Retrograde Motion pre
... The planets orbit the Sun in a counterclockwise direction, as viewed from a point above the solar system. Why is it that a superior planet will proceed to eastern quadrature, and not western quadrature, following opposition? Retrograde Motion As the orbital velocity of the Earth is greater than that ...
... The planets orbit the Sun in a counterclockwise direction, as viewed from a point above the solar system. Why is it that a superior planet will proceed to eastern quadrature, and not western quadrature, following opposition? Retrograde Motion As the orbital velocity of the Earth is greater than that ...
Astronomy Curriculum
... elective, with elements of physics and mathematics, intended for those students who wish to further explore their interests in physical science. Students in astronomy will develop the skills to observe and record objects in the sky, aided by various elements of observational technology such as binoc ...
... elective, with elements of physics and mathematics, intended for those students who wish to further explore their interests in physical science. Students in astronomy will develop the skills to observe and record objects in the sky, aided by various elements of observational technology such as binoc ...
Gravity Kepler`s Laws - historical remarks - UW
... German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer, and key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution. He is best known for his eponymous laws of planetary motion, codified by later astronomers based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican Astronomy. They also p ...
... German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer, and key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution. He is best known for his eponymous laws of planetary motion, codified by later astronomers based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican Astronomy. They also p ...
Physics 20 Lesson 23 Orbits and Satellites
... At low speeds, a horizontal projectile will fall toward and hit the ground in a short time. As the speed of the horizontal projectile is increased, it will land further and further away from the starting point. For a flat Earth the projectile would always hit the ground; no matter how fast the proje ...
... At low speeds, a horizontal projectile will fall toward and hit the ground in a short time. As the speed of the horizontal projectile is increased, it will land further and further away from the starting point. For a flat Earth the projectile would always hit the ground; no matter how fast the proje ...
Introduction to Sun Motion
... which a steady light is needed; for that quarter of the sky grows neither light nor dark with the course of the sun, but remains steady and unshifting all day long. ...
... which a steady light is needed; for that quarter of the sky grows neither light nor dark with the course of the sun, but remains steady and unshifting all day long. ...
francesco ingoli`s essay to galileo: tycho brahe
... Omnipotence, would be vulnerable to the charge of being an absurd theory -- vulnerable not from a scriptural standpoint, but from a ...
... Omnipotence, would be vulnerable to the charge of being an absurd theory -- vulnerable not from a scriptural standpoint, but from a ...
Astronomy and Cosmology - spring 2003 - final exam
... 21. At what approximate time does a full moon rise? A) midnight B) sunrise C) noon D) sunset 22. Which of the following will never be seen from Earth as a crescent? A) Mercury B) Venus C) Mars D) Moon 23. The Moon rises later each day because each day it has moved farther along its orbit around Eart ...
... 21. At what approximate time does a full moon rise? A) midnight B) sunrise C) noon D) sunset 22. Which of the following will never be seen from Earth as a crescent? A) Mercury B) Venus C) Mars D) Moon 23. The Moon rises later each day because each day it has moved farther along its orbit around Eart ...
View SKYTRACK_Glossary of Terms
... In the case of an exterior planet (Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune), the Retrograde Motion is due to the parallax effect when the Earth catches up with, and passes the planet. In the case of an interior planet (Mercury and Venus), the Retrograde Motion is due to the parallax effect when b ...
... In the case of an exterior planet (Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune), the Retrograde Motion is due to the parallax effect when the Earth catches up with, and passes the planet. In the case of an interior planet (Mercury and Venus), the Retrograde Motion is due to the parallax effect when b ...
Stellar aberration
... linear speed. At this linear speed, no planetary body in solar system can orbit around sun but may orbit about sun. Planetary body moves with sun at median linear speed equal to sun’s linear speed. It moves in wavy path about sun, periodically moving to front and to rear of sun. Linear speed of eart ...
... linear speed. At this linear speed, no planetary body in solar system can orbit around sun but may orbit about sun. Planetary body moves with sun at median linear speed equal to sun’s linear speed. It moves in wavy path about sun, periodically moving to front and to rear of sun. Linear speed of eart ...
Physics 20 Concept 22 Orbits and Satellites
... At low speeds, a horizontal projectile will fall toward and hit the ground in a short time. As the speed of the horizontal projectile is increased, it will land further and further away from the starting point. For a flat Earth the projectile would always hit the ground; no matter how fast the proje ...
... At low speeds, a horizontal projectile will fall toward and hit the ground in a short time. As the speed of the horizontal projectile is increased, it will land further and further away from the starting point. For a flat Earth the projectile would always hit the ground; no matter how fast the proje ...
3. COMMENTS ON KEPLER`S NEW ASTRONOMY
... registered at intervals of about every 15 days, made the Sun appear in six different, but inverted positions, as in a mirror image, at points 1', 2', 3', 4', 5', 6', on the surface of the Celestial Sphere, EFGH. This gives the observer on Earth the impression that the sun moves from East to West, wh ...
... registered at intervals of about every 15 days, made the Sun appear in six different, but inverted positions, as in a mirror image, at points 1', 2', 3', 4', 5', 6', on the surface of the Celestial Sphere, EFGH. This gives the observer on Earth the impression that the sun moves from East to West, wh ...
03_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... D) the fine line between science and pseudoscience E) the shaving implement of a medieval scholar Answer: C 44) Which of the following statements about scientific theories is not true? A) A theory cannot be taken seriously by scientists if it contradicts other theories developed by scientists over t ...
... D) the fine line between science and pseudoscience E) the shaving implement of a medieval scholar Answer: C 44) Which of the following statements about scientific theories is not true? A) A theory cannot be taken seriously by scientists if it contradicts other theories developed by scientists over t ...
Looking Back in Time Space Flight to the Stars
... The next nearest star to Earth after the Sun is actually part of a group of three stars that orbit each other. This group is called the Centauri system (Figure 7.8). It lies about 4.3 ly away from the solar system. If it were possible for you to have a cellphone conversation with someone living near ...
... The next nearest star to Earth after the Sun is actually part of a group of three stars that orbit each other. This group is called the Centauri system (Figure 7.8). It lies about 4.3 ly away from the solar system. If it were possible for you to have a cellphone conversation with someone living near ...
SKYTRACK Glossary of Terms
... In the case of an exterior planet (Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune), the Retrograde Motion is due to the parallax effect when the Earth catches up with, and passes the planet. In the case of an interior planet (Mercury and Venus), the Retrograde Motion is due to the parallax effect when b ...
... In the case of an exterior planet (Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune), the Retrograde Motion is due to the parallax effect when the Earth catches up with, and passes the planet. In the case of an interior planet (Mercury and Venus), the Retrograde Motion is due to the parallax effect when b ...
PHYS103 Hour Exam No. 1 Page: 1 1 Which of the following
... 7 Einstein’s Theory of Gravity has passed every well-understood observational test for over 100 years. However there are some observations, which are not well-understood. For example, the Pioneer space probe is showing tiny deviations from its predicted course as it leaves the neighborhood of our so ...
... 7 Einstein’s Theory of Gravity has passed every well-understood observational test for over 100 years. However there are some observations, which are not well-understood. For example, the Pioneer space probe is showing tiny deviations from its predicted course as it leaves the neighborhood of our so ...
Newton*s Theory of Gravity and Planetary Motion
... • Ptolemy (Alexandrian Greek) 85-65AD Heliocentric Viewpoints • Aristarchus (Greek)310-230 BC • Copernicus (Poland and Italy) 1473-1543 • Galileo Galilei (Italian) 1564-1642 ...
... • Ptolemy (Alexandrian Greek) 85-65AD Heliocentric Viewpoints • Aristarchus (Greek)310-230 BC • Copernicus (Poland and Italy) 1473-1543 • Galileo Galilei (Italian) 1564-1642 ...
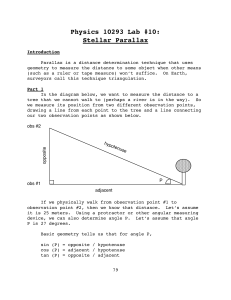
Lab #10 (Apr 10-13)
... study of the solar system and our galaxy. In the earlier Venus lab, we learned about the story of Captain Cook’s expedition to Tahiti. Part of his mission was to measure the timing of the transit of Venus across the Sun. While Cook was making his measurements, astronomers were also timing the transi ...
... study of the solar system and our galaxy. In the earlier Venus lab, we learned about the story of Captain Cook’s expedition to Tahiti. Part of his mission was to measure the timing of the transit of Venus across the Sun. While Cook was making his measurements, astronomers were also timing the transi ...
Chapter 17 PowerPoint
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
Chapter 17 Earth`s Cycles
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
Chapter 17 Earth`s Cycles
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
What is the sun?
... to the other side of its orbit. That part of the earth is now farther away from the sun and has it winter and the other part has its summer, Between wummer and winter, both halves of the earth are the same distance from the sun. Then they have spring and autumn. As the earth goes round in its orbit, ...
... to the other side of its orbit. That part of the earth is now farther away from the sun and has it winter and the other part has its summer, Between wummer and winter, both halves of the earth are the same distance from the sun. Then they have spring and autumn. As the earth goes round in its orbit, ...
Chapter 17 Earth`s Cycles
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
... see the Moon because it reflects sunlight off its surface. The Moon orbits around Earth in an elliptical orbit. It takes the Moon about 27.3 days to complete one revolution around Earth. Like Earth, the Moon rotates on its axis. As the Moon orbits Earth, the SAME SIDE of the Moon always faces Earth. ...
winter
... By an incredible coincidence, Polaris is almost directly over the North Pole. So it can be used to help us navigate. This is a temporary situation, however. Since the Earth is wobbling like a top, the pole slowly moves. This is called precession. ...
... By an incredible coincidence, Polaris is almost directly over the North Pole. So it can be used to help us navigate. This is a temporary situation, however. Since the Earth is wobbling like a top, the pole slowly moves. This is called precession. ...
doc - Discover Earth Science
... revolved eastward (counterclockwise) around the Sun b. it does explain what you see in the nighttime sky - it could be correct c. it DOES account for terrestrial motions and phenomenon like the Foucault Pendulum and the Coriolis effect d. it’s a much simpler model which explains more things D. The n ...
... revolved eastward (counterclockwise) around the Sun b. it does explain what you see in the nighttime sky - it could be correct c. it DOES account for terrestrial motions and phenomenon like the Foucault Pendulum and the Coriolis effect d. it’s a much simpler model which explains more things D. The n ...
Copernican heliocentrism

Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. It positioned the Sun near the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets rotating around it in circular paths modified by epicycles and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model departed from the Ptolemaic system that prevailed in Western culture for centuries, placing Earth at the center of the Universe, and is often regarded as the launching point to modern astronomy and the Scientific Revolution.Copernicus was aware that the ancient Greek Aristarchus had already proposed a heliocentric theory, and cited him as a proponent of it in a reference that was deleted before publication, but there is no evidence that Copernicus had knowledge of, or access to, the specific details of Aristarchus' theory. Although he had circulated an outline of his own heliocentric theory to colleagues sometime before 1514, he did not decide to publish it until he was urged to do so late in his life by his pupil Rheticus. Copernicus's challenge was to present a practical alternative to the Ptolemaic model by more elegantly and accurately determining the length of a solar year while preserving the metaphysical implications of a mathematically ordered cosmos. Thus his heliocentric model retained several of the Ptolemaic elements causing the inaccuracies, such as the planets' circular orbits, epicycles, and uniform speeds, while at the same time re-introducing such innovations as,Earth is one of several planets revolving around a stationary Sun in a determined orderEarth has three motions: daily rotation, annual revolution, and annual tilting of its axisRetrograde motion of the planets is explained by Earth's motionDistance from Earth to the Sun is small compared to the distance to the stars.↑ 1.0 1.1 ↑