Chapter 5
... 〉What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? 〉If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge. ...
... 〉What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? 〉If an atom gains or loses electrons, it no longer has an equal number of electrons and protons. Because the charges do not cancel completely, the atom has a net electric charge. ...
Atomic Crossword Name: Period: ____
... 11. A _____________ electron is in the outermost shell of an atom 12. Formed when atoms share electrons 14. Has a different number of neutrons than normal 15. The splitting of an atomic nucleus (usually with heavy elements) 17. British scientist who formulated our modern atomic theory 22. The mergin ...
... 11. A _____________ electron is in the outermost shell of an atom 12. Formed when atoms share electrons 14. Has a different number of neutrons than normal 15. The splitting of an atomic nucleus (usually with heavy elements) 17. British scientist who formulated our modern atomic theory 22. The mergin ...
I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
IPC Atoms and Periodic Table
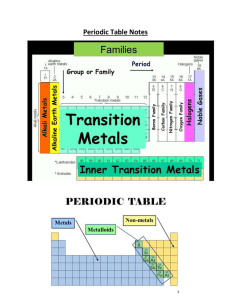
... Transition Metal • any element in any of the series of elements with atomic numbers 21–29, 39– 47, 57–79, and 89– 107, that in a given inner orbital has less than a full quota of electrons ...
... Transition Metal • any element in any of the series of elements with atomic numbers 21–29, 39– 47, 57–79, and 89– 107, that in a given inner orbital has less than a full quota of electrons ...
Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table Electron Dot Diagrams
... Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table The symbols for the elements in Periods 2 and 3 are shown below. Complete the electron dot diagrams for nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, and argon. ...
... Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table The symbols for the elements in Periods 2 and 3 are shown below. Complete the electron dot diagrams for nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, silicon, and argon. ...
here
... 2. Describe how ionization energy and electronegativity change as you move from left to right along the periodic table and from top to bottom. Explain how all three of these plays a role in determining whether an atom “wants” to give away or take electrons. 3. Define what an atom’s atomic radius is. ...
... 2. Describe how ionization energy and electronegativity change as you move from left to right along the periodic table and from top to bottom. Explain how all three of these plays a role in determining whether an atom “wants” to give away or take electrons. 3. Define what an atom’s atomic radius is. ...
Dmitri MendeleevанааA Russian chemist, noticed a repeating
... pattern of chemical properties in the elements that were known at the time. Mendeleev arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic mass to form something close to the modern day periodic table. The pattern of repeating order is called periodicity. ...
... pattern of chemical properties in the elements that were known at the time. Mendeleev arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic mass to form something close to the modern day periodic table. The pattern of repeating order is called periodicity. ...
Fall Final Exam Review Questions
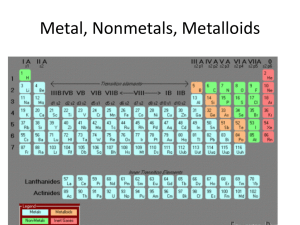
... 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and where are they generally located? 44. Make sure you know the major groups/chemical families ...
... 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and where are they generally located? 44. Make sure you know the major groups/chemical families ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
... gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
Ions and isotopes
... Quick Review • Atoms are made up of three particles: • Protons • Neutrons • Electrons • Question: Which of the three particles identifies what element an atom is? • The PROTON! (very important) ...
... Quick Review • Atoms are made up of three particles: • Protons • Neutrons • Electrons • Question: Which of the three particles identifies what element an atom is? • The PROTON! (very important) ...
Ions
... particle called an ion. When an atom loses an electron it has more protons therefore becoming positively charged. When an atom gains an electron it has more electrons therefore becoming negatively charged. ...
... particle called an ion. When an atom loses an electron it has more protons therefore becoming positively charged. When an atom gains an electron it has more electrons therefore becoming negatively charged. ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
Chapter 14 Review
... 9. What information can be obtained by knowing the atomic number of an element? ...
... 9. What information can be obtained by knowing the atomic number of an element? ...
Period Table, valence Electrons and Ion Notes
... Example: Na = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Add up the e-‘s found in the last energy level, in this case there is only 1 so Na has 1 valence e**You have to do this for the Transition metal every time** ...
... Example: Na = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Add up the e-‘s found in the last energy level, in this case there is only 1 so Na has 1 valence e**You have to do this for the Transition metal every time** ...
Chemical Basis of Life
... Title: The Chemical Basis of Life 1- Introduction: Your body is an elaborate chemical system. Chemical reactions power all of the body’s activities. At the most basic level, life is about chemicals and how they interact with each other. 2- Matter – Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space ...
... Title: The Chemical Basis of Life 1- Introduction: Your body is an elaborate chemical system. Chemical reactions power all of the body’s activities. At the most basic level, life is about chemicals and how they interact with each other. 2- Matter – Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space ...
CHEMISTRY TERMS Period: Elements in the same horizontal row
... state energy level. Periodic Law: Elements list in order of their atomic numbers that fall into reoccurring groups. Ionic Radius: the radius of an atom’s ion, measured by the distance between ions in a crystal lattice. Atomic Radius: one-half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms in a di ...
... state energy level. Periodic Law: Elements list in order of their atomic numbers that fall into reoccurring groups. Ionic Radius: the radius of an atom’s ion, measured by the distance between ions in a crystal lattice. Atomic Radius: one-half the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms in a di ...
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW Electron Configurations Explain the
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...