Classical Conditioning
... observed. On the other hand, most cognitive psychologists consider memory to be an abstract construct, which can only be studied indirectly through empirical measures. It is also helpful to consider the historical roots of these two sub-disciplines. Learning grew from the behaviorist school, while t ...
... observed. On the other hand, most cognitive psychologists consider memory to be an abstract construct, which can only be studied indirectly through empirical measures. It is also helpful to consider the historical roots of these two sub-disciplines. Learning grew from the behaviorist school, while t ...
KS2 Newsletter 1
... For a few weeks I and my two colleagues – a teaching assistant and a learning support assistant -- observed the children working. We quickly identified the pupils who saw group work as a ‘free ride’ and those who would need support. We tried different combinations of children and following a few tw ...
... For a few weeks I and my two colleagues – a teaching assistant and a learning support assistant -- observed the children working. We quickly identified the pupils who saw group work as a ‘free ride’ and those who would need support. We tried different combinations of children and following a few tw ...
Chapter 6 – Perception
... A. Operant conditioning: association of behaviors with their consequences: more likely to repeat rewarded, reinforced behaviors and less likely to repeat punished behaviors B. Difference between classical and operant: classical conditioning forms an association between stimuli and involves responde ...
... A. Operant conditioning: association of behaviors with their consequences: more likely to repeat rewarded, reinforced behaviors and less likely to repeat punished behaviors B. Difference between classical and operant: classical conditioning forms an association between stimuli and involves responde ...
Chapter 5 - Learning
... genetic influences. For Skinner, the mind was a “black box” whose contents cannot be illuminated by science. For Skinner, behavior is shaped by its consequences. Reinforcer – is any stimulus event that increases the likelihood that the behavior it follows will be repeated. Skinner coined the term ...
... genetic influences. For Skinner, the mind was a “black box” whose contents cannot be illuminated by science. For Skinner, behavior is shaped by its consequences. Reinforcer – is any stimulus event that increases the likelihood that the behavior it follows will be repeated. Skinner coined the term ...
Learning - Ramsey School District
... CAN, dish, king, cape, apple, CAN, dog, blue, can, dish, CAN, take, call, brick, pair, CAN, spin, chair, CAN, camp. ...
... CAN, dish, king, cape, apple, CAN, dog, blue, can, dish, CAN, take, call, brick, pair, CAN, spin, chair, CAN, camp. ...
Chapter 6 Learning powerpoints
... Is supplemented by a cognitive perspective on conditioning • But researchers discovered several situations in which the traditional view was an insufficient explanation of behavior • These observations indicated that psychologists needed to consider stuff (motivation, cognition, beliefs, expectatio ...
... Is supplemented by a cognitive perspective on conditioning • But researchers discovered several situations in which the traditional view was an insufficient explanation of behavior • These observations indicated that psychologists needed to consider stuff (motivation, cognition, beliefs, expectatio ...
$doc.title
... of enumeration problems. Its impact was to show the inherent difficulty in counting the number of solutions not just to computationally hard problems, but also to those whose decision complexity is relatively “easy.” This work led to the theory of algebraic computation, which established a framework ...
... of enumeration problems. Its impact was to show the inherent difficulty in counting the number of solutions not just to computationally hard problems, but also to those whose decision complexity is relatively “easy.” This work led to the theory of algebraic computation, which established a framework ...
Behaviorism Study Guide Spring 2013
... Task analysis Positive practice Notes from Guidelines: Encouraging Positive Behaviors (pg. 288): Response cost Group consequences Contingency contract Token Economy (token reinforcement system) Fading (not in text) Self-management ...
... Task analysis Positive practice Notes from Guidelines: Encouraging Positive Behaviors (pg. 288): Response cost Group consequences Contingency contract Token Economy (token reinforcement system) Fading (not in text) Self-management ...
Chapter 1 Development Across the Lifespan
... the model that seeks to identify the ways individuals take in, use, and store information b. The theory grew out the computer age. c. They assume that even complex behaviors such as learning, remembering, categorizing, and thinking can be broken down into a series of individual steps. d. They sugges ...
... the model that seeks to identify the ways individuals take in, use, and store information b. The theory grew out the computer age. c. They assume that even complex behaviors such as learning, remembering, categorizing, and thinking can be broken down into a series of individual steps. d. They sugges ...
Crash Course Study Guide for AP Psychology Exam
... Crash Course Study Guide for AP Psychology Exam INTRODUCTION Psychology is the scientific study of thought and behavior. Psychologists study how the brain creates thoughts, feelings, and actions, and how internal and external environments affect them. Four primary goals of psychology: describe behav ...
... Crash Course Study Guide for AP Psychology Exam INTRODUCTION Psychology is the scientific study of thought and behavior. Psychologists study how the brain creates thoughts, feelings, and actions, and how internal and external environments affect them. Four primary goals of psychology: describe behav ...
Ecological Theories Derived from Learning Theories
... birth provide the foundation for later development Assumption # 4: Behavior is both the cause and the effect of later behavior: behavior does not occur in isolation, it always affect other parts of the individual behavioral system. ...
... birth provide the foundation for later development Assumption # 4: Behavior is both the cause and the effect of later behavior: behavior does not occur in isolation, it always affect other parts of the individual behavioral system. ...
Learning
... objectively (by observing behaviors) Classical conditioning can be helpful in treatment programs ...
... objectively (by observing behaviors) Classical conditioning can be helpful in treatment programs ...
Social Learning Theory
... Attributional style of depressed person: He/she attributes bad events to causes that are internal, stable, and global. Good results are believed to result from situational, unstable, and specific causes (e.g., luck). Attributional style of ‘non-depressed” person: He/she takes a bright view of good ...
... Attributional style of depressed person: He/she attributes bad events to causes that are internal, stable, and global. Good results are believed to result from situational, unstable, and specific causes (e.g., luck). Attributional style of ‘non-depressed” person: He/she takes a bright view of good ...
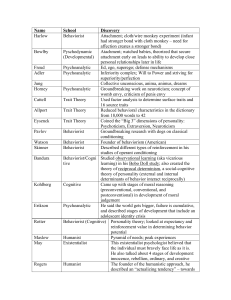
Theorist Names - HallquistCPHS.com
... Founder of structuralism, the analysis of mental structures (early schools) Founded the first psychological laboratory in Leipzig; observed and recorded your own perceptions, thoughts, feelings Like Darwin, this early theorist studied how an individual adapts to and functions in their environmeny De ...
... Founder of structuralism, the analysis of mental structures (early schools) Founded the first psychological laboratory in Leipzig; observed and recorded your own perceptions, thoughts, feelings Like Darwin, this early theorist studied how an individual adapts to and functions in their environmeny De ...
Artificial Neural Networks : An Introduction
... Supervised Learning • Child learns from a teacher • Each input vector requires a ...
... Supervised Learning • Child learns from a teacher • Each input vector requires a ...
Introduction to Psychology
... What students need to do: Define learning as relatively permanent changes of behavior resulting from experience Distinguish learning from performance Recognize learning as a vehicle to promote adaptation through experience Explain how, according to Pavlov’s theory, a neutral stimulus becomes ...
... What students need to do: Define learning as relatively permanent changes of behavior resulting from experience Distinguish learning from performance Recognize learning as a vehicle to promote adaptation through experience Explain how, according to Pavlov’s theory, a neutral stimulus becomes ...
Learning
... ! Type of learning in which we learn to associate a response and its consequence ! Thus, we learn to repeat acts followed by good results and to avoid acts followed by bad results Let’s take a closer look. ...
... ! Type of learning in which we learn to associate a response and its consequence ! Thus, we learn to repeat acts followed by good results and to avoid acts followed by bad results Let’s take a closer look. ...
Learning - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... Conditioned Response (CR) learned response to a previously neutral ...
... Conditioned Response (CR) learned response to a previously neutral ...
Motivation Theories Essay Assignment
... to document how people learn vicariously from observation of others. Bandura noted that our behavior is changed when we see a person take a specific action and be rewarded for that action. In the future we are more likely to take that same action. This is vicarious learning in which we learn through ...
... to document how people learn vicariously from observation of others. Bandura noted that our behavior is changed when we see a person take a specific action and be rewarded for that action. In the future we are more likely to take that same action. This is vicarious learning in which we learn through ...
Flipped Classroom - "C. Marchesi" – Mascalucia
... Class activities may include: using math manipulatives and emerging mathematical technologies, in-depth laboratory experiments, original document analysis, debate or speech presentation, current event discussions, project-based learning, and skill development or concept practice. ...
... Class activities may include: using math manipulatives and emerging mathematical technologies, in-depth laboratory experiments, original document analysis, debate or speech presentation, current event discussions, project-based learning, and skill development or concept practice. ...
Liturgical Catechesis - Catechetical Resources
... WHAT we did… 1) List the 5 precepts of the Church. ...
... WHAT we did… 1) List the 5 precepts of the Church. ...
HERE
... BEHAVIOURISM Behaviorism (also called the behaviorist approach) was the primary paradigm in psychology between 1920s to 1950: • Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior. • B ...
... BEHAVIOURISM Behaviorism (also called the behaviorist approach) was the primary paradigm in psychology between 1920s to 1950: • Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior. • B ...
Chapter 11
... improve with experience. Top-down approach Generate ideas Develop models Validate models Bottom-up approach Discover new (unknown) patterns Find key relationships in data ...
... improve with experience. Top-down approach Generate ideas Develop models Validate models Bottom-up approach Discover new (unknown) patterns Find key relationships in data ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.