Unit 2 : Astronomy A. Earth`s motion 1. rotation – turning or spinning
... 2. Earth’s axis maintains the same angle of tilt, but the direction of the axis points changes slightly over a long period of time 3. Currently the Earth is pointing to the star Polaris but eventually it will point to ...
... 2. Earth’s axis maintains the same angle of tilt, but the direction of the axis points changes slightly over a long period of time 3. Currently the Earth is pointing to the star Polaris but eventually it will point to ...
Physical Science Lecture Notes
... 1. Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five “stars” that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars. They called them Wander Stars “planets”. 2. “Wandering Stars” were: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn 3. Greek Astronomer Ptolemy (pronounced “tall-o ...
... 1. Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five “stars” that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars. They called them Wander Stars “planets”. 2. “Wandering Stars” were: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn 3. Greek Astronomer Ptolemy (pronounced “tall-o ...
How much do we make
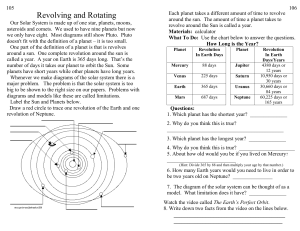
... doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet is that is revolves around a sun. One complete revolution around the sun is called a year. A year on Earth is 365 days long. That’s the number of days it takes our planet to orbit the Sun. Some plan ...
... doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet is that is revolves around a sun. One complete revolution around the sun is called a year. A year on Earth is 365 days long. That’s the number of days it takes our planet to orbit the Sun. Some plan ...
Revolving and Rotating
... doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet is that is revolves around a sun. One complete revolution around the sun is called a year. A year on Earth is 365 days long. That’s the number of days it takes our planet to orbit the Sun. Some plan ...
... doesn't fit with the definition of a planet – it is too small. One part of the definition of a planet is that is revolves around a sun. One complete revolution around the sun is called a year. A year on Earth is 365 days long. That’s the number of days it takes our planet to orbit the Sun. Some plan ...
Summary of Objectives for Test 1
... In one hour, the Moon, Sun, and stars move about how many degrees on the sky? How can you easily calculate that number (hint: how far does the Earth rotate in 24 hours)? ...
... In one hour, the Moon, Sun, and stars move about how many degrees on the sky? How can you easily calculate that number (hint: how far does the Earth rotate in 24 hours)? ...
Questionnaire Answers After students have completed the
... The Sun turns off at night. FALSE. We can’t see the Sun at night, but it does not turn off. Earth is always rotating on its axis, so the Sun appears to move across the sky. At sunrise, the Earth’s rotation brings our homes into sunlight. By midday, the Earth has rotated so the Sun is high in the sky ...
... The Sun turns off at night. FALSE. We can’t see the Sun at night, but it does not turn off. Earth is always rotating on its axis, so the Sun appears to move across the sky. At sunrise, the Earth’s rotation brings our homes into sunlight. By midday, the Earth has rotated so the Sun is high in the sky ...
doc - UWM
... The Sun turns off at night. FALSE. We can’t see the Sun at night, but it does not turn off. Earth is always rotating on its axis, so the Sun appears to move across the sky. At sunrise, the Earth’s rotation brings our homes into sunlight. By midday, the Earth has rotated so the Sun is high in the sky ...
... The Sun turns off at night. FALSE. We can’t see the Sun at night, but it does not turn off. Earth is always rotating on its axis, so the Sun appears to move across the sky. At sunrise, the Earth’s rotation brings our homes into sunlight. By midday, the Earth has rotated so the Sun is high in the sky ...
1.1 Organization of the Universe
... 2.What was the theory proposed before the heliocentric model? What did this theory state? ...
... 2.What was the theory proposed before the heliocentric model? What did this theory state? ...
File
... objects and phenomena that exist outside of the Earth’s atmosphere. The movements of the sun, the Earth, and stars are tracked, recorded, and continuously observed by scientists. Giant telescopes and various space missions allow us to keep track of what is going on in our galaxy, and to monitor the ...
... objects and phenomena that exist outside of the Earth’s atmosphere. The movements of the sun, the Earth, and stars are tracked, recorded, and continuously observed by scientists. Giant telescopes and various space missions allow us to keep track of what is going on in our galaxy, and to monitor the ...
Seasons and the Changing Sky
... • Rising and setting of Sun, Moon, stars as viewed from Earth → Rotating celestial sphere • Celestial poles: the points around which the stars appear to rotate • Celestial equator: an extension of the Earth’s equator onto the celestial sphere Circumpolar star! ...
... • Rising and setting of Sun, Moon, stars as viewed from Earth → Rotating celestial sphere • Celestial poles: the points around which the stars appear to rotate • Celestial equator: an extension of the Earth’s equator onto the celestial sphere Circumpolar star! ...
1 Chapter 1 1-1. How long does it take the Earth to orbit the Sun? a
... 1-13. What type of motion leads to the Sun rising and setting? a.) Earth’s rotation X b.) Earth’s revolution c.) The Sun’s revolution d.) The Sun’s rotation 1-14. What type of motion leads to stars rising approximately 4 minutes earlier each day than it did the day before? a.) Earth’s rotation b.) E ...
... 1-13. What type of motion leads to the Sun rising and setting? a.) Earth’s rotation X b.) Earth’s revolution c.) The Sun’s revolution d.) The Sun’s rotation 1-14. What type of motion leads to stars rising approximately 4 minutes earlier each day than it did the day before? a.) Earth’s rotation b.) E ...
Word doc - UC
... in front of) their host star as seen from Earth. (For comparison, if Earth transited the Sun as viewed another star system exactly in the plane of Earth’s orbit, the Sun’s light would be dimmed by 100 parts per million—a hundredth of a percent—for about 12 hours once every 365 days.) Although Kepler ...
... in front of) their host star as seen from Earth. (For comparison, if Earth transited the Sun as viewed another star system exactly in the plane of Earth’s orbit, the Sun’s light would be dimmed by 100 parts per million—a hundredth of a percent—for about 12 hours once every 365 days.) Although Kepler ...
Inferior planets.
... Newton’s greatest triumph- the discovery of Neptune • Herschel- discovered Uranus by accident on March 13, 1781. By 1790 it was realized that its orbit was not as expected. Conclusion: another unknown planet was “perturbing” its motion. • 1845- Adams calculated a position for the unknown planet and ...
... Newton’s greatest triumph- the discovery of Neptune • Herschel- discovered Uranus by accident on March 13, 1781. By 1790 it was realized that its orbit was not as expected. Conclusion: another unknown planet was “perturbing” its motion. • 1845- Adams calculated a position for the unknown planet and ...
Core Theme 3: The Solar System
... astronomers placed the Earth in the center of their models of the universe. They thought, if the heavens are divine, and the gods created man, well then certainly the universe must be geocentric, meaning the Earth is the center of the universe. ...
... astronomers placed the Earth in the center of their models of the universe. They thought, if the heavens are divine, and the gods created man, well then certainly the universe must be geocentric, meaning the Earth is the center of the universe. ...
5.1-The process of Science - Homework
... • The duration of one rotation of the Earth, or occassionally another celestial body, on its axis. Its is measured by successive transits of a reference point on the celestial sphere over the meridian, and each type takes its name from the reference used… www.reson.com/Gloss-d.htm • 1. A basic time ...
... • The duration of one rotation of the Earth, or occassionally another celestial body, on its axis. Its is measured by successive transits of a reference point on the celestial sphere over the meridian, and each type takes its name from the reference used… www.reson.com/Gloss-d.htm • 1. A basic time ...
1 Introduction - Numerical Recipes
... so the Universe near us and physics near us are typical of contemporaneous parts of the Universe | unless, of course, we nd factual evidence to the contrary (and this should be, in each such case, only by rare good or bad luck.) When does astronomy turn into astrophysics? No hard-and-fast line, but ...
... so the Universe near us and physics near us are typical of contemporaneous parts of the Universe | unless, of course, we nd factual evidence to the contrary (and this should be, in each such case, only by rare good or bad luck.) When does astronomy turn into astrophysics? No hard-and-fast line, but ...
BROCK UNIVERSITY Return both the exam script
... model of the solar system, which allowed him to determine the relative distances of the planets from the Sun. (a) heliocentric (b) geocentric (c) celestial sphere (d) epicycle ...
... model of the solar system, which allowed him to determine the relative distances of the planets from the Sun. (a) heliocentric (b) geocentric (c) celestial sphere (d) epicycle ...
origins of the Universe
... in the early 1900’s astronomers started to find evidence that pointed to a Big Bang. • In 1922, astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the universe was expanding. The most distant galaxies he could see through his telescope were moving away at about 40 000 km per second. • This observation led to wha ...
... in the early 1900’s astronomers started to find evidence that pointed to a Big Bang. • In 1922, astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the universe was expanding. The most distant galaxies he could see through his telescope were moving away at about 40 000 km per second. • This observation led to wha ...
ph512-10-lec5
... instantaneous motion with respect to some constant reference frame (say the Sun's motion), the displacement is δ θ = v sin θ /c. The amplitude of this annual aberration is 30 km/s × 206264.8 arcsec / c or 20 arcseconds in each direction. A given star then sweeps out an apparent ellipse of this semi- ...
... instantaneous motion with respect to some constant reference frame (say the Sun's motion), the displacement is δ θ = v sin θ /c. The amplitude of this annual aberration is 30 km/s × 206264.8 arcsec / c or 20 arcseconds in each direction. A given star then sweeps out an apparent ellipse of this semi- ...
Answers to Science Semester 1Review Possible hazards in the lab
... 32. Planets that have retrograde rotation are: Venus, Uranus, and Pluto. 33. Rotation is the spinning or turning about an axis. 34. Planet’s rotation tells us the length of day. 35. Revolution is the motion of a body orbiting another body in space. 36. Planet’s revolution tells us the length of the ...
... 32. Planets that have retrograde rotation are: Venus, Uranus, and Pluto. 33. Rotation is the spinning or turning about an axis. 34. Planet’s rotation tells us the length of day. 35. Revolution is the motion of a body orbiting another body in space. 36. Planet’s revolution tells us the length of the ...
Final Exam: Review Questions
... a. The earth is spherical b. The earth is revolving 12. What is the name given to the day when there are equal amounts of daylight and darkness on all parts of the planet. 13. Calculate the average distance to the sun of a planet in AUs if it takes 24 yrs to make one orbit. (Hint: p2 = a3) ...
... a. The earth is spherical b. The earth is revolving 12. What is the name given to the day when there are equal amounts of daylight and darkness on all parts of the planet. 13. Calculate the average distance to the sun of a planet in AUs if it takes 24 yrs to make one orbit. (Hint: p2 = a3) ...
5th Grade Astronomy Test Study Guide
... Comets: a space object made of ice and dust that orbits a star and develops a long bright tail as it nears its star Gravity: the force that pulls all objects towards each other Gravitational Pull: when gravity attracts two objects together Seasons: a period of the year that has special climate condi ...
... Comets: a space object made of ice and dust that orbits a star and develops a long bright tail as it nears its star Gravity: the force that pulls all objects towards each other Gravitational Pull: when gravity attracts two objects together Seasons: a period of the year that has special climate condi ...
Copernican heliocentrism

Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. It positioned the Sun near the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets rotating around it in circular paths modified by epicycles and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model departed from the Ptolemaic system that prevailed in Western culture for centuries, placing Earth at the center of the Universe, and is often regarded as the launching point to modern astronomy and the Scientific Revolution.Copernicus was aware that the ancient Greek Aristarchus had already proposed a heliocentric theory, and cited him as a proponent of it in a reference that was deleted before publication, but there is no evidence that Copernicus had knowledge of, or access to, the specific details of Aristarchus' theory. Although he had circulated an outline of his own heliocentric theory to colleagues sometime before 1514, he did not decide to publish it until he was urged to do so late in his life by his pupil Rheticus. Copernicus's challenge was to present a practical alternative to the Ptolemaic model by more elegantly and accurately determining the length of a solar year while preserving the metaphysical implications of a mathematically ordered cosmos. Thus his heliocentric model retained several of the Ptolemaic elements causing the inaccuracies, such as the planets' circular orbits, epicycles, and uniform speeds, while at the same time re-introducing such innovations as,Earth is one of several planets revolving around a stationary Sun in a determined orderEarth has three motions: daily rotation, annual revolution, and annual tilting of its axisRetrograde motion of the planets is explained by Earth's motionDistance from Earth to the Sun is small compared to the distance to the stars.↑ 1.0 1.1 ↑