I - Wiley
... Applying Psychology to Everyday Life: Operant Conditioning – The influence of operant conditioning principles have numerous real life applications. Often prejudice and discrimination are positively reinforced. To control high blood pressure and anxiety, some researchers use biofeedback—a procedure i ...
... Applying Psychology to Everyday Life: Operant Conditioning – The influence of operant conditioning principles have numerous real life applications. Often prejudice and discrimination are positively reinforced. To control high blood pressure and anxiety, some researchers use biofeedback—a procedure i ...
student copy - learning - APPsychBCA
... sick, but not when it’s announced by a noise; so Pavlov was wrong in claiming that any stimulus could serve as a conditioned stimulus. -We are biologically prepared to learn certain associations and not others: we learn to fear snakes, but not flowers -Taste aversions result from biology. The smell ...
... sick, but not when it’s announced by a noise; so Pavlov was wrong in claiming that any stimulus could serve as a conditioned stimulus. -We are biologically prepared to learn certain associations and not others: we learn to fear snakes, but not flowers -Taste aversions result from biology. The smell ...
Learning and Memory
... •Can store vast amounts of information without removing old memories •You may think you’ve forgotten something, but a clue or hint can help you reconstruct it •Short-term memories must be consolidated into long-term ones •Meaningful and emotional events don’t require effort to consolidate (flashbulb ...
... •Can store vast amounts of information without removing old memories •You may think you’ve forgotten something, but a clue or hint can help you reconstruct it •Short-term memories must be consolidated into long-term ones •Meaningful and emotional events don’t require effort to consolidate (flashbulb ...
Cognitive component - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... • Crucial for adaptive behavior. • Associations are formed not only between the US/CS, but also between the events and the situations in which the conditioning takes place. ...
... • Crucial for adaptive behavior. • Associations are formed not only between the US/CS, but also between the events and the situations in which the conditioning takes place. ...
Role of Learning Theories in Training While Training the
... an operant is a response that has some effect on the situation or environment. Fincham and Rhodes, (1999) emphasize that operant conditioning deals with learned not reflexive behavior and it works by enforcing (rewarding) and pushing behaviour based on the consequences it produces. Reinforcement is ...
... an operant is a response that has some effect on the situation or environment. Fincham and Rhodes, (1999) emphasize that operant conditioning deals with learned not reflexive behavior and it works by enforcing (rewarding) and pushing behaviour based on the consequences it produces. Reinforcement is ...
CB Lecture
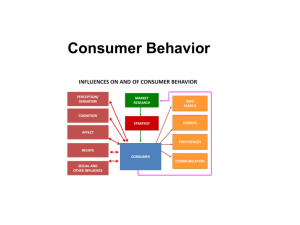
... Consumer behavior: consists of the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. ...
... Consumer behavior: consists of the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. ...
n e w s a n d ...
... approached this issue in different ways and each can inform and motivate future directions in motor control. In psychology, reward and punishment have long been recognized as instrumental for learning. As early as 1898, Edward Thorndike’s law of effect stated that if a response leads to a “satisfyin ...
... approached this issue in different ways and each can inform and motivate future directions in motor control. In psychology, reward and punishment have long been recognized as instrumental for learning. As early as 1898, Edward Thorndike’s law of effect stated that if a response leads to a “satisfyin ...
Learning - sevenlakespsychology
... Classical Conditioning and Humans • John Watson brought Classical Conditioning to psychology with his Baby Albert experiment. ...
... Classical Conditioning and Humans • John Watson brought Classical Conditioning to psychology with his Baby Albert experiment. ...
3. Observational Learning
... Punished behavior is not forgotten, it is suppressed Physical punishment increases aggression through modeling Can also create fear that will generalize Does not tell you “what to do”! Punishment if used swiftly, works best when accompanied with explanation and positive reinforcement for appro ...
... Punished behavior is not forgotten, it is suppressed Physical punishment increases aggression through modeling Can also create fear that will generalize Does not tell you “what to do”! Punishment if used swiftly, works best when accompanied with explanation and positive reinforcement for appro ...
Theory Reflections: Contact Theory / Contact Hypothesis / Intergroup
... While exposure is essential to the process, what students choose to do with that exposure is paramount. With the exception of a few extremely motivated and self-sufficient learners, most students do not have the necessary skills and knowledge to create their own learning opportunities and reflect up ...
... While exposure is essential to the process, what students choose to do with that exposure is paramount. With the exception of a few extremely motivated and self-sufficient learners, most students do not have the necessary skills and knowledge to create their own learning opportunities and reflect up ...
Drive Reduction Theory
... itself. Reinforcement can serve as motivator for learning and enhance a response, yet it does not necessarily enhance learning of a response. This idea was later known as the Hull-Spence hypothesis of conditioning and learning. It was Spence's idea that performance in learned behavior cannot be attr ...
... itself. Reinforcement can serve as motivator for learning and enhance a response, yet it does not necessarily enhance learning of a response. This idea was later known as the Hull-Spence hypothesis of conditioning and learning. It was Spence's idea that performance in learned behavior cannot be attr ...
Behaviorism - Bethel University
... • Los Horcones and social engineering • Twin Oaks originally founded on Skinnerian principles • Behaviorists for Social Responsibility ...
... • Los Horcones and social engineering • Twin Oaks originally founded on Skinnerian principles • Behaviorists for Social Responsibility ...
LEARNING
... environment. Two other interactions assumptions of this theory are that the environment shapes behavior and that taking internal mental states such as thoughts, feelings and emotions into consideration is useless in explaining behavior. ...
... environment. Two other interactions assumptions of this theory are that the environment shapes behavior and that taking internal mental states such as thoughts, feelings and emotions into consideration is useless in explaining behavior. ...
Chapter 3
... Chapter 3 Learning & Memory I. Introduction A. Learning 1. The process by which experience leads to changes in knowledge, attitude, &/or behavior. 2. Essentially, it is the process of adding 3. We look at how people learn in two ways. Marketers use both of the following approaches: B. Cognitive Appr ...
... Chapter 3 Learning & Memory I. Introduction A. Learning 1. The process by which experience leads to changes in knowledge, attitude, &/or behavior. 2. Essentially, it is the process of adding 3. We look at how people learn in two ways. Marketers use both of the following approaches: B. Cognitive Appr ...
Learning
... • Do you associate any food/smells with being sick? What happened? • How do you learn “right/wrong” behaviors? • When you were little, did you copy your mom/dad/brother/sister/friends? In what ways? ...
... • Do you associate any food/smells with being sick? What happened? • How do you learn “right/wrong” behaviors? • When you were little, did you copy your mom/dad/brother/sister/friends? In what ways? ...
Unit Descriptor - Solent Online Learning
... provides opportunity for learning and development relevant to the programme. PREREQUISITES AND CO-REQUISITES: None Students enrolling on the Foundation Diploma are likely to be relatively new to the internal communication arena and could be working as an assistant or junior member of the team. UNIT ...
... provides opportunity for learning and development relevant to the programme. PREREQUISITES AND CO-REQUISITES: None Students enrolling on the Foundation Diploma are likely to be relatively new to the internal communication arena and could be working as an assistant or junior member of the team. UNIT ...
Classical conditioning(def.)
... When you associate two things together, describe what you are doing. Give an example of two things you have associated together. ...
... When you associate two things together, describe what you are doing. Give an example of two things you have associated together. ...
Basic Forms of Learning Classical Conditioning Evidence of
... • We automatically learn what stimuli are associated with situations that trigger a reflexive bodily or emotional response. Those stimuli, because of learning, can come to trigger a similar body or emotion response. • Classical conditioning is useful because learning to predict what’s coming allows ...
... • We automatically learn what stimuli are associated with situations that trigger a reflexive bodily or emotional response. Those stimuli, because of learning, can come to trigger a similar body or emotion response. • Classical conditioning is useful because learning to predict what’s coming allows ...
vocab review unit 6 Learning
... • A neutral stimulus that after an association with an unconditioned stimulus (UCS), comes to trigger a CR. ...
... • A neutral stimulus that after an association with an unconditioned stimulus (UCS), comes to trigger a CR. ...
Shelly Cashman Series Discovering Computers A Link to the
... • Social constructivist theory – Learning is significantly influenced by social development ...
... • Social constructivist theory – Learning is significantly influenced by social development ...
File
... 2. Operant conditioning occurs when we learn to associate our own behavior (or our response) and its consequence. We therefore repeat behaviors with good results, we cut down on behaviors with bad results. 3. Observational learning occurs by watching others’ experiences. 4. One additional form of le ...
... 2. Operant conditioning occurs when we learn to associate our own behavior (or our response) and its consequence. We therefore repeat behaviors with good results, we cut down on behaviors with bad results. 3. Observational learning occurs by watching others’ experiences. 4. One additional form of le ...
path to dependence
... How does dependence develop? Why does it happen to some people and not others? ...
... How does dependence develop? Why does it happen to some people and not others? ...
classical conditioning
... Exposure to one stimulus can increase the speed with which we can retrieve other information ...
... Exposure to one stimulus can increase the speed with which we can retrieve other information ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.