conditioned reinforcer
... • Contingency: the outcome is "contingent on" a particular response – positive contingency response produces outcome – negative contingency response prevents or eliminates outcome ...
... • Contingency: the outcome is "contingent on" a particular response – positive contingency response produces outcome – negative contingency response prevents or eliminates outcome ...
Classical Conditioning: The Elements of Associative Learning
... The schools of behaviorism Behaviorism Classic Methodological Watson ...
... The schools of behaviorism Behaviorism Classic Methodological Watson ...
Page 1 ! ! ! ! ! ! ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) Page 2 Learning)and
... Implication:!You!can!think!that!a!behavior!has!ceased!but!it!can!easily!return.!Need!to!be!aware!of!this!and! make!clients!aware!of!this.! Stimulus/Generalization:!a!CR!(salivation)!to!one!CS!seems!to!generalize!to!other!closely!related!stimuli!–! e.g.!bells!with!slightly!different!tones! Implicatio ...
... Implication:!You!can!think!that!a!behavior!has!ceased!but!it!can!easily!return.!Need!to!be!aware!of!this!and! make!clients!aware!of!this.! Stimulus/Generalization:!a!CR!(salivation)!to!one!CS!seems!to!generalize!to!other!closely!related!stimuli!–! e.g.!bells!with!slightly!different!tones! Implicatio ...
Learning
... Cognitive Processes and Classical Conditioning • Behaviorism: The view that (1) psychology should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes – Founded by Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner ...
... Cognitive Processes and Classical Conditioning • Behaviorism: The view that (1) psychology should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes – Founded by Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner ...
NEW HAMPSHIRE COMMUNITY TECHNICAL COLLEGE 2020
... 10. Explain how perception of distance and depth is helped by clues provided by movements of the eye muscles, binocular vision, interposition, linear perspective, and relative size of objects. 11. Understand how we answer the question What does it mean? through the element of perception called inter ...
... 10. Explain how perception of distance and depth is helped by clues provided by movements of the eye muscles, binocular vision, interposition, linear perspective, and relative size of objects. 11. Understand how we answer the question What does it mean? through the element of perception called inter ...
Conditioning and Learning
... which an organism produces different responses to two similar stimuli. ...
... which an organism produces different responses to two similar stimuli. ...
Learning Chapter 6 - Mrs. Short`s AP Psychology Class
... by being rewarded or punished itself (behaviorism), they can learn from watching somebody being rewarded or punished, too (observational learning) – important because they sparked many more studies on the effects of observational learning • practical implication, e.g. how children can be influenced ...
... by being rewarded or punished itself (behaviorism), they can learn from watching somebody being rewarded or punished, too (observational learning) – important because they sparked many more studies on the effects of observational learning • practical implication, e.g. how children can be influenced ...
Instrumental & Operant Conditioning
... The sudden awareness of the solution to a problem Wolfgang Kohler, The Mentality of Apes ...
... The sudden awareness of the solution to a problem Wolfgang Kohler, The Mentality of Apes ...
How the Brain Learns
... what the reader is learning and what the reader already knows. The physiological functions of learning are the same for everyone. Differences in learning occur not physiologically, but based on what each reader already knows. How Does this Chapter Connect to Chapters that will Follow? The cognitive ...
... what the reader is learning and what the reader already knows. The physiological functions of learning are the same for everyone. Differences in learning occur not physiologically, but based on what each reader already knows. How Does this Chapter Connect to Chapters that will Follow? The cognitive ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... delivering electrical impulses to the brain to monitoring the reactions of subjects given a specific task. I will show how a connection can be made between theoretical psychology and practical electrophysiology and how these two different approaches can be used together in an effort to understand ho ...
... delivering electrical impulses to the brain to monitoring the reactions of subjects given a specific task. I will show how a connection can be made between theoretical psychology and practical electrophysiology and how these two different approaches can be used together in an effort to understand ho ...
How do people learn behaviors?
... • All learning occurs as a result of environmental influences (not the individual’s efforts or choices) • The motivation for learning a behavior is to receive a reward or avoid a punishment • Only studies observable behaviors Theories • Classical Conditioning • Operant Conditioning Researchers • Pav ...
... • All learning occurs as a result of environmental influences (not the individual’s efforts or choices) • The motivation for learning a behavior is to receive a reward or avoid a punishment • Only studies observable behaviors Theories • Classical Conditioning • Operant Conditioning Researchers • Pav ...
iClicker Questions Section 6.2
... The organism learns an association between a behavior and a punishment. The organism learns an association between a behavior and a consequence. E. None of the above ...
... The organism learns an association between a behavior and a punishment. The organism learns an association between a behavior and a consequence. E. None of the above ...
Chapter 11: Behaviorism: After the Founding
... Punishment works if the 3 Ss are met If these three conditions are not met, then the misbehavior actually becomes negatively reinforced on a Variable Ratio schedule of reinforcement Verbal Behavior ...
... Punishment works if the 3 Ss are met If these three conditions are not met, then the misbehavior actually becomes negatively reinforced on a Variable Ratio schedule of reinforcement Verbal Behavior ...
Learning - Deerfield High School
... stimuli similar to the CS is called generalization. Pavlov conditioned the dog’s salivation (CR) by using miniature vibrators (CS) on the thigh. When he subsequently stimulated other parts of the dog’s body, salivation dropped. ...
... stimuli similar to the CS is called generalization. Pavlov conditioned the dog’s salivation (CR) by using miniature vibrators (CS) on the thigh. When he subsequently stimulated other parts of the dog’s body, salivation dropped. ...
Chapter Outlines - Cengage Learning
... skill can be performed automatically for perceptual-motor skills. For cognitive skills, practice should focus on retrieval of information from memory. Feedback lets the learner know if she or he is correct and may provide understanding of the cognitive and physical processes used in the skill. Feedb ...
... skill can be performed automatically for perceptual-motor skills. For cognitive skills, practice should focus on retrieval of information from memory. Feedback lets the learner know if she or he is correct and may provide understanding of the cognitive and physical processes used in the skill. Feedb ...
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES Tools for Distance Education: Toward
... The Open University (England) is using connected DVDs for delivery of distance ed courses. The University of Wollongong (Australia) is implementing a hybrid environment for distance education of DVD and WebCT in order to use media-rich content and try to span the digital divide between the bandwidth ...
... The Open University (England) is using connected DVDs for delivery of distance ed courses. The University of Wollongong (Australia) is implementing a hybrid environment for distance education of DVD and WebCT in order to use media-rich content and try to span the digital divide between the bandwidth ...
Learning: Operant Conditioning
... the Skinner Box, the rat will learn to press the bar to get food. This is a type of reinforcement. Reinforcement – a consequence that occurs after a behavior and increases the chance that the behavior will occur again. Examples of consequences that people respond to are social approval, money, a ...
... the Skinner Box, the rat will learn to press the bar to get food. This is a type of reinforcement. Reinforcement – a consequence that occurs after a behavior and increases the chance that the behavior will occur again. Examples of consequences that people respond to are social approval, money, a ...
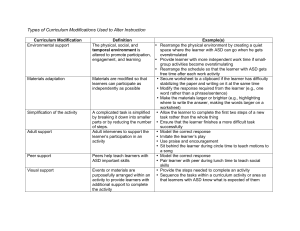
Types of Curriculum Modifications Used to Alter Instruction
... • Rearrange the schedule so that the learner with ASD gets free time after each work activity Materials are modified so that • Secure worksheet to a clipboard if the learner has difficulty learners can participate as stabilizing the paper and writing on it at the same time independently as possible ...
... • Rearrange the schedule so that the learner with ASD gets free time after each work activity Materials are modified so that • Secure worksheet to a clipboard if the learner has difficulty learners can participate as stabilizing the paper and writing on it at the same time independently as possible ...
Behavioral therapy
... 2. Abnormal behaviors are nonpathological “problems of living” 3. Abnormal behavior assumed to be acquired and maintained in the same manner as normal behavior 4. Behavior assessment focuses on current determinants rather than on the analysis of possible historical antecedents 5. Rooted in the notio ...
... 2. Abnormal behaviors are nonpathological “problems of living” 3. Abnormal behavior assumed to be acquired and maintained in the same manner as normal behavior 4. Behavior assessment focuses on current determinants rather than on the analysis of possible historical antecedents 5. Rooted in the notio ...
PSYC-1001-D-Mock-Final-Exam
... work, trying to decide what colour to paint the shed or wondering where to spend the holidays, when you hit a mental block, you simply cannot think straight. It might be that the number of options is overwhelming or, at the other extreme, that you can’t come up with a single idea. Either way you’re ...
... work, trying to decide what colour to paint the shed or wondering where to spend the holidays, when you hit a mental block, you simply cannot think straight. It might be that the number of options is overwhelming or, at the other extreme, that you can’t come up with a single idea. Either way you’re ...
Operant Conditioning
... “Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire” Tally up the Yes responses of odd and even numbers: ...
... “Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire” Tally up the Yes responses of odd and even numbers: ...
LCog read ch 5
... manager" is not the only who can control behavior through the use of operant conditioning (even if it occurs unwittingly). 5. What are the differences among punishment, extinction, and negative reinforcement? Although punishment and extinction both are means to decrease behavior, their respective me ...
... manager" is not the only who can control behavior through the use of operant conditioning (even if it occurs unwittingly). 5. What are the differences among punishment, extinction, and negative reinforcement? Although punishment and extinction both are means to decrease behavior, their respective me ...
Operant Conditioning - Stephen F. Austin State University
... • Behavior modification - the use of operant conditioning techniques to bring about desired changes in behavior. • Token economy - type of behavior modification in which desired behavior is rewarded with tokens. • Time-out - a form of mild punishment by removal in which a misbehaving animal, child, ...
... • Behavior modification - the use of operant conditioning techniques to bring about desired changes in behavior. • Token economy - type of behavior modification in which desired behavior is rewarded with tokens. • Time-out - a form of mild punishment by removal in which a misbehaving animal, child, ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.