Biology 102 Lecture 11: DNA
... Virtually all cell function is a result of proteins and their interactions ...
... Virtually all cell function is a result of proteins and their interactions ...
dna - Kowenscience.com
... Hershey (1953) Find that only DNA from virus enters cells and directs reproduction of new viruses ...
... Hershey (1953) Find that only DNA from virus enters cells and directs reproduction of new viruses ...
Nucleic Acid Structure Nucleic Acid Sequence Abbreviations
... Ribosomal RNA • “Scaffold” for proteins involved in protein synthesis • RNA has catalytic activity as the “peptidyl transferase” which forms the peptide bond • Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have slightly different ribosomal structures (See Figure 11.25) • Ribosomal RNA contains some modified nucleoside ...
... Ribosomal RNA • “Scaffold” for proteins involved in protein synthesis • RNA has catalytic activity as the “peptidyl transferase” which forms the peptide bond • Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have slightly different ribosomal structures (See Figure 11.25) • Ribosomal RNA contains some modified nucleoside ...
mouse. However, some technical and prac-
... exchanging fragments of closely homologous genes provides an efficient way to generate proteins with new traits1,2. The resulting molecules are very different, at least in sequence, from those that might be obtained by more local searches of protein space, for example by random mutagenesis. The DNA ...
... exchanging fragments of closely homologous genes provides an efficient way to generate proteins with new traits1,2. The resulting molecules are very different, at least in sequence, from those that might be obtained by more local searches of protein space, for example by random mutagenesis. The DNA ...
1. What are the 3 parts of DNA nucleotide?
... 2. How is DNA different from RNA? DNA: 2 strands, deoxyribose sugar, contains thymine; RNA: 1 strand, ribose sugar, contains uracil instead of thymine. 3. What scientists: First determined the structure of DNA? Watson and Crick X-rayed DNA, giving necessary clues to its structure? Rosalind Franklin ...
... 2. How is DNA different from RNA? DNA: 2 strands, deoxyribose sugar, contains thymine; RNA: 1 strand, ribose sugar, contains uracil instead of thymine. 3. What scientists: First determined the structure of DNA? Watson and Crick X-rayed DNA, giving necessary clues to its structure? Rosalind Franklin ...
History_of_DNA
... E.Coli DNA polymerase I requires: 1. All four dNTPs (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP) 2. A primer chain with a free 3`-OH end 3. A template strand to which the primer is basepaired • Double-stranded DNA that is fully intact and lacking a free 3`-OH end will not be replicated (Ex: Intact circular DNA) 4. M ...
... E.Coli DNA polymerase I requires: 1. All four dNTPs (dATP, dGTP, dCTP and dTTP) 2. A primer chain with a free 3`-OH end 3. A template strand to which the primer is basepaired • Double-stranded DNA that is fully intact and lacking a free 3`-OH end will not be replicated (Ex: Intact circular DNA) 4. M ...
Bio290-08-Week 9
... • More common in plants • Correlation between the number of chromosome sets and size of organism • Autopolyploids: multiple chromosomes from one species • Allopolyploids: sets of chromosomes from two or more different species ...
... • More common in plants • Correlation between the number of chromosome sets and size of organism • Autopolyploids: multiple chromosomes from one species • Allopolyploids: sets of chromosomes from two or more different species ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint Notes (DNA)
... to DNA’s structure: (1) The amount of adenine relative to guanine differs from one species to the next, (2) the amount of adenine in a DNA molecule is always equal to the amount of thymine & the amount of guanine is always equal to the amount of cytosine! ...
... to DNA’s structure: (1) The amount of adenine relative to guanine differs from one species to the next, (2) the amount of adenine in a DNA molecule is always equal to the amount of thymine & the amount of guanine is always equal to the amount of cytosine! ...
DNA - Paxon Biology
... simultaneously. This requires the cooperation of over a dozen enzymes & proteins. - Extremely Rapid: In prokaryotes, up to 500 nucleotides are added per second. It takes only a few hours to copy the 6 billion bases of a single human cell. - Accurate: Only about one in a billion nucleotides are incor ...
... simultaneously. This requires the cooperation of over a dozen enzymes & proteins. - Extremely Rapid: In prokaryotes, up to 500 nucleotides are added per second. It takes only a few hours to copy the 6 billion bases of a single human cell. - Accurate: Only about one in a billion nucleotides are incor ...
Multiple Choice. ______1. Which of the following molecules
... ______35. Which of the following statements about prokaryotes is true? a. They generally live in static environments. b. The most efficient means of regulation of gene expression in these organisms is usually at the level of transcription. c. By making certain proteins only when needed, they save e ...
... ______35. Which of the following statements about prokaryotes is true? a. They generally live in static environments. b. The most efficient means of regulation of gene expression in these organisms is usually at the level of transcription. c. By making certain proteins only when needed, they save e ...
Targeted Fluorescent Reporters: Additional slides
... moving DNA polymerase has a higher affinity for the correct nucleotide than an incorrect one because only the correct one can base pair with the template. 11. After nucleotide binding, but before the nucleotide is covalently bonded to the chain, the enzyme undergoes a conformational change and incor ...
... moving DNA polymerase has a higher affinity for the correct nucleotide than an incorrect one because only the correct one can base pair with the template. 11. After nucleotide binding, but before the nucleotide is covalently bonded to the chain, the enzyme undergoes a conformational change and incor ...
Answers to Problem Set 3A
... Because the transposase gene in Ds elements is at least partially deleted and thus nonfunctional, so they need to use a transposase protein produced by an Ac element. 6. What is the function and structure of most centromeres? They serve as attachment sites for the spindle apparatus for the point of ...
... Because the transposase gene in Ds elements is at least partially deleted and thus nonfunctional, so they need to use a transposase protein produced by an Ac element. 6. What is the function and structure of most centromeres? They serve as attachment sites for the spindle apparatus for the point of ...
Chromosome Mapping by Recombination Genes on the same
... A: Chargaff’s rules are that A=T and G=C. Because this is not observed, the most likely interpretation is that the DNA is single-stranded. The phage would first have to synthesize a complementary strand before it could begin to make multiple copies of itself. Rosalind Franklin Got an X-ray diffracti ...
... A: Chargaff’s rules are that A=T and G=C. Because this is not observed, the most likely interpretation is that the DNA is single-stranded. The phage would first have to synthesize a complementary strand before it could begin to make multiple copies of itself. Rosalind Franklin Got an X-ray diffracti ...
Ch 14- 17 Unit Test - Akron Central Schools
... • B) the leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end • C) the lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultim ...
... • B) the leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end • C) the lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultim ...
chapter11
... The two strands of the double helix unwind. Each strands serves as a template for the formation of a new complementary strand. DNA replication is semiconservative: each daughter double helix contains one strand from the parent DNA and one newly synthesized strand. ...
... The two strands of the double helix unwind. Each strands serves as a template for the formation of a new complementary strand. DNA replication is semiconservative: each daughter double helix contains one strand from the parent DNA and one newly synthesized strand. ...
DNA and RNA Chapter 12-1
... questions about genes: • What is a gene made of? • How do genes work? • How do genes determine characteristics of organisms? ...
... questions about genes: • What is a gene made of? • How do genes work? • How do genes determine characteristics of organisms? ...
Gene Expression - Phillips Scientific Methods
... 1. Write out the sequence of BOTH products of replication. What do you notice about these products? ...
... 1. Write out the sequence of BOTH products of replication. What do you notice about these products? ...
document
... DNA Replication – Each strand of the double helix of DNA serves as a template, or model, for the new strand. – Results in 2 identical DNA strands. – Replication is carried out by enzymes. These enzymes “unzip” DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. ...
... DNA Replication – Each strand of the double helix of DNA serves as a template, or model, for the new strand. – Results in 2 identical DNA strands. – Replication is carried out by enzymes. These enzymes “unzip” DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. ...
Biology DNA and Protein Syn
... • James Watson and Francis Crick were working on the structure of DNA in the 1950s. • Using information from Chargaff, Franklin, and other scientists, they put together a 3-D model of DNA. • Watson and Crick’s model was a double helix, with hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases holding the stran ...
... • James Watson and Francis Crick were working on the structure of DNA in the 1950s. • Using information from Chargaff, Franklin, and other scientists, they put together a 3-D model of DNA. • Watson and Crick’s model was a double helix, with hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen bases holding the stran ...
Unit 4
... two DNA strands re-form the double helix. The RNA polymerase continues to elongate the RNA molecule until it reaches the termination site, a specific sequence of nucleotides along the DNA that signals the end of the transcription unit. The mRNA, a transcripts of the gene, is released, and the polyme ...
... two DNA strands re-form the double helix. The RNA polymerase continues to elongate the RNA molecule until it reaches the termination site, a specific sequence of nucleotides along the DNA that signals the end of the transcription unit. The mRNA, a transcripts of the gene, is released, and the polyme ...
File - cOACH RICH`S BIOLOGY CLASS
... • The exact copying of DNA • Replication occurs in both directions • DNA must be copied before cells divide each daughter cell has a complete set of DNA • Original strands serve as templates for new strands ...
... • The exact copying of DNA • Replication occurs in both directions • DNA must be copied before cells divide each daughter cell has a complete set of DNA • Original strands serve as templates for new strands ...
Agilent 101: An Introduction to Microarrays and Genomics
... G, C, or T. Taken together, three adjacent bases represent an instruction to add an amino acid, or to tell the ribosome to start or stop making a protein. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and are assembled by the ribosome according to the instruction specified by the messenger RNA. Th ...
... G, C, or T. Taken together, three adjacent bases represent an instruction to add an amino acid, or to tell the ribosome to start or stop making a protein. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and are assembled by the ribosome according to the instruction specified by the messenger RNA. Th ...
Ch. 16 - ltcconline.net
... 2. Explain how Watson and Crick deduced the structure of DNA and describe the evidence they used. 3. Explain the significance of the research of Rosalind Franklin. 4. Diagram the structure of DNA. Explain the base-pairing rule and describe its significance. 5. Describe the semiconservative model of ...
... 2. Explain how Watson and Crick deduced the structure of DNA and describe the evidence they used. 3. Explain the significance of the research of Rosalind Franklin. 4. Diagram the structure of DNA. Explain the base-pairing rule and describe its significance. 5. Describe the semiconservative model of ...
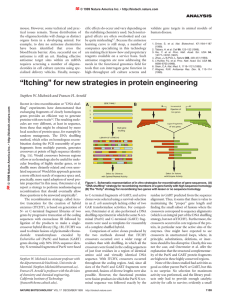
Holliday junction

A Holliday junction is a branched nucleic acid structure that contains four double-stranded arms joined together. These arms may adopt one of several conformations depending on buffer salt concentrations and the sequence of nucleobases closest to the junction. The structure is named after the molecular biologist Robin Holliday, who proposed its existence in 1964.In biology, Holliday junctions are a key intermediate in many types of genetic recombination, as well as in double-strand break repair. These junctions usually have a symmetrical sequence and are thus mobile, meaning that the four individual arms may slide though the junction in a specific pattern that largely preserves base pairing. Additionally, four-arm junctions similar to Holliday junctions appear in some functional RNA molecules.Immobile Holliday junctions, with asymmetrical sequences that lock the strands in a specific position, were artificially created by scientists to study their structure as a model for natural Holliday junctions. These junctions also later found use as basic structural building blocks in DNA nanotechnology, where multiple Holliday junctions can be combined into specific designed geometries that provide molecules with a high degree of structural rigidity.