System Software and Operating Systems
... in that they execute two or more applications running simultaneously (actually they switch back and forth between the applications) Older single-tasking operating systems could only do one thing at a time ...
... in that they execute two or more applications running simultaneously (actually they switch back and forth between the applications) Older single-tasking operating systems could only do one thing at a time ...
System Software and Operating Systems
... in that they execute two or more applications running simultaneously (actually they switch back and forth between the applications) Older single-tasking operating systems could only do one thing at a time ...
... in that they execute two or more applications running simultaneously (actually they switch back and forth between the applications) Older single-tasking operating systems could only do one thing at a time ...
Operating Systems Questions
... 1. Write a definition for an operating system; 2. Describe the main features of an operating system for example: the cost, reliability, ease of use, type of interface and how they can be customised. You need to make sure you’re using different operating systems as examples; 3. Explain what an interr ...
... 1. Write a definition for an operating system; 2. Describe the main features of an operating system for example: the cost, reliability, ease of use, type of interface and how they can be customised. You need to make sure you’re using different operating systems as examples; 3. Explain what an interr ...
Ceng 334 - Operating Systems
... hardware using software. So different Oses can work in the same machine at the same time ...
... hardware using software. So different Oses can work in the same machine at the same time ...
now
... Provides the file system, CPU scheduling, memory management, and other operating-system functions; a large number of functions for one level ...
... Provides the file system, CPU scheduling, memory management, and other operating-system functions; a large number of functions for one level ...
Operating Systems
... increases the amount of data that can be held in memory at one time. When the memory chips get full, some of the data is paged out to the hard disk. This is called swapping. Windows uses a swap file for this purpose. Storage A more technical task is that of disk management. Under some operating syst ...
... increases the amount of data that can be held in memory at one time. When the memory chips get full, some of the data is paged out to the hard disk. This is called swapping. Windows uses a swap file for this purpose. Storage A more technical task is that of disk management. Under some operating syst ...
Operating Systems
... from the manufacturer’s site) that is installed so that it is part of the OS. This software is a device driver. • Modern OS’s usually have device drivers for most standard hardware, so you don’t have to do anything. • But if a new device does not seem to work some or all of the time, check to see if ...
... from the manufacturer’s site) that is installed so that it is part of the OS. This software is a device driver. • Modern OS’s usually have device drivers for most standard hardware, so you don’t have to do anything. • But if a new device does not seem to work some or all of the time, check to see if ...
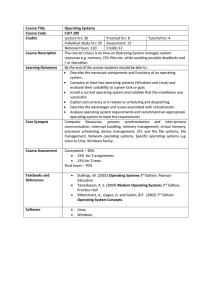
Course Title Operating Systems Course Code CUIT 109 Credits
... Credits 12 The course’s focus is on how an Operating System manages system resources e.g. memory, CPU files etc, while avoiding possible deadlocks and / or starvation. By the end of the course students should be able to : Describe the necessary components and functions of an operating system. Co ...
... Credits 12 The course’s focus is on how an Operating System manages system resources e.g. memory, CPU files etc, while avoiding possible deadlocks and / or starvation. By the end of the course students should be able to : Describe the necessary components and functions of an operating system. Co ...
CS323 - Operating Systems
... Course Objectives: Having successfully completed this course, the student will be able to: 1. Develop an appreciation of operating system operation, design and implementation. 2. Recognize and memorize the fundamentals and features of modern operating systems. 3. Distinguish between different ty ...
... Course Objectives: Having successfully completed this course, the student will be able to: 1. Develop an appreciation of operating system operation, design and implementation. 2. Recognize and memorize the fundamentals and features of modern operating systems. 3. Distinguish between different ty ...
CENG334 Introduction to Operating Systems
... Save programmers a lot of trouble when building applications Allow apps to be ported across a wide range of hardware platforms ...
... Save programmers a lot of trouble when building applications Allow apps to be ported across a wide range of hardware platforms ...
1. Operating system
... e.g. no matter how many cylinders or what sector size the file system looks the same on all disks ...
... e.g. no matter how many cylinders or what sector size the file system looks the same on all disks ...
Microsoft & Linux What Is an Operating System?
... Types of Operating Systems Real-Time OS - Features and settings not accessible by user. The primary goal of an RTOS is to ensure that a specific set of operations occur within a precise time period. Embedded OS - A single-user, single-tasking OS used on many small hand-held devices such as personal ...
... Types of Operating Systems Real-Time OS - Features and settings not accessible by user. The primary goal of an RTOS is to ensure that a specific set of operations occur within a precise time period. Embedded OS - A single-user, single-tasking OS used on many small hand-held devices such as personal ...
Buzz Words
... would be a good idea to (12) defrag her hard drive regularly so that all the files lined up in sequentially ordered (13) sectors and so that it was more efficient. She also looked into (14) file compression utilities, which would help her reduce the size of her files when she sent them to others ove ...
... would be a good idea to (12) defrag her hard drive regularly so that all the files lined up in sequentially ordered (13) sectors and so that it was more efficient. She also looked into (14) file compression utilities, which would help her reduce the size of her files when she sent them to others ove ...
3460:426/526 Operating Systems
... Introduction to various types of operating systems: batch processing systems, multiprogramming systems and interacting processes: storage management; process and resource control; deadlock problem. Course is independent of any particular operating system. Detailed Description: Operating systems defi ...
... Introduction to various types of operating systems: batch processing systems, multiprogramming systems and interacting processes: storage management; process and resource control; deadlock problem. Course is independent of any particular operating system. Detailed Description: Operating systems defi ...
Operating systems
... In the early 1950s, a computer could execute only one program at a time. Each user had sole use of the computer for a limited period of time and would arrive at a scheduled time with program and data on punched paper cards or punched tape. The program would be loaded into the machine, and the machin ...
... In the early 1950s, a computer could execute only one program at a time. Each user had sole use of the computer for a limited period of time and would arrive at a scheduled time with program and data on punched paper cards or punched tape. The program would be loaded into the machine, and the machin ...
User view
... A computer system can be divided into four components; Hardware OS Application programs Users Hardware – provides basic computing resources CPU, memory, I/O devices Operating system Controls and coordinates use of hardware among various applications and users Application programs The w ...
... A computer system can be divided into four components; Hardware OS Application programs Users Hardware – provides basic computing resources CPU, memory, I/O devices Operating system Controls and coordinates use of hardware among various applications and users Application programs The w ...
Judul - Binus Repository
... – Click on the Start button on the lower left corner of the Windows desktop – Click on the My Computer icon on the desktop, find the application executable on your hard disk, and click it – Click on the My Documents icon on the desktop, find the document you want to open, and click it. It should aut ...
... – Click on the Start button on the lower left corner of the Windows desktop – Click on the My Computer icon on the desktop, find the application executable on your hard disk, and click it – Click on the My Documents icon on the desktop, find the document you want to open, and click it. It should aut ...
BA471 Management Information Systems
... Compilers convert software (including OS’s) into machine language (0,1) Source Code ...
... Compilers convert software (including OS’s) into machine language (0,1) Source Code ...
Components of an operating system
... Components of an operating system An operating system is a software program that provides an interface between the user and the computer and manages thousands of applications. Most computer systems are sold with an operating system installed. Computers that are designed for individual users are call ...
... Components of an operating system An operating system is a software program that provides an interface between the user and the computer and manages thousands of applications. Most computer systems are sold with an operating system installed. Computers that are designed for individual users are call ...
Software: Operating Systems and Utilities
... Application Software Application software includes programs that perform a single task such as spreadsheet analysis. ...
... Application Software Application software includes programs that perform a single task such as spreadsheet analysis. ...
Chapter 4
... Application Software Application software includes programs that perform a single task such as spreadsheet analysis. ...
... Application Software Application software includes programs that perform a single task such as spreadsheet analysis. ...
Telecommunications
... Application Software Application software includes programs that perform a single task such as spreadsheet analysis. ...
... Application Software Application software includes programs that perform a single task such as spreadsheet analysis. ...