CHAPTER 2 FOUNDATIONS OF INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR
... to avoid something they don't want" (p. 42). "Behavior is assumed to be determined from without – that is, learned – rather than from within – reflexive or unlearned. Skinner argued that creating pleasing consequences to follow specific forms of behavior would increase the frequency of that behavior ...
... to avoid something they don't want" (p. 42). "Behavior is assumed to be determined from without – that is, learned – rather than from within – reflexive or unlearned. Skinner argued that creating pleasing consequences to follow specific forms of behavior would increase the frequency of that behavior ...
Classical Conditioning
... Reinforcement: It is central to operant conditioning theory. A reinforcer is any event which changes subsequent behavior when it follows behavior in time. B F Skinner used reinforcement as a procedure for controlling behavior. It is event that enhances the rate of responding in subject. Reinforcer i ...
... Reinforcement: It is central to operant conditioning theory. A reinforcer is any event which changes subsequent behavior when it follows behavior in time. B F Skinner used reinforcement as a procedure for controlling behavior. It is event that enhances the rate of responding in subject. Reinforcer i ...
Position paper - SDDU
... spite of the general territory of higher education having undergone significant changes in its landscape over the intervening 15 years, which Becher and Trowler outline in the first chapter of the revised book. The significant cultural changes that have taken place pose certain challenges to the ide ...
... spite of the general territory of higher education having undergone significant changes in its landscape over the intervening 15 years, which Becher and Trowler outline in the first chapter of the revised book. The significant cultural changes that have taken place pose certain challenges to the ide ...
The Learning Perspective
... vicarious or direct learning • Negative expectancies can have broad influence on behavior, particularly when ...
... vicarious or direct learning • Negative expectancies can have broad influence on behavior, particularly when ...
Genre Study: Teaching with Fiction and Nonfiction Books (K–8)
... • A story about the life of a person who has made a difference • A strong character who overcame adversity and made a contribution to the world, to society • The story can tell about the whole life or a part of the life • The subject of the story is inspirational • There are people of all cultures w ...
... • A story about the life of a person who has made a difference • A strong character who overcame adversity and made a contribution to the world, to society • The story can tell about the whole life or a part of the life • The subject of the story is inspirational • There are people of all cultures w ...
Ch 25 - Molecular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... Sensitization of the Gill-Withdrawal Reflex ...
... Sensitization of the Gill-Withdrawal Reflex ...
Skinner and Operant Conditioning
... Skinner and Operant Conditioning Slide One: Two characteristics help us distinguish between the two forms of associative learning. As you learned in classical conditioning, the organism learns associations between events that the organism does not control, and responses are automatic. This is also k ...
... Skinner and Operant Conditioning Slide One: Two characteristics help us distinguish between the two forms of associative learning. As you learned in classical conditioning, the organism learns associations between events that the organism does not control, and responses are automatic. This is also k ...
PMHS - VitaAPPsych
... reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. _____________________ _________________ 21.A relatively permanent change in an organism’s behavior due to experience. ________________________ 22.Classical conditioning is also called this, due to the researcher who first described and studied ...
... reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. _____________________ _________________ 21.A relatively permanent change in an organism’s behavior due to experience. ________________________ 22.Classical conditioning is also called this, due to the researcher who first described and studied ...
File - McMurray VMC
... • An association between 2 stimuli Associating music with scary part of movie ...
... • An association between 2 stimuli Associating music with scary part of movie ...
ODE`s Glossary of Curriculum, Assessment and Instruction Terms
... referred to as “assessment for learning” rather than “assessment of learning.” Oregon Assessment of Knowledge and Skills (OAKS) Official name for Oregon’s statewide Knowledge and Skills Tests in Reading/Literature, Mathematics, Science, and Social Sciences. OAKS also includes performance assessment ...
... referred to as “assessment for learning” rather than “assessment of learning.” Oregon Assessment of Knowledge and Skills (OAKS) Official name for Oregon’s statewide Knowledge and Skills Tests in Reading/Literature, Mathematics, Science, and Social Sciences. OAKS also includes performance assessment ...
O.C. Day 1
... They both use acquisition, discrimination, Spontaneous Recovery, generalization and extinction. ...
... They both use acquisition, discrimination, Spontaneous Recovery, generalization and extinction. ...
Employees` Development - WordPress.com
... Learners progress through stages or phases Material should be organized and presented in small ...
... Learners progress through stages or phases Material should be organized and presented in small ...
File
... • Aim: What are the different ways humans can learn to do things? • Do Now: How would you deal with the following scenario if you were a teacher? Let’s say kids just won’t go to class – they stand in the hall acting ridiculous all morning – what behavioral techniques could you use to stop that? ...
... • Aim: What are the different ways humans can learn to do things? • Do Now: How would you deal with the following scenario if you were a teacher? Let’s say kids just won’t go to class – they stand in the hall acting ridiculous all morning – what behavioral techniques could you use to stop that? ...
File
... OPERANT CHAMBER Skinner Developed the Operant chamber, or the Skinner box Used this to teach animals behaviors that were unlike their natural behavior ...
... OPERANT CHAMBER Skinner Developed the Operant chamber, or the Skinner box Used this to teach animals behaviors that were unlike their natural behavior ...
Employees’ Development
... Learners progress through stages or phases Material should be organized and presented in small ...
... Learners progress through stages or phases Material should be organized and presented in small ...
Learning Notes
... - associative learning - learning that certain events occur together; the events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning). I. Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which an organism comes to associate stimuli. A neutra ...
... - associative learning - learning that certain events occur together; the events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequences (as in operant conditioning). I. Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which an organism comes to associate stimuli. A neutra ...
1. A stimulus change that increases the future frequency of behavior
... 3. A stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer 4. A therapeutic technique in which the client learns appropriate behavior through imitation of someone else. 5. An innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need 6. Circumst ...
... 3. A stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer 4. A therapeutic technique in which the client learns appropriate behavior through imitation of someone else. 5. An innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need 6. Circumst ...
punishment
... Punishment can create strong negative emotions that can interfere with learning the desired response. For all of these reasons, punishment should be used sparingly and only when other operant conditioning procedures either cannot be used or will not work. ...
... Punishment can create strong negative emotions that can interfere with learning the desired response. For all of these reasons, punishment should be used sparingly and only when other operant conditioning procedures either cannot be used or will not work. ...
Correctional Theory: Past to Present
... • Some argue that individuals hold values that unconditionally approve of crime • Studies have found few people unconditionally approve of crime • Rather, some are amoral—neither approve nor condemn crime ...
... • Some argue that individuals hold values that unconditionally approve of crime • Studies have found few people unconditionally approve of crime • Rather, some are amoral—neither approve nor condemn crime ...
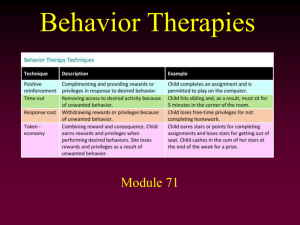
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... • Aversive conditioning is not very effective – Cognition interferes – people know they won’t get sick when not taking the treatment so it doesn’t generalize over to normal life ...
... • Aversive conditioning is not very effective – Cognition interferes – people know they won’t get sick when not taking the treatment so it doesn’t generalize over to normal life ...
Learning Jeopardy
... The tendency for subjects to respond to stimuli similar to the conditioned stimuli. ...
... The tendency for subjects to respond to stimuli similar to the conditioned stimuli. ...
Chap10a
... being exposed to inescapable shock. Step 1 – expose dogs to 3 conditions: escapable shock, inescapable shock (yoke), no shock Step 2 – escape training Results – yoked dogs did not learn to escape. ...
... being exposed to inescapable shock. Step 1 – expose dogs to 3 conditions: escapable shock, inescapable shock (yoke), no shock Step 2 – escape training Results – yoked dogs did not learn to escape. ...
Ch.6 Learning Power Point Notes
... (ex. food, water, & adequate warmth) • ______________ or CONDITIONED REINFORCERS (ex. money) ...
... (ex. food, water, & adequate warmth) • ______________ or CONDITIONED REINFORCERS (ex. money) ...
Unit 1 History and Approaches - Teacher Version
... “introspection” and explain why current psychological researchers would be unlikely to use introspection to gather data. 2. William James developed his theory of functionalism around the same time Charles Darwin was developing the theory of evolution. How do you think Darwin's theory influenced Jame ...
... “introspection” and explain why current psychological researchers would be unlikely to use introspection to gather data. 2. William James developed his theory of functionalism around the same time Charles Darwin was developing the theory of evolution. How do you think Darwin's theory influenced Jame ...
Learning theory (education)
Learning theories are conceptual frameworks describing how information is absorbed, processed, and retained during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a world view, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained.Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of conditioning and will advocate a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behavior is too narrow and prefer to study the learner rather than their environment and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies to a large extent on what he already knows and understands, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses upon the often-necessary change that is required in a learner's preconceptions and world view.Outside the realm of educational psychology, techniques to directly observe the functioning of the brain during the learning process, such as event-related potential and functional magnetic resonance imaging, are used in educational neuroscience. As of 2012, such studies are beginning to support a theory of multiple intelligences, where learning is seen as the interaction between dozens of different functional areas in the brain each with their own individual strengths and weaknesses in any particular human learner.