Some Background Concerning Life Science Content Standards for
... including many fungi, insects, and microorganisms, recycle matter from dead plants and animals.” “Plant and animal wastes, including their dead remains, provide food for decomposer organisms such as bacteria, insects, fungi, and earthworms. Decomposers are adept at breaking down and consuming waste ...
... including many fungi, insects, and microorganisms, recycle matter from dead plants and animals.” “Plant and animal wastes, including their dead remains, provide food for decomposer organisms such as bacteria, insects, fungi, and earthworms. Decomposers are adept at breaking down and consuming waste ...
Ecology Vocabulary Words
... 15. Energy Pyramid - A diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web 16. Exponential Growth- If a population has a constant birth rate through time and is never limited by food or disease. The birth rate alone controls how fast/slow the population ...
... 15. Energy Pyramid - A diagram that shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web 16. Exponential Growth- If a population has a constant birth rate through time and is never limited by food or disease. The birth rate alone controls how fast/slow the population ...
Ecology - Humble ISD
... Why must there be so many more individuals at lower trophic levels? Higher trophic levels have to eat more to get the same amount of energy due to the 10% rule. ...
... Why must there be so many more individuals at lower trophic levels? Higher trophic levels have to eat more to get the same amount of energy due to the 10% rule. ...
What`s the function of
... ____ 32. Scientists classify living things into three domains and six kingdoms. Which of the following best describes characteristics of the protist kingdom? A. may be plant-like, animal-like, or fungus-like B. do not make food from sunlight; feed on dead or decayed materials C. are vascular or nonv ...
... ____ 32. Scientists classify living things into three domains and six kingdoms. Which of the following best describes characteristics of the protist kingdom? A. may be plant-like, animal-like, or fungus-like B. do not make food from sunlight; feed on dead or decayed materials C. are vascular or nonv ...
Ch 2.5 Food Webs and Ecological Pyramids
... - Producers are found in the 1st. trophic level, herbivores (first order consumer) are found in the 2nd trophic level. Carnivores (second, third, fourth order consumers) are found in sequential trophic levels. - Food chains arte artificial and are not found in nature, but are used to simplify feedin ...
... - Producers are found in the 1st. trophic level, herbivores (first order consumer) are found in the 2nd trophic level. Carnivores (second, third, fourth order consumers) are found in sequential trophic levels. - Food chains arte artificial and are not found in nature, but are used to simplify feedin ...
What is ecology?
... What is Ecology?? • The study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environment. • It explains how living organisms affect each other and the world they live in. copyright cmassengale ...
... What is Ecology?? • The study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environment. • It explains how living organisms affect each other and the world they live in. copyright cmassengale ...
Lecture 3: Plankton, benthos, biomass assessment Plankton Live
... Lecture 4: Food and Feeding Habits of Fish Food habits and feeding ecology research are a fundamental tool to understand fish roles within their ecosystems since they indicate relationships based on feeding resources and indirectly indicate community energy flux (Yánez-Arancibia & Nugent 1977, Hajis ...
... Lecture 4: Food and Feeding Habits of Fish Food habits and feeding ecology research are a fundamental tool to understand fish roles within their ecosystems since they indicate relationships based on feeding resources and indirectly indicate community energy flux (Yánez-Arancibia & Nugent 1977, Hajis ...
Ecology and Food
... What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotrophy? An autotroph produces energy from natural abiotic sources, primarily sunlight. A heterotrophy gets its energy from other individuals through feeding. Why are top predators usually rare? Because energy is lost at each trophic level as yo ...
... What is the difference between an autotroph and a heterotrophy? An autotroph produces energy from natural abiotic sources, primarily sunlight. A heterotrophy gets its energy from other individuals through feeding. Why are top predators usually rare? Because energy is lost at each trophic level as yo ...
Food Chains Begin with Photosynthesis
... Unicellular algae: single celled photosynthetic organisms. Protist: general name for unicellular life. Enzymes: protein molecules that catalyze reactions such as the digestion of largeorganic molecules, breaking them down into their molecular building blocks. Phagocytosis: the engulfment for food pa ...
... Unicellular algae: single celled photosynthetic organisms. Protist: general name for unicellular life. Enzymes: protein molecules that catalyze reactions such as the digestion of largeorganic molecules, breaking them down into their molecular building blocks. Phagocytosis: the engulfment for food pa ...
September 2012 Ecology PowerPoint
... receives benefits from the other without affecting or damaging it. •Barnacles adhering to the skin of a whale or shell of a mollusk: barnacle is a mollusks that benefits by finding a habitat where nutrients are available. (In the case of lodging on the living organism, the barnacle is transported to ...
... receives benefits from the other without affecting or damaging it. •Barnacles adhering to the skin of a whale or shell of a mollusk: barnacle is a mollusks that benefits by finding a habitat where nutrients are available. (In the case of lodging on the living organism, the barnacle is transported to ...
Unit 8 -Ecology Populations, Communities, Ecosystems, and Biomes
... Remember: Because of ___________ ____________ every organism has a variety of __________________ that are suited to it’s specific living conditions. The role of an organism in it’s habitat is called its _________________. (what it eats, how it gets the food, what eats it, how and when it reproduces, ...
... Remember: Because of ___________ ____________ every organism has a variety of __________________ that are suited to it’s specific living conditions. The role of an organism in it’s habitat is called its _________________. (what it eats, how it gets the food, what eats it, how and when it reproduces, ...
Food Web Construction and Manipulation
... Take out pictures representing the animals in the food web 1. Trophic Levels Through a Energy Pyramid: Using the third set of pictures, create a food pyramid with the animals. Remember to place all producers in the bottom level. On the next level, place primary consumers (eat only producers). On th ...
... Take out pictures representing the animals in the food web 1. Trophic Levels Through a Energy Pyramid: Using the third set of pictures, create a food pyramid with the animals. Remember to place all producers in the bottom level. On the next level, place primary consumers (eat only producers). On th ...
Within each ecosystem, there are habitats which may also vary in size
... Species are the different kinds of organisms found on the Earth. A more exact definition of species is a group of interbreeding organisms that do not ordinarily breed with members of other groups. If a species interbreeds freely with other species, it would no longer be a distinctive kind of organis ...
... Species are the different kinds of organisms found on the Earth. A more exact definition of species is a group of interbreeding organisms that do not ordinarily breed with members of other groups. If a species interbreeds freely with other species, it would no longer be a distinctive kind of organis ...
1 Study Questions Ch.16, sec. 1 1. Which word in the
... the previous trophic level they only get 10% of the energy that was eaten by that organism. 5. Some animals such as humans can switch trophic levels depending on what they eat. 6. Plants - Fish - Raccoon - alligator – human 7. Food chain is one single pathway through a food web. ...
... the previous trophic level they only get 10% of the energy that was eaten by that organism. 5. Some animals such as humans can switch trophic levels depending on what they eat. 6. Plants - Fish - Raccoon - alligator – human 7. Food chain is one single pathway through a food web. ...
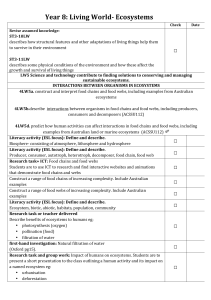
Year 8: Living World-‐ Ecosystems
... Research task or teacher delivered Compare energy usage of Australia and other countries Numeracy and ICT: Ecological footprint (Oxford pg37) Determine students’ ecological footprint using available online calculator ...
... Research task or teacher delivered Compare energy usage of Australia and other countries Numeracy and ICT: Ecological footprint (Oxford pg37) Determine students’ ecological footprint using available online calculator ...
Species
... ◦ Assortment, or variety, of living things in an ecosystem High area of biodiversity = rainforests Rainforest covers less than 7% of Earth’s surface but accounts for over 50% of planet’s plant and animal species Rainforests are considered hot spots (area that is rich in biodiversity) ...
... ◦ Assortment, or variety, of living things in an ecosystem High area of biodiversity = rainforests Rainforest covers less than 7% of Earth’s surface but accounts for over 50% of planet’s plant and animal species Rainforests are considered hot spots (area that is rich in biodiversity) ...
Organ
... increases the number of different species that can live in an ecosystem. Predators limit the size of prey populations. As a result, food and other resources are less likely to become scarce, and competition between species is reduced. ...
... increases the number of different species that can live in an ecosystem. Predators limit the size of prey populations. As a result, food and other resources are less likely to become scarce, and competition between species is reduced. ...
What to Say - Chapman University
... Disease Control and Prevention and the US Department of Agriculture have also endorsed the safety of irradiated food ...
... Disease Control and Prevention and the US Department of Agriculture have also endorsed the safety of irradiated food ...
Food Security with Sovereignty in the Americas
... regional and international agencies working in the region to promote cooperation mechanisms and programs that support this effort. ...
... regional and international agencies working in the region to promote cooperation mechanisms and programs that support this effort. ...
2016-2017 STUDY GUIDE ECOLOGY W ANSWERS
... 47. Populations can be reduced through density dependent factors. Which of the following does not depend on the density of a population? a. flooding b. competition c. predation d. parasites and disease 48. Which of the following are density dependent factors? (more than 1 answer) a. flooding ...
... 47. Populations can be reduced through density dependent factors. Which of the following does not depend on the density of a population? a. flooding b. competition c. predation d. parasites and disease 48. Which of the following are density dependent factors? (more than 1 answer) a. flooding ...
ATLAST Flow of Matter and Energy in Living Systems Benchmark
... comes from another source. Plants (or other living organisms) take in and use some substances, and produce others. These are separate events – substances taken in are not raw materials for the products. Food is anything that goes into an organism – CO2, water, sunlight, oxygen, etc. Food is what is ...
... comes from another source. Plants (or other living organisms) take in and use some substances, and produce others. These are separate events – substances taken in are not raw materials for the products. Food is anything that goes into an organism – CO2, water, sunlight, oxygen, etc. Food is what is ...
File - Mr. Derrick Baker
... around the earth 10-30 North and South of the equator. Cacti are well adapted to lack of water. They are often referred to as Xerophytes. ...
... around the earth 10-30 North and South of the equator. Cacti are well adapted to lack of water. They are often referred to as Xerophytes. ...
Ecology ppt
... 78%-80% of air. Organisms can not use it in that form. Lightning and bacteria convert nitrogen into ...
... 78%-80% of air. Organisms can not use it in that form. Lightning and bacteria convert nitrogen into ...
STUDY GUIDE
... Population: A group of similar life forms in an area. (Ex- Herd of zebras.) Community: Groups of populations that interact with each other. (Ex.zebras, trees, lions, rabbits, grass) Ecosystem: Communities & their abiotic surroundings. (Desert: owls, rain, cacti, scorpions, sunlight) Biosphere: All t ...
... Population: A group of similar life forms in an area. (Ex- Herd of zebras.) Community: Groups of populations that interact with each other. (Ex.zebras, trees, lions, rabbits, grass) Ecosystem: Communities & their abiotic surroundings. (Desert: owls, rain, cacti, scorpions, sunlight) Biosphere: All t ...
Local food

Local food or the local food movement is a movement which aims to connect food producers and food consumers in the same geographic region; in order to develop more self-reliant and resilient food networks, improve local economies, or for health, environmental, community, or social impact in a particular place. The term has also been extended to include not only geographic location of supplier and consumer but can also be ""defined in terms of social and supply chain characteristics."" For example, local food initiatives often promote sustainable and organic farming practices, although these are not explicitly related to the geographic proximity of the producer and consumer.Local food represents an alternative to the global food model, a model which often sees food travelling long distances before it reaches the consumer. A local food network involves relationships between food producers, distributors, retailers, and consumers in a particular place where they work together to increase food security and ensure economic, ecological and social sustainability of a community