Classical Conditioning - District 196 e
... ► What are some of the main lessons you must teach a dog and how do you teach them? ► What are some techniques your parents used to show you right from wrong? ► Which techniques worked the best/worst? ...
... ► What are some of the main lessons you must teach a dog and how do you teach them? ► What are some techniques your parents used to show you right from wrong? ► Which techniques worked the best/worst? ...
Chapter 6 LEARNING
... APPLICATION OF THE PRINCIPLES OF OPERANT CONDITIONING (continued) ! Programmed Learning – assumes that any task can be broken down into small steps that can be shaped individually and combined to form the more complicated whole ! Classroom discipline – using principles of learning to change classroo ...
... APPLICATION OF THE PRINCIPLES OF OPERANT CONDITIONING (continued) ! Programmed Learning – assumes that any task can be broken down into small steps that can be shaped individually and combined to form the more complicated whole ! Classroom discipline – using principles of learning to change classroo ...
leadership
... If we are the same then we could study human behaviors and human learnings by studying non-human organisms ...
... If we are the same then we could study human behaviors and human learnings by studying non-human organisms ...
SOCIALIZATION
... Comprises the basic understandings we need to function in the society into which we are born (use language, eat, practice hygiene, deal with our emotions, how to behave) ...
... Comprises the basic understandings we need to function in the society into which we are born (use language, eat, practice hygiene, deal with our emotions, how to behave) ...
EBC motivation essay Melissa Lettis 27/1/14 Motivation is inherent
... because we want to achieve an external reward as B. F. Skinner advocated (Skinner, Operant Conditioning), or due to an inherent need for achievement as David McClelland describes as “nach” people in his presentation of three motivation styles (McClelland, Achievement Motivation Needs Theory), often ...
... because we want to achieve an external reward as B. F. Skinner advocated (Skinner, Operant Conditioning), or due to an inherent need for achievement as David McClelland describes as “nach” people in his presentation of three motivation styles (McClelland, Achievement Motivation Needs Theory), often ...
Improving Horse-Handler Communication Using Concepts of
... the clipping. In other words, when we start clipping and the horse moves, we should continue the clipping without interruption. When none of the horse’s behaviors cause the clipping to stop, it gets habituated to the clipper and stops reacting. This sequence refers to the application of nonassociat ...
... the clipping. In other words, when we start clipping and the horse moves, we should continue the clipping without interruption. When none of the horse’s behaviors cause the clipping to stop, it gets habituated to the clipper and stops reacting. This sequence refers to the application of nonassociat ...
Slide 1
... -Developmental psychologists: study human growth and changes over their lifetime -Personality psychologists: study unique personal characteristics and behaviors -Social psychologists: focus on the individual as a member of a group -Environmental psychologists: study the relationship between people’ ...
... -Developmental psychologists: study human growth and changes over their lifetime -Personality psychologists: study unique personal characteristics and behaviors -Social psychologists: focus on the individual as a member of a group -Environmental psychologists: study the relationship between people’ ...
Human Behavioural Science Course 303
... b- environmental factors primarily shape behavior c- learning environmental factors primarily shape behavior d- childhood experiences and motivation primarily shape behavior e- childhood experiences shape behavior 3-The elements of learning definition are: a- new behavior must be due to level of thi ...
... b- environmental factors primarily shape behavior c- learning environmental factors primarily shape behavior d- childhood experiences and motivation primarily shape behavior e- childhood experiences shape behavior 3-The elements of learning definition are: a- new behavior must be due to level of thi ...
psychological foundations and research
... methodology, and vocabulary. Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. It is a unique science that often necessitates the use of special measurements and research methods. The course has four sections: psychological foundations and research; biological foundations; change ...
... methodology, and vocabulary. Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. It is a unique science that often necessitates the use of special measurements and research methods. The course has four sections: psychological foundations and research; biological foundations; change ...
Psychology312-2_001 - Northwestern University
... In other words, As noted, site was chosen for surgical ...
... In other words, As noted, site was chosen for surgical ...
Lewis FT 1923 The significance of the term hippocampus. J Comp
... Imagine a female who mates with different males over the course of time. Such a female might learn which male is a good mate by keeping track of the number of eggs she laid when associated with each male. ...
... Imagine a female who mates with different males over the course of time. Such a female might learn which male is a good mate by keeping track of the number of eggs she laid when associated with each male. ...
Learning
... Punished behavior is not forgotten, it is suppressed Physical punishment increases aggression through modeling Can also create fear that will generalize Does not tell you “what to do”! Punishment if used swiftly, works best when accompanied with explanation and positive reinforcement for appro ...
... Punished behavior is not forgotten, it is suppressed Physical punishment increases aggression through modeling Can also create fear that will generalize Does not tell you “what to do”! Punishment if used swiftly, works best when accompanied with explanation and positive reinforcement for appro ...
051 Classical Conditioning
... Answer the following questions in YOUR OWN WORDS. You only have to do ONE of the questions marked with asterisks *** ...
... Answer the following questions in YOUR OWN WORDS. You only have to do ONE of the questions marked with asterisks *** ...
Observational Learning
... • Based on principle that punishment tells you what not to do, reinforcement tells you what to do – A swat is used only as backup to milder disciplinary tactics, like a time-out, removing them from reinforcing surroundings – Swatting with a generous dose of reasoning ...
... • Based on principle that punishment tells you what not to do, reinforcement tells you what to do – A swat is used only as backup to milder disciplinary tactics, like a time-out, removing them from reinforcing surroundings – Swatting with a generous dose of reasoning ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 26
... The tendency of organisms to associate a response and its consequence forms the basis for ________________ conditioning. (1 pt) ...
... The tendency of organisms to associate a response and its consequence forms the basis for ________________ conditioning. (1 pt) ...
Ch 7_iClicker
... After getting ill from eating her friend’s Thanksgiving turkey, Natalia couldn’t stand the the sight or smell of turkey. However, when her friend baked a whole chicken, Natalia thought it sounded good. This illustrates: A. B. C. D. ...
... After getting ill from eating her friend’s Thanksgiving turkey, Natalia couldn’t stand the the sight or smell of turkey. However, when her friend baked a whole chicken, Natalia thought it sounded good. This illustrates: A. B. C. D. ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide What is learning? What is associative
... 45. On the chart below, come up with how the terms would impact each type of learning. Classical Acquisition Extinction Spontaneous recovery Generalization Discrimination Cognitive constraints Biological constraints ...
... 45. On the chart below, come up with how the terms would impact each type of learning. Classical Acquisition Extinction Spontaneous recovery Generalization Discrimination Cognitive constraints Biological constraints ...
Tutoring with the Brain-Based Natural Human Learning
... • If students haven’t had the opportunity to grow the foundation dendrites for a new topic or skill, they don’t have the basis from which to grow—on which to connect and construct—the dendrites for the higher levels off skill kill and d knowledge. k l d • Should we judge them as incapable or of less ...
... • If students haven’t had the opportunity to grow the foundation dendrites for a new topic or skill, they don’t have the basis from which to grow—on which to connect and construct—the dendrites for the higher levels off skill kill and d knowledge. k l d • Should we judge them as incapable or of less ...
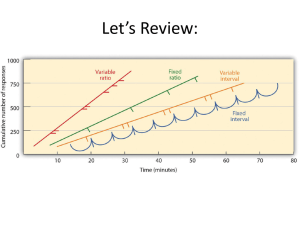
LEARNING BY ASSOCIATION: CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
... conditioned response, or CR). – Extinction occurs when the CS is repeatedly presented without the US, and the CR eventually disappears, although it may reappear later in a process known as spontaneous recovery. ...
... conditioned response, or CR). – Extinction occurs when the CS is repeatedly presented without the US, and the CR eventually disappears, although it may reappear later in a process known as spontaneous recovery. ...
Traditional Learning Theories
... Fatigue method: The eliciting stimulus is presented so often that the person is so fatigued that the old habit cannot be performed. At that point, a new response will occur and a new S-R association will be learned, or no response will occur. 2) Threshold method: the stimulus is presented at a lev ...
... Fatigue method: The eliciting stimulus is presented so often that the person is so fatigued that the old habit cannot be performed. At that point, a new response will occur and a new S-R association will be learned, or no response will occur. 2) Threshold method: the stimulus is presented at a lev ...
Sleep and Dreams - VCC Library
... Dreams express our ongoing concerns of conscious waking life (relationships, work, health etc.) and provide an opportunity to resolve current concerns and problems. In this theory, symbols of a dream convey its true meaning. Dream as a modified version of the cognitive activity that goes on when we ...
... Dreams express our ongoing concerns of conscious waking life (relationships, work, health etc.) and provide an opportunity to resolve current concerns and problems. In this theory, symbols of a dream convey its true meaning. Dream as a modified version of the cognitive activity that goes on when we ...
Sleep and Dreams - VCC Library
... Dreams express our ongoing concerns of conscious waking life (relationships, work, health etc.) and provide an opportunity to resolve current concerns and problems. In this theory, symbols of a dream convey its true meaning. Dream as a modified version of the cognitive activity that goes on when we ...
... Dreams express our ongoing concerns of conscious waking life (relationships, work, health etc.) and provide an opportunity to resolve current concerns and problems. In this theory, symbols of a dream convey its true meaning. Dream as a modified version of the cognitive activity that goes on when we ...
Types of learning
... Habituation Main article: Habituation In psychology, habituation is an example of non-associative learning in which there is a progressive diminution of behavioral response probability with repetition of a stimulus. It is another form of integration. An animal first responds to a stimulus, but if it ...
... Habituation Main article: Habituation In psychology, habituation is an example of non-associative learning in which there is a progressive diminution of behavioral response probability with repetition of a stimulus. It is another form of integration. An animal first responds to a stimulus, but if it ...
THE EVOLUTION OF PSYCHOLOGY
... • COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGISTS are interested in the way people think about things, the internal mental events that influence how we behave. They believe our behavior is a product of our INTERPRETATION of environmental stimuli that are influenced by our MEMORIES from the past which lead us to form EXPECT ...
... • COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGISTS are interested in the way people think about things, the internal mental events that influence how we behave. They believe our behavior is a product of our INTERPRETATION of environmental stimuli that are influenced by our MEMORIES from the past which lead us to form EXPECT ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.