1 Life processes
... Food wheels and food pyramids Scientists around the world study food and do experiments to learn what types of food are healthier. They write about their investigations in scientific magazines. However, they use very difficult words so their texts are very hard to understand! Fortunately, health exp ...
... Food wheels and food pyramids Scientists around the world study food and do experiments to learn what types of food are healthier. They write about their investigations in scientific magazines. However, they use very difficult words so their texts are very hard to understand! Fortunately, health exp ...
No Such Thing as a Free Lunch
... Links project: encourages community development and brings together individuals and communities in partnership with food producers to increase access to fresh local produce enabling long-term social, environmental, health and economic benefits. ...
... Links project: encourages community development and brings together individuals and communities in partnership with food producers to increase access to fresh local produce enabling long-term social, environmental, health and economic benefits. ...
good food hygiene
... PROTECTION of food from risk of contamination by bacteria, poisons, viruses & foreign bodies. PREVENTION of bacteria present in food multiplying to numbers that would result in illness of people or result in premature spoilage of food. DESTROYING any harmful bacteria in the food by proper cooking ...
... PROTECTION of food from risk of contamination by bacteria, poisons, viruses & foreign bodies. PREVENTION of bacteria present in food multiplying to numbers that would result in illness of people or result in premature spoilage of food. DESTROYING any harmful bacteria in the food by proper cooking ...
Food Webbing - School Webmasters
... What are “wetlands”? Two main types of wetlands are marshes and swamps. Explain the difference between a marsh and a swamp. List and Explain 3 ecological functions that wetlands provide. A subtype of wetlands, can be Mangroves. Explain 2 ecological functions that Mangrove trees/forests provide. What ...
... What are “wetlands”? Two main types of wetlands are marshes and swamps. Explain the difference between a marsh and a swamp. List and Explain 3 ecological functions that wetlands provide. A subtype of wetlands, can be Mangroves. Explain 2 ecological functions that Mangrove trees/forests provide. What ...
Environmental-Science-Jeopardy
... protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
... protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
Environmental Science Jeopardy
... protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
... protect the tree from potential predators. The tree has learned to produce this food and ants learned how to protect the tree over a long period of time. What kind of relationship is this? ...
Principles of Ecology
... 4. Synthesize Why might an ecologist use a food chain for one study and a food web for another study? ...
... 4. Synthesize Why might an ecologist use a food chain for one study and a food web for another study? ...
A. Food webs
... What are the two components of nutrient use efficiency? How do they relate to the basic principle of environmental control and plant responses to nutrient limitation discussed in Chap. 5 (e.g., SLA, photosynthetic capacity)? Under which environmental conditions is it most competitively advantageous ...
... What are the two components of nutrient use efficiency? How do they relate to the basic principle of environmental control and plant responses to nutrient limitation discussed in Chap. 5 (e.g., SLA, photosynthetic capacity)? Under which environmental conditions is it most competitively advantageous ...
Bio101 Topic 10
... • Pyramid of production shows loss of energy from producers to higher trophic levels. • Amount of energy available to top-level consumers is relatively small. • Most food chains have only three to five levels. ...
... • Pyramid of production shows loss of energy from producers to higher trophic levels. • Amount of energy available to top-level consumers is relatively small. • Most food chains have only three to five levels. ...
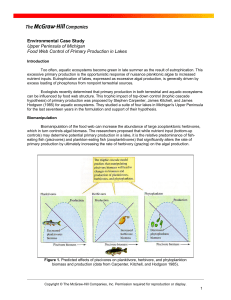
Food Web Control of Primary Production in Lakes
... Carpenter and associates further tested the hypothesis by directly fertilizing lakes (bottom-up controls) that had contrasting food webs. Algal biomass accumulated in one of their study lakes with an abundance of zooplantivorous fishes and small species of zooplankton grazers. In another study lake ...
... Carpenter and associates further tested the hypothesis by directly fertilizing lakes (bottom-up controls) that had contrasting food webs. Algal biomass accumulated in one of their study lakes with an abundance of zooplantivorous fishes and small species of zooplankton grazers. In another study lake ...
Community_Ecology - Svetz-wiki
... next is called a food chain • A food chain is simplified • Only one organism at each level are ...
... next is called a food chain • A food chain is simplified • Only one organism at each level are ...
FOOD WEB
... • A group of organisms that can use the energy in sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into Glucose (food) • Autotrophs are also called Producers because they produce all of the food that heterotrophs use • Without autotrophs, there would be no life on this planet • Ex. Plants and Algae ...
... • A group of organisms that can use the energy in sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into Glucose (food) • Autotrophs are also called Producers because they produce all of the food that heterotrophs use • Without autotrophs, there would be no life on this planet • Ex. Plants and Algae ...
Ecology ppt - Madison County Schools
... and their environments, focusing on energy transfer • It is a science of relationships. ...
... and their environments, focusing on energy transfer • It is a science of relationships. ...
BIOLOGY IGCSE Revision Checklists Form 3 2017-2018
... • Explain reasons for conservation programmes, to include: – reducing extinction ...
... • Explain reasons for conservation programmes, to include: – reducing extinction ...
Prentice Hall Biology
... The lowest trophic level of the pyramid represents the producers and contains the most energy. The second level represents the primary consumers. A 90% decrease in useable energy The third level or secondary consumers will have 10% of the energy from the level below to ...
... The lowest trophic level of the pyramid represents the producers and contains the most energy. The second level represents the primary consumers. A 90% decrease in useable energy The third level or secondary consumers will have 10% of the energy from the level below to ...
ecology final ppt - Harrison High School
... • Abiotic factors- nonliving parts of the environment ...
... • Abiotic factors- nonliving parts of the environment ...
Food for Thought - Chicago Botanic Garden
... http://www.pbs.org/wnet/nature/episodes/arctic-bears/the-melting-arctics-impact-on-itsecosystem/780/. If you have individual paper copies of the article for each student, have them circle the name of each organism that they read, ask them to begin to picture the food web of interacting arctic organi ...
... http://www.pbs.org/wnet/nature/episodes/arctic-bears/the-melting-arctics-impact-on-itsecosystem/780/. If you have individual paper copies of the article for each student, have them circle the name of each organism that they read, ask them to begin to picture the food web of interacting arctic organi ...
Ecology - Fort Bend ISD
... The Flow of Energy • Producers - Plants capture the sun’s energy and store it in food • Primary Consumers (herbivores) - Animals that receive their energy directly from plants • Secondary Consumers (carnivores) Consumers that feed on primary consumers • Energy flows from the sun to the producer, th ...
... The Flow of Energy • Producers - Plants capture the sun’s energy and store it in food • Primary Consumers (herbivores) - Animals that receive their energy directly from plants • Secondary Consumers (carnivores) Consumers that feed on primary consumers • Energy flows from the sun to the producer, th ...
Ecosystems and Food Webs
... fungi decompose them, releasing these and other nutrients (phosphorous, nitrogen, and sulfur) into the soil, water, and air. These nutrients are available to plants again, which use them to convert the sun’s energy into carbohydrates. Decomposers are often referred to as nutrient recyclers because ...
... fungi decompose them, releasing these and other nutrients (phosphorous, nitrogen, and sulfur) into the soil, water, and air. These nutrients are available to plants again, which use them to convert the sun’s energy into carbohydrates. Decomposers are often referred to as nutrient recyclers because ...
Community Ecology
... of predators or competitors varies along a gradient of primary productivity. In unproductive habitats herbivores are rare because there is not enough forage to support them. At the highest productivity there will only be few herbivores because herbivores are limited by predators. At intermediate pro ...
... of predators or competitors varies along a gradient of primary productivity. In unproductive habitats herbivores are rare because there is not enough forage to support them. At the highest productivity there will only be few herbivores because herbivores are limited by predators. At intermediate pro ...
Ecosystems and Food Webs
... fungi decompose them, releasing these and other nutrients (phosphorous, nitrogen, and sulfur) into the soil, water, and air. These nutrients are available to plants again, which use them to convert the sun’s energy into carbohydrates. Decomposers are often referred to as nutrient recyclers because ...
... fungi decompose them, releasing these and other nutrients (phosphorous, nitrogen, and sulfur) into the soil, water, and air. These nutrients are available to plants again, which use them to convert the sun’s energy into carbohydrates. Decomposers are often referred to as nutrient recyclers because ...
Food Additive
... Sometimes a 1000 safety factor depending on the nature of toxic effects noted and quality of available toxicity data The dietary intake of an additive which can be safely ingested over a lifetime without appreciable risk from the known information ...
... Sometimes a 1000 safety factor depending on the nature of toxic effects noted and quality of available toxicity data The dietary intake of an additive which can be safely ingested over a lifetime without appreciable risk from the known information ...
Local food

Local food or the local food movement is a movement which aims to connect food producers and food consumers in the same geographic region; in order to develop more self-reliant and resilient food networks, improve local economies, or for health, environmental, community, or social impact in a particular place. The term has also been extended to include not only geographic location of supplier and consumer but can also be ""defined in terms of social and supply chain characteristics."" For example, local food initiatives often promote sustainable and organic farming practices, although these are not explicitly related to the geographic proximity of the producer and consumer.Local food represents an alternative to the global food model, a model which often sees food travelling long distances before it reaches the consumer. A local food network involves relationships between food producers, distributors, retailers, and consumers in a particular place where they work together to increase food security and ensure economic, ecological and social sustainability of a community