earthworms
... 3. true coelom: body cavity 4. body is divided into segments 5. organ systems are well developed 6. have setae: external bristles that help move and burrow into the dirt. B. Digestive system/excretory systems 1. mouth and anus 2. feed on soil and organic matter 3. how food moves through digestive sy ...
... 3. true coelom: body cavity 4. body is divided into segments 5. organ systems are well developed 6. have setae: external bristles that help move and burrow into the dirt. B. Digestive system/excretory systems 1. mouth and anus 2. feed on soil and organic matter 3. how food moves through digestive sy ...
Unit 11 Animal Evolution Chp 33 Invertebrate
... Specialized gas exchange Well-developed sensory organs Cephalization is extensive ...
... Specialized gas exchange Well-developed sensory organs Cephalization is extensive ...
Exam 2 Review Key - Iowa State University
... E) a four chambered heart Follow up: What are the four characteristics shared by all chordates? Notochord, pharyngeal slits, postanal tail 10.) Why is the amniotic egg considered such an important evolutionary breakthrough? A) Without amniotic eggs there would be no Denny's B) The shell allows repro ...
... E) a four chambered heart Follow up: What are the four characteristics shared by all chordates? Notochord, pharyngeal slits, postanal tail 10.) Why is the amniotic egg considered such an important evolutionary breakthrough? A) Without amniotic eggs there would be no Denny's B) The shell allows repro ...
LEARNING TO MEASURE
... Food is digested. This means that it is changed into simpler, liquid form. The chemicals that do this are called enzymes. Digestion mainly takes place in the stomach and small intestine. But it begins in the mouth. As you chew an enzyme called amylase in your saliva starts to break down any starch i ...
... Food is digested. This means that it is changed into simpler, liquid form. The chemicals that do this are called enzymes. Digestion mainly takes place in the stomach and small intestine. But it begins in the mouth. As you chew an enzyme called amylase in your saliva starts to break down any starch i ...
Phylum/
... Water- vascular system. Muscular sac called ampulla (inside of tube feet) for movement ...
... Water- vascular system. Muscular sac called ampulla (inside of tube feet) for movement ...
Lecture Outline: ORGANISATION OF THE BODY
... from the front, palms displayed. Prone: lying on your front; Supine: lying on your back ...
... from the front, palms displayed. Prone: lying on your front; Supine: lying on your back ...
BIO 2125 - Animal Form and Function Midterm
... Midterm examination Worth either 10% or 15% of your final grade Tuesday March 14, 2006 Place your name and student number in the space provided below. Be sure that your name is on the top of each page because the exam will be separated to facilitate marking Circle the lab section for your lab. Check ...
... Midterm examination Worth either 10% or 15% of your final grade Tuesday March 14, 2006 Place your name and student number in the space provided below. Be sure that your name is on the top of each page because the exam will be separated to facilitate marking Circle the lab section for your lab. Check ...
Animals Review - OG
... 5. Mantle – sheath of skin surround the space of the clam, attached to shell 6. Secretes for shell, houses respiratory organs (which are…?) and houses visceral mass 7. Visceral mass contains: Stomach, intestines, gonads, mouth 8. Food is used for – locomotion Octopus/squid have siphon for jet propu ...
... 5. Mantle – sheath of skin surround the space of the clam, attached to shell 6. Secretes for shell, houses respiratory organs (which are…?) and houses visceral mass 7. Visceral mass contains: Stomach, intestines, gonads, mouth 8. Food is used for – locomotion Octopus/squid have siphon for jet propu ...
ORAL MUCOSA
... – submaxillary duct: 5 cm. long • opens by a narrow orifice on the summit of a small papilla, at the side of the frenulum linguæ • lies between the lingual and hypoglossal nerves, but at the anterior border of the muscle it is crossed laterally by the lingual nerve ...
... – submaxillary duct: 5 cm. long • opens by a narrow orifice on the summit of a small papilla, at the side of the frenulum linguæ • lies between the lingual and hypoglossal nerves, but at the anterior border of the muscle it is crossed laterally by the lingual nerve ...
Animals: Invertebrates
... moves through their porous bodies and phagocytosing it e. They lack a _________ stage during embryonic development f. They lack true __________ and organs (no muscles, nerves, or digestive tract) but have 3 cell ________: 1) Inner layer has flagellated _____________ (collar cells) that trap and ...
... moves through their porous bodies and phagocytosing it e. They lack a _________ stage during embryonic development f. They lack true __________ and organs (no muscles, nerves, or digestive tract) but have 3 cell ________: 1) Inner layer has flagellated _____________ (collar cells) that trap and ...
animal ppt
... saclike organs that extract wastes from the blood and then add them to feces that move through the gut. • Aquatic arthropods wastes diffuse from cells into water. ...
... saclike organs that extract wastes from the blood and then add them to feces that move through the gut. • Aquatic arthropods wastes diffuse from cells into water. ...
The small intestine
... It curves around the head of the pancreas to the left and backwards. • It is important because it receives the opening of the bile and pancreatic ducts. ...
... It curves around the head of the pancreas to the left and backwards. • It is important because it receives the opening of the bile and pancreatic ducts. ...
Jejunum and Ileum Location and Description
... • It is 3”(3 inch) long • runs downward vertically on the right side • In front of the Rt.kidney • next to the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae. • halfway of it, The bile duct and the main pancreatic duct pierce the medial wall, and then form the ampulla that opens in the major duodenal papilla. • The a ...
... • It is 3”(3 inch) long • runs downward vertically on the right side • In front of the Rt.kidney • next to the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae. • halfway of it, The bile duct and the main pancreatic duct pierce the medial wall, and then form the ampulla that opens in the major duodenal papilla. • The a ...
Anatomy
... laryngeal nerve) There are 3 longitudinal muscles – palatopharyngeus, salpinopharyngeus, and stylopharyngeus – and these are the internal layer, which elevate the pharynx in the action of swallowing and yawning. ...
... laryngeal nerve) There are 3 longitudinal muscles – palatopharyngeus, salpinopharyngeus, and stylopharyngeus – and these are the internal layer, which elevate the pharynx in the action of swallowing and yawning. ...
liver
... is extremely rich in glucose from digested food. Hepatocytes absorb much of this glucose and store it as the macromolecule glycogen, a branched polysaccharide that allows the hepatocytes to pack away large amounts of glucose and quickly release glucose between meals. The absorption and release of gl ...
... is extremely rich in glucose from digested food. Hepatocytes absorb much of this glucose and store it as the macromolecule glycogen, a branched polysaccharide that allows the hepatocytes to pack away large amounts of glucose and quickly release glucose between meals. The absorption and release of gl ...
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... drink is converted to acetaldehyde by enzymes contained in liver peroxisomes 3. In humans catalase and D-amino acid oxidase, as well as alcohol dehydrogenase are found in peroxisomes. ...
... drink is converted to acetaldehyde by enzymes contained in liver peroxisomes 3. In humans catalase and D-amino acid oxidase, as well as alcohol dehydrogenase are found in peroxisomes. ...
THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD Define problem Research and collect
... Mechanical – physical change, large chunks of food is broken down into smaller pieces (done by chewing, stomach churning) ...
... Mechanical – physical change, large chunks of food is broken down into smaller pieces (done by chewing, stomach churning) ...
Marine Animals
... • Glides along the bottom by moving its head side to side • Cilia are attached to cells on the its ventral side • Have two eyespots which are surrounded by ganglia (nerve clusters) • Ganglia act like a simple brain which sends nerve impulses along two ventral nerve cords to the rest of its body ...
... • Glides along the bottom by moving its head side to side • Cilia are attached to cells on the its ventral side • Have two eyespots which are surrounded by ganglia (nerve clusters) • Ganglia act like a simple brain which sends nerve impulses along two ventral nerve cords to the rest of its body ...
Fetal Pig Dissection - learningtosavetheearth.com
... pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus) and other associated structures/organs/glands (salivary glands, gall bladder, liver, pancreas). The cavity behind the teeth and gums is the oral cavity. Note the papillae on the tongue. These provide friction for food handl ...
... pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus) and other associated structures/organs/glands (salivary glands, gall bladder, liver, pancreas). The cavity behind the teeth and gums is the oral cavity. Note the papillae on the tongue. These provide friction for food handl ...
FROG DISSECTION External Anatomy
... 15. With the forceps, lift the skin and insert the point of the scissors to right of the midline near the pelvis. Make the first incision from the pelvis to the throat as shown by line a in Figure 1. 16. At the forelimbs and the hind limbs, make transverse cuts on the lines b, c, d, and e as shown i ...
... 15. With the forceps, lift the skin and insert the point of the scissors to right of the midline near the pelvis. Make the first incision from the pelvis to the throat as shown by line a in Figure 1. 16. At the forelimbs and the hind limbs, make transverse cuts on the lines b, c, d, and e as shown i ...
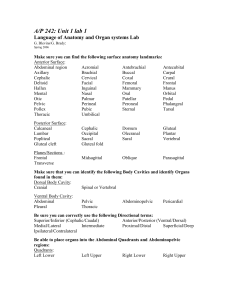
Language of Anatomy and Organ systems Lab
... Parietal Peritoneum Parietal Pericardium Parietal Pleura ...
... Parietal Peritoneum Parietal Pericardium Parietal Pleura ...
The major salivary glands
... Salivary Glands: Consist of two classes : The major salivary glands & the minor salivary glands. The major salivary glands are paired glands with long ducts that empty into the oral cavity. The major salivary glands, as noted above, consist of the paired parotid, submandibular, and sublingual gl ...
... Salivary Glands: Consist of two classes : The major salivary glands & the minor salivary glands. The major salivary glands are paired glands with long ducts that empty into the oral cavity. The major salivary glands, as noted above, consist of the paired parotid, submandibular, and sublingual gl ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.