1. Define each of the following terms: a.Alkaline earth metals
... m.Chemical property = a property that describes the behavior of a substance n.Physical property = a property that describes the appearance of a substance o.Electron = a negatively charged subatomic particle found in the orbits of an atom ...
... m.Chemical property = a property that describes the behavior of a substance n.Physical property = a property that describes the appearance of a substance o.Electron = a negatively charged subatomic particle found in the orbits of an atom ...
Atoms and Elements
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Since atomic mass is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons, how can you have a fractional number? How was an atomic mass value of 35.45 arrived at? Since in a “handful” of Cl there is a mixture of two isotopes in the abundances shown on the left, an average atomic mass has been defi ...
... Since atomic mass is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons, how can you have a fractional number? How was an atomic mass value of 35.45 arrived at? Since in a “handful” of Cl there is a mixture of two isotopes in the abundances shown on the left, an average atomic mass has been defi ...
cba #1 review - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... How can you determine valence electrons using the periodic table: Write the Electron configuration, short hand, Lewis dot, Bohr Model, Bohr electron configuration for the following elements: ...
... How can you determine valence electrons using the periodic table: Write the Electron configuration, short hand, Lewis dot, Bohr Model, Bohr electron configuration for the following elements: ...
GY 111 Lecture Note Series Elemental Chemistry
... becomes O2_ and Cl becomes Cl-. They are no longer atoms. Now they are ions. Ions are charged atoms. There are two broad types: cations are positively charged ions and anions are negatively charged particles. (2) the size of the ion changes. A cation has less electrons than protons so every electron ...
... becomes O2_ and Cl becomes Cl-. They are no longer atoms. Now they are ions. Ions are charged atoms. There are two broad types: cations are positively charged ions and anions are negatively charged particles. (2) the size of the ion changes. A cation has less electrons than protons so every electron ...
Groups of the Periodic Table
... the object (ex: colour, odor, texture, density, melting point, boiling point) • Chemical Property: Cannot be determined by simply viewing or touching the object; only becomes evident during a chemical reaction (ex: reactivity with other chemicals, flammability, heat of combustion) ...
... the object (ex: colour, odor, texture, density, melting point, boiling point) • Chemical Property: Cannot be determined by simply viewing or touching the object; only becomes evident during a chemical reaction (ex: reactivity with other chemicals, flammability, heat of combustion) ...
Study Guide Answers
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus. 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? Explain. Positive char ...
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus. 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? Explain. Positive char ...
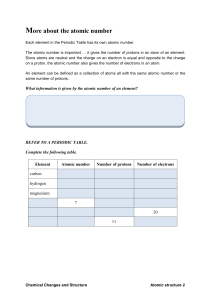
14 more about the atomic number
... More about the atomic number Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number ...
... More about the atomic number Each element in the Periodic Table has its own atomic number. The atomic number is important it gives the number of protons in an atom of an element. Since atoms are neutral and the charge on an electron is equal and opposite to the charge on a proton, the atomic number ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... Bohr Model of the Atom • Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. • Electrons orbit the nucleus in specific orbits with each orbit corresponding to a different energy level. – Ground state (most stable state) when electrons are in energy levels as near as possible to the nucleus – Excited s ...
... Bohr Model of the Atom • Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. • Electrons orbit the nucleus in specific orbits with each orbit corresponding to a different energy level. – Ground state (most stable state) when electrons are in energy levels as near as possible to the nucleus – Excited s ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions - GW
... multiply the mass of each isotope by its natural abundance, expressed as a decimal, and then add the products ...
... multiply the mass of each isotope by its natural abundance, expressed as a decimal, and then add the products ...
Academic Chemistry
... 9. Rutherford’s gold-foil experiment demonstrated that ________ A. electrons have a negative charge B. most of the atom is empty space C. X-rays are characteristic of the metal used as the anode D. energy is given off in little packets 10. Oxygen – 18 has an atomic number of 8. How many neutrons do ...
... 9. Rutherford’s gold-foil experiment demonstrated that ________ A. electrons have a negative charge B. most of the atom is empty space C. X-rays are characteristic of the metal used as the anode D. energy is given off in little packets 10. Oxygen – 18 has an atomic number of 8. How many neutrons do ...
800 - Paint Valley Local Schools
... The early work of Democritus (indivisible atoms), Dalton (atoms are solid spheres), Thomson (Plum pudding model), Rutherford (planetary model), and Bohr (electrons are in shells around the nucleus) in relation to the views on atomic theory have led us to the current belief that electrons are found i ...
... The early work of Democritus (indivisible atoms), Dalton (atoms are solid spheres), Thomson (Plum pudding model), Rutherford (planetary model), and Bohr (electrons are in shells around the nucleus) in relation to the views on atomic theory have led us to the current belief that electrons are found i ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... No. of neutrons in an atom = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass ...
... No. of neutrons in an atom = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass ...
a worksheet on C1.1
... Candidates will be expected to calculate the number of each sub-atomic particle in an atom from its atomic number and mass number. h) Electrons occupy particular energy levels. Each electron in an atom is at a particular energy level (in a particular shell). The electrons in an atom occupy the lowes ...
... Candidates will be expected to calculate the number of each sub-atomic particle in an atom from its atomic number and mass number. h) Electrons occupy particular energy levels. Each electron in an atom is at a particular energy level (in a particular shell). The electrons in an atom occupy the lowes ...
Vocabulary for Periodic Table
... 3) Nucleus: the central region of an atom where most of the atom’s mass is found in protons and neutrons. 4) Electron: a negatively charged particle located outside an atom’s nucleus. 5) Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of proton ...
... 3) Nucleus: the central region of an atom where most of the atom’s mass is found in protons and neutrons. 4) Electron: a negatively charged particle located outside an atom’s nucleus. 5) Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 6) Atomic mass number: the total number of proton ...
Semester Exam Review Guide
... 18. Which of the statement about the periodic table is true: a. elements are arranged by atomic number. b. metallic elements are placed on the right-hand side. c. elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. d. both a and c. 19. __________ brought back the concept of the ato ...
... 18. Which of the statement about the periodic table is true: a. elements are arranged by atomic number. b. metallic elements are placed on the right-hand side. c. elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. d. both a and c. 19. __________ brought back the concept of the ato ...
Final Exam Review
... 59. An atom of an element has two electrons in the first energy level and five electrons in the second energy level. Write the electron configuration for this atom and and name the element. How many unpaired electrons does an atom of this element have? 1. Select the correct electron configuration fo ...
... 59. An atom of an element has two electrons in the first energy level and five electrons in the second energy level. Write the electron configuration for this atom and and name the element. How many unpaired electrons does an atom of this element have? 1. Select the correct electron configuration fo ...
3. atomic structure
... For example, the moon has an orbit about the earth Electrons do not follow a particular path around the nucleus Instead, an orbital describes the areas around the nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found (probability of location) The exact path of an electron in this area is not known ...
... For example, the moon has an orbit about the earth Electrons do not follow a particular path around the nucleus Instead, an orbital describes the areas around the nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found (probability of location) The exact path of an electron in this area is not known ...
ChLM Final Review Name: Period: Base Knowledge 1. Classify the
... 1. Classify the following as observations or inferences a) The liquid is green because food coloring was added. b) The beaker has green liquid in it. c) The beaker can hold up to 250 mL. d) The beaker will be the best tool for this lab. 2. Measure the following, circle your estimated digit and inclu ...
... 1. Classify the following as observations or inferences a) The liquid is green because food coloring was added. b) The beaker has green liquid in it. c) The beaker can hold up to 250 mL. d) The beaker will be the best tool for this lab. 2. Measure the following, circle your estimated digit and inclu ...
Unit 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry
... atom. They will explain how nuclear changes impact the parts of the atom and its identity. Students will identify how nuclear chemistry is used in today’s society and how it can impact their lives. Expected learning outcomes: 1. Develop atomic theory in an historical perspective comparing and contra ...
... atom. They will explain how nuclear changes impact the parts of the atom and its identity. Students will identify how nuclear chemistry is used in today’s society and how it can impact their lives. Expected learning outcomes: 1. Develop atomic theory in an historical perspective comparing and contra ...
are made up of
... Severalscientists,including Newlands, Meyer, and Mendeleevworked on classificationsystems that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron a ...
... Severalscientists,including Newlands, Meyer, and Mendeleevworked on classificationsystems that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron a ...
New Title
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
ionization energies
... • A direct indication of the arrangement of electrons about a nucleus is given by the ionization energies of the atom • Ionization energy (IE) is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron (form a cation) completely from a gaseous atom • Ionizations are successive. • As you remove one electron, ...
... • A direct indication of the arrangement of electrons about a nucleus is given by the ionization energies of the atom • Ionization energy (IE) is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron (form a cation) completely from a gaseous atom • Ionizations are successive. • As you remove one electron, ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. 3. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 4. Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one e ...
... 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. 3. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 4. Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one e ...
Matter - Moodle
... help to ___________________and ______________________ substances • Characteristic Properties are the _______________or _____________________ characteristics the substance is known for Example: • Helium is light and non-flammable so it is good for _____________________ element A substance that cannot ...
... help to ___________________and ______________________ substances • Characteristic Properties are the _______________or _____________________ characteristics the substance is known for Example: • Helium is light and non-flammable so it is good for _____________________ element A substance that cannot ...