What is an Operating System?
... cards) and submitted this to the computer operator. The job was in the form of punch cards, and at some later time the output was generated by the system—user didn’t get to interact with his/her job. The output consisted of the result of the program, as well as a dump of the final memory and registe ...
... cards) and submitted this to the computer operator. The job was in the form of punch cards, and at some later time the output was generated by the system—user didn’t get to interact with his/her job. The output consisted of the result of the program, as well as a dump of the final memory and registe ...
Introduction to OS - EECG Toronto
... Google is developing an OS called “Fuchsia,” runs on All the Things (androidpolice, Aug 12, 2016) o o ...
... Google is developing an OS called “Fuchsia,” runs on All the Things (androidpolice, Aug 12, 2016) o o ...
13. Operating Systems
... Does not load instructions into main memory No user interface except for I/O routines provided with executing program Is idle when waiting for user input No facility to store, retrieve, or manipulate files No ability to control peripheral devices Can run only one program at a time Chapte ...
... Does not load instructions into main memory No user interface except for I/O routines provided with executing program Is idle when waiting for user input No facility to store, retrieve, or manipulate files No ability to control peripheral devices Can run only one program at a time Chapte ...
No Slide Title
... operating system kernel as though they were all hardware. • A virtual machine provides an interface identical to the underlying bare hardware. • The operating system creates the illusion of multiple processes, each executing on its own processor with its own (virtual) memory. ...
... operating system kernel as though they were all hardware. • A virtual machine provides an interface identical to the underlying bare hardware. • The operating system creates the illusion of multiple processes, each executing on its own processor with its own (virtual) memory. ...
Operating Systems CIS 250
... • Simple - interfaces and level of functionality are not well separated; limited by hardware – MS-DOS - no dual mode operation – original UNIX - two parts: kernel and system programs ...
... • Simple - interfaces and level of functionality are not well separated; limited by hardware – MS-DOS - no dual mode operation – original UNIX - two parts: kernel and system programs ...
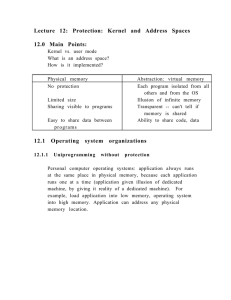
Lecture 12: Protection: Kernel and Address Spaces 12.0 Main Points
... spaces to share a region of memory, but that violates the whole notion of why we have address spaces -- to protect each program from bugs in the other programs. So why do UNIXes support shared memory? One reason is that it provides a cheap way to simulate threads on systems that don’t support them - ...
... spaces to share a region of memory, but that violates the whole notion of why we have address spaces -- to protect each program from bugs in the other programs. So why do UNIXes support shared memory? One reason is that it provides a cheap way to simulate threads on systems that don’t support them - ...
Lecture_01
... 1999 – Linux available for PowerPC (Apple) Now – adopted by many companies and most ...
... 1999 – Linux available for PowerPC (Apple) Now – adopted by many companies and most ...
Mid1_Revision
... • Define a monolithic kernel and compare it to a microkernel? • A monolithic kernel essentially is designed to have all the system services encapsulated in one module with a tight communication and sharing of structures between the individual OS components. As opposed to a microkernel which takes th ...
... • Define a monolithic kernel and compare it to a microkernel? • A monolithic kernel essentially is designed to have all the system services encapsulated in one module with a tight communication and sharing of structures between the individual OS components. As opposed to a microkernel which takes th ...
Background - The University of Alabama in Huntsville
... – processors share access to I/O devices – all processors can perform the same functions – the system is controlled by an integrated operating system that supports interaction between processors and their programs ...
... – processors share access to I/O devices – all processors can perform the same functions – the system is controlled by an integrated operating system that supports interaction between processors and their programs ...
Apple Rhapsody Installation Guide Developer Release 2
... 1998. Rhapsody was first demonstrated at the 1997 Worldwide Developer Conference (WWDC). There were two subsequent Developer Releases for computers with Intel x86 or PowerPC processors. The full version was intended for release in spring of 1998. At the 1998 MacWorld Expo in New York, Steve Jobs ann ...
... 1998. Rhapsody was first demonstrated at the 1997 Worldwide Developer Conference (WWDC). There were two subsequent Developer Releases for computers with Intel x86 or PowerPC processors. The full version was intended for release in spring of 1998. At the 1998 MacWorld Expo in New York, Steve Jobs ann ...
PDF
... Programmers don’t want to deal with paging their own code and data in and out of limited physical memory (and want protection/isolation from other processes) => virtual memory Programmers want running processes to be able to communicate (not complete protection and isolation) => shared memory region ...
... Programmers don’t want to deal with paging their own code and data in and out of limited physical memory (and want protection/isolation from other processes) => virtual memory Programmers want running processes to be able to communicate (not complete protection and isolation) => shared memory region ...
What is an operating system (OS)?
... Medium-term queue - programs that are partially executed, but have been swapped out of memory to disk Long-term queue - user has requested the a program be executed, but it has not yet been loaded into memory ...
... Medium-term queue - programs that are partially executed, but have been swapped out of memory to disk Long-term queue - user has requested the a program be executed, but it has not yet been loaded into memory ...
Fulltext PDF
... In a uniprogramming system, main memory is divided into two parts: one part for the operating system (resident monitor, kernel) and the other for the program currently being executed. In a multiprogrammed system, the 'user' part of memory must be further sub-divided to accommodate multiple processes ...
... In a uniprogramming system, main memory is divided into two parts: one part for the operating system (resident monitor, kernel) and the other for the program currently being executed. In a multiprogrammed system, the 'user' part of memory must be further sub-divided to accommodate multiple processes ...
Operating Systems I: Chapter 3
... – Main memory is a volatile storage device. It loses its contents in the case of system failure – It is a repository of quickly accessible data shared by the CPU and I/O devices For a program to be executed it must be mapped to absolute addresses and loaded into main memory – To improve CPU utilizat ...
... – Main memory is a volatile storage device. It loses its contents in the case of system failure – It is a repository of quickly accessible data shared by the CPU and I/O devices For a program to be executed it must be mapped to absolute addresses and loaded into main memory – To improve CPU utilizat ...
Presentation4
... • SCO Unix for PC became a lucrative business market • operating system provided security on a PC where DOS couldn’t… ...
... • SCO Unix for PC became a lucrative business market • operating system provided security on a PC where DOS couldn’t… ...
OS - Deyes High School
... In the world of programming these are known as events! It is why when you hit a key the letter appears in the right window. The OS is controlling where the message gets sent to! ...
... In the world of programming these are known as events! It is why when you hit a key the letter appears in the right window. The OS is controlling where the message gets sent to! ...
COS 318: Operating Systems OS Structures and System Calls Kai Li
... Pass by registers # of registers # of usable registers # of parameters in system call Spill/fill code in compiler ...
... Pass by registers # of registers # of usable registers # of parameters in system call Spill/fill code in compiler ...
CS111 Operating Systems Principles Introduction to Operating
... • Most CS discussions involve OS concepts • Many hard problems have been solved in OS ...
... • Most CS discussions involve OS concepts • Many hard problems have been solved in OS ...
OS Basics
... The kernel is a program that constitutes the central core of a computer operating system. It has complete control over everything that occurs in the system. It provides the very basic facilities for the management such as ...
... The kernel is a program that constitutes the central core of a computer operating system. It has complete control over everything that occurs in the system. It provides the very basic facilities for the management such as ...
Answer
... I/O that depends on secondary storage management is critical to the speed of many programs and hence I think it is best relegated to the operating systems to manage it than giving individual users the control of it. It is not difficult for the user-level programs to provide these services but for ab ...
... I/O that depends on secondary storage management is critical to the speed of many programs and hence I think it is best relegated to the operating systems to manage it than giving individual users the control of it. It is not difficult for the user-level programs to provide these services but for ab ...
Ch. 4 Operating System Fundamentals
... • Virtual memory is used to describe memory that is not what it appears to be. Hard disk drive space is manipulated to seem like RAM. • It is the basis of multitasking in Windows 9x. Without virtual memory, it would be almost impossible to run most of the software in use today. ...
... • Virtual memory is used to describe memory that is not what it appears to be. Hard disk drive space is manipulated to seem like RAM. • It is the basis of multitasking in Windows 9x. Without virtual memory, it would be almost impossible to run most of the software in use today. ...
Computer Hardware and Software Infrastructure Operating System
... The OS must prevent independent processes from interfering with each other’s memory, both data and instructions. ...
... The OS must prevent independent processes from interfering with each other’s memory, both data and instructions. ...
1: Welcome and Overview COM S 414
... code and data in and out of limited physical memory (and want protection/isolation from other processes) => virtual memory Programmers want running processes to be able to communicate (not complete protection and isolation) => shared memory regions, pipes, sockets, events Users don’t want a single t ...
... code and data in and out of limited physical memory (and want protection/isolation from other processes) => virtual memory Programmers want running processes to be able to communicate (not complete protection and isolation) => shared memory regions, pipes, sockets, events Users don’t want a single t ...