Chapter 2 Knowing the Heavens
... meridian transits of the Sun IF it moved at a constant rate (exactly 24 hrs). • Sidereal time: the interval of time between two successive meridian transits of a star (23 hrs 56 min). ...
... meridian transits of the Sun IF it moved at a constant rate (exactly 24 hrs). • Sidereal time: the interval of time between two successive meridian transits of a star (23 hrs 56 min). ...
The Milky Way
... Copernicus’ New (and Correct) Explanation for the Retrograde Motion of the Planets ...
... Copernicus’ New (and Correct) Explanation for the Retrograde Motion of the Planets ...
Chapter03
... issue is whether Egyptian science contributed to Greek science or whether it was primarily devoted to engineering applications. 3. Early Greek Astronomy The timeline in this section is important to combat the notion that the Greek astronomers were all contemporaries of one another. Many historians o ...
... issue is whether Egyptian science contributed to Greek science or whether it was primarily devoted to engineering applications. 3. Early Greek Astronomy The timeline in this section is important to combat the notion that the Greek astronomers were all contemporaries of one another. Many historians o ...
NOVA COLLEGE-WIDE COURSE CONTENT SUMMARY PHY 150
... Describe how electromagnetic radiation is produced and utilized by astronomers to understand phenomena that lie at remote distances from the Earth and how studying greater distances correlates to a view of the universe further back in time Describe how studying exotic forms of life on Earth may assi ...
... Describe how electromagnetic radiation is produced and utilized by astronomers to understand phenomena that lie at remote distances from the Earth and how studying greater distances correlates to a view of the universe further back in time Describe how studying exotic forms of life on Earth may assi ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... Into what colors is sunlight dispersed when passed through a prism? In what way are colors of stars used to indicate their temperature? ...
... Into what colors is sunlight dispersed when passed through a prism? In what way are colors of stars used to indicate their temperature? ...
Astronomy and Humanism by Ray Thompson A. EARLY
... other galaxies and that the sun was certainly a star in the Milky Way galaxy. He was also interested in pairs of stars that were close together and verified that, in many cases, they were actually orbitting one-another and were indeed double star systems. Finally his crowning achievement was the dis ...
... other galaxies and that the sun was certainly a star in the Milky Way galaxy. He was also interested in pairs of stars that were close together and verified that, in many cases, they were actually orbitting one-another and were indeed double star systems. Finally his crowning achievement was the dis ...
February 2012
... along the sequence of the Zodiac. However, as the Earth moves around the Sun, our view of planets occasionally makes them appear to reverse their motion. Mars will have appeared to stop moving on January 24th, and a backing up motion will proceed until mid-April. Careful observers can use Regulus, t ...
... along the sequence of the Zodiac. However, as the Earth moves around the Sun, our view of planets occasionally makes them appear to reverse their motion. Mars will have appeared to stop moving on January 24th, and a backing up motion will proceed until mid-April. Careful observers can use Regulus, t ...
AST 220 Introduction to Astronomy
... Students are expected to attend all classes for which they are registered. Students who are unable to attend class regularly, regardless of the reason or circumstance, should withdraw from that class before poor attendance interferes with the student’s ability to achieve the objectives required in t ...
... Students are expected to attend all classes for which they are registered. Students who are unable to attend class regularly, regardless of the reason or circumstance, should withdraw from that class before poor attendance interferes with the student’s ability to achieve the objectives required in t ...
Seasonal Motion
... – Study variation of the rising/setting points of the sun over time – Need at least 10 sunrises or sunsets; more is better – Measure time and azimuth (angle relative to North) – Note position of sunrise/sunset on horizon – Measure angle to that position relative to some fixed landmark (mountain, etc ...
... – Study variation of the rising/setting points of the sun over time – Need at least 10 sunrises or sunsets; more is better – Measure time and azimuth (angle relative to North) – Note position of sunrise/sunset on horizon – Measure angle to that position relative to some fixed landmark (mountain, etc ...
Ancient astronomy Part 6
... records of phenomena like supernovae and comets are still used in modern astronomy. Their interest in ‘guest stars’ which suddenly appeared among the fixed stars led them to their most famous observation, the 1054 supernova which created the Crab Nebula. Chinese records identify that it remained vi ...
... records of phenomena like supernovae and comets are still used in modern astronomy. Their interest in ‘guest stars’ which suddenly appeared among the fixed stars led them to their most famous observation, the 1054 supernova which created the Crab Nebula. Chinese records identify that it remained vi ...
Astronomy, Mr - Mentor Public Schools
... Why study astronomy? Is astrology related to astronomy? The Early Astronomers Backyard Astronomy #1--Constellations Astronomy during the middle ages—the rise of science. Science, Technology and Society-- Copernicus, Brahe, Kepler, Galileo Newton--Gravity, Laws of motion The electromagnetic spectrum ...
... Why study astronomy? Is astrology related to astronomy? The Early Astronomers Backyard Astronomy #1--Constellations Astronomy during the middle ages—the rise of science. Science, Technology and Society-- Copernicus, Brahe, Kepler, Galileo Newton--Gravity, Laws of motion The electromagnetic spectrum ...
Topic 9/10
... Nuclear fusion- where the sun gets its energy, 2 hydrogens fuse (combine) to form a helium Sunspots- temporary storms on the visible surface of the sun Galaxy- large body of stars and matter in space, there are over 100 billion galaxies with an average of 100 billion stars in each Red-shift- evidenc ...
... Nuclear fusion- where the sun gets its energy, 2 hydrogens fuse (combine) to form a helium Sunspots- temporary storms on the visible surface of the sun Galaxy- large body of stars and matter in space, there are over 100 billion galaxies with an average of 100 billion stars in each Red-shift- evidenc ...
Presentation 2
... Question: What causes the observed circular motions of the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets about the celestial pole? • Hypothesis 1: The Earth is stationary, and the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets revolve around it. • Hypothesis 2: The stars, Sun, Moon, and planets are not revolving about the Earth; i ...
... Question: What causes the observed circular motions of the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets about the celestial pole? • Hypothesis 1: The Earth is stationary, and the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets revolve around it. • Hypothesis 2: The stars, Sun, Moon, and planets are not revolving about the Earth; i ...
Seasonal Motion
... Earth axis is tilted w.r.t. ecliptic by 23 ½ degrees Equivalent: ecliptic is tilted by 23 ½ degrees w.r.t. equator! Sun appears to be sometime above (e.g. summer solstice), sometimes below, and sometimes on the celestial equator ...
... Earth axis is tilted w.r.t. ecliptic by 23 ½ degrees Equivalent: ecliptic is tilted by 23 ½ degrees w.r.t. equator! Sun appears to be sometime above (e.g. summer solstice), sometimes below, and sometimes on the celestial equator ...
CelestialSphere
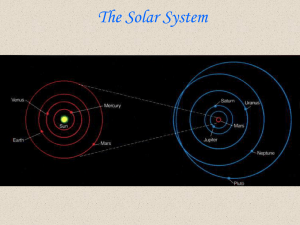
... against the stars. This is due to the fact that the Earth moves around the Sun faster than they do, causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. T ...
... against the stars. This is due to the fact that the Earth moves around the Sun faster than they do, causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. T ...
CelestialSphere02
... against the stars. This is due to the fact that the Earth moves around the Sun faster than they do, causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. T ...
... against the stars. This is due to the fact that the Earth moves around the Sun faster than they do, causing us to overtake them periodically, during which time they appear to move “backwards” in the sky. This caused a lot of headaches for those trying to explain the apparent motion of the planets. T ...
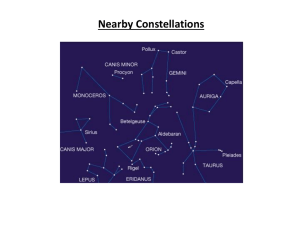
Nearby Constellations
... “Precession” of Earth’s Axis, and the temporary nature of the “North Star” . . . ...
... “Precession” of Earth’s Axis, and the temporary nature of the “North Star” . . . ...
friends of the planetarium newsletter - june 2010
... As our exploration of the Solar System continues, the surprises just keep on coming. In a development that has transformed the appearance of the solar system's largest planet, one of Jupiter's two main cloud belts has completely disappeared. "This is a big event," says planetary scientist Glenn Ort ...
... As our exploration of the Solar System continues, the surprises just keep on coming. In a development that has transformed the appearance of the solar system's largest planet, one of Jupiter's two main cloud belts has completely disappeared. "This is a big event," says planetary scientist Glenn Ort ...
Astronomy 1001
... • Calendars are historically complicated – Egyptian calendar had 365 days, resulting in a shift of equinoxes by 1 day every 4 years – Julius Caesar introduced leap years in 50 BC – Equinoxes still shifting over periods of centuries – Pope Gregory XIII modified the leap years to account for this ...
... • Calendars are historically complicated – Egyptian calendar had 365 days, resulting in a shift of equinoxes by 1 day every 4 years – Julius Caesar introduced leap years in 50 BC – Equinoxes still shifting over periods of centuries – Pope Gregory XIII modified the leap years to account for this ...
PowerPoint on Brief History of Astronomy
... America too where temples were built by the Mayan and Aztec empires. These were often aligned with the rising of a solstice Sun or other significant positions, such as points where the planet Venus rose and set. ...
... America too where temples were built by the Mayan and Aztec empires. These were often aligned with the rising of a solstice Sun or other significant positions, such as points where the planet Venus rose and set. ...
Archaeoastronomy

Archaeoastronomy (also spelled archeoastronomy) is the study of how people in the past ""have understood the phenomena in the sky, how they used these phenomena and what role the sky played in their cultures."" Clive Ruggles argues it is misleading to consider archaeoastronomy to be the study of ancient astronomy, as modern astronomy is a scientific discipline, while archaeoastronomy considers symbolically rich cultural interpretations of phenomena in the sky by other cultures. It is often twinned with ethnoastronomy, the anthropological study of skywatching in contemporary societies. Archaeoastronomy is also closely associated with historical astronomy, the use of historical records of heavenly events to answer astronomical problems and the history of astronomy, which uses written records to evaluate past astronomical practice.Archaeoastronomy uses a variety of methods to uncover evidence of past practices including archaeology, anthropology, astronomy, statistics and probability, and history. Because these methods are diverse and use data from such different sources, integrating them into a coherent argument has been a long-term difficulty for archaeoastronomers. Archaeoastronomy fills complementary niches in landscape archaeology and cognitive archaeology. Material evidence and its connection to the sky can reveal how a wider landscape can be integrated into beliefs about the cycles of nature, such as Mayan astronomy and its relationship with agriculture. Other examples which have brought together ideas of cognition and landscape include studies of the cosmic order embedded in the roads of settlements.Archaeoastronomy can be applied to all cultures and all time periods. The meanings of the sky vary from culture to culture; nevertheless there are scientific methods which can be applied across cultures when examining ancient beliefs. It is perhaps the need to balance the social and scientific aspects of archaeoastronomy which led Clive Ruggles to describe it as: ""...[A] field with academic work of high quality at one end but uncontrolled speculation bordering on lunacy at the other.""