The Outer Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars How are the
... 2. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? For each characteristic, explain or describe the possible options in each category. For example: Size of stars – what are the difference sizes, how are stars measured, what star examples fall into each category? ...
... 2. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? For each characteristic, explain or describe the possible options in each category. For example: Size of stars – what are the difference sizes, how are stars measured, what star examples fall into each category? ...
ISP205 Spring 2001 Exam #1 Study Guide
... Know the difference between Geocentric - Earth centered - and Heliocentric - Sun centered models of the solar system. Ptolemy devised a successful Earth centered model based on circles and epicycles. Why was the Ptolemy’s system accepted? It worked pretty well. Contributions of Galileo: Sun spots, M ...
... Know the difference between Geocentric - Earth centered - and Heliocentric - Sun centered models of the solar system. Ptolemy devised a successful Earth centered model based on circles and epicycles. Why was the Ptolemy’s system accepted? It worked pretty well. Contributions of Galileo: Sun spots, M ...
Origin of the Solar System – Notes Rings encircle Jupiter, Saturn
... Moon), Mars has two, Jupiter has at least 63, Saturn at least 61, Uranus at least 27, and Neptune at least 13. Like the terrestrial planets, all of the moons of the planets have solid surfaces. In addition to the eight planets, many smaller objects orbit the Sun. Asteroids and meteoroids are rocky o ...
... Moon), Mars has two, Jupiter has at least 63, Saturn at least 61, Uranus at least 27, and Neptune at least 13. Like the terrestrial planets, all of the moons of the planets have solid surfaces. In addition to the eight planets, many smaller objects orbit the Sun. Asteroids and meteoroids are rocky o ...
TOP 78 ASTRONOMY FACTS 1. The solar system consists of the
... 39. A complete cycle of moon phases takes about 29.5 days to complete. 40. During the first quarter phase and the third quarter phase, we see half of the moon’s lighted side. 41. Summers are hotter because there are longer days and more direct sun rays. 42. During the new moon, the side of the moon ...
... 39. A complete cycle of moon phases takes about 29.5 days to complete. 40. During the first quarter phase and the third quarter phase, we see half of the moon’s lighted side. 41. Summers are hotter because there are longer days and more direct sun rays. 42. During the new moon, the side of the moon ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... 28. At the time of Galileo and Kepler, which of the following observations was the strongest evidence for a heliocentric model of the solar system? (a) The moons of Jupiter. (b) Stellar parallax. (c) The sunspots. (d) The gibbous and the quarter phases of Venus. 29. The ancient Greek astronomer who ...
... 28. At the time of Galileo and Kepler, which of the following observations was the strongest evidence for a heliocentric model of the solar system? (a) The moons of Jupiter. (b) Stellar parallax. (c) The sunspots. (d) The gibbous and the quarter phases of Venus. 29. The ancient Greek astronomer who ...
Astronomical Imaging: Overview
... – decrease of 5 magnitudes from one star to another star increase in brightness by factor 100 – decrease of 2.5 magnitudes from one star to another increase in brightness by factor 10 ...
... – decrease of 5 magnitudes from one star to another star increase in brightness by factor 100 – decrease of 2.5 magnitudes from one star to another increase in brightness by factor 10 ...
Gestalting Structures in Physics
... celestial objects. Ptolemy’s Almagest (Ptolemy c. 85-165 AD, 3,4) remained the main work and authority in astronomy for more than one thousand years. Copernicus’s work in the 16th century combined metaphysical conception and the empirical understanding of celestial motions. In the preface of his De ...
... celestial objects. Ptolemy’s Almagest (Ptolemy c. 85-165 AD, 3,4) remained the main work and authority in astronomy for more than one thousand years. Copernicus’s work in the 16th century combined metaphysical conception and the empirical understanding of celestial motions. In the preface of his De ...
Observation & Inference - East Hanover Schools Online
... which planets are the gas planets? What are three of their primary differences? The terrestrial planets are made of rock, smaller, closer together, do not have rings, and are closer to the sun. ...
... which planets are the gas planets? What are three of their primary differences? The terrestrial planets are made of rock, smaller, closer together, do not have rings, and are closer to the sun. ...
Lookback Time in Our Everyday Lives
... We use the Astronomical Unit as our unit of length for measuring distances in the Solar System. However, because stellar distances are so large, astronomers use another unit of length, the light-year (ly). The light-year is defined as the distance light travels in one year, 9.46 trillion kilometers ...
... We use the Astronomical Unit as our unit of length for measuring distances in the Solar System. However, because stellar distances are so large, astronomers use another unit of length, the light-year (ly). The light-year is defined as the distance light travels in one year, 9.46 trillion kilometers ...
Perfect Little Planet
... distances between planets in the Solar System. The first activity requires a large outdoor space (1030 yards) while the second activity can be accomplished in less space (37 yards). The first activity, “The Thousand and Thirty-Yard Solar System,” requires a large area but is preferable to the second ...
... distances between planets in the Solar System. The first activity requires a large outdoor space (1030 yards) while the second activity can be accomplished in less space (37 yards). The first activity, “The Thousand and Thirty-Yard Solar System,” requires a large area but is preferable to the second ...
Can we prove God Exists? Part 1 How can modern science help us
... During the last decade cosmology/astronomy has become increasingly friendly to the Creator model. Discoveries about the origin of the Big Bang as well as the requirements for life on a planet like earth reveal more and more the hand of a Creator and make it less and less likely this could all have h ...
... During the last decade cosmology/astronomy has become increasingly friendly to the Creator model. Discoveries about the origin of the Big Bang as well as the requirements for life on a planet like earth reveal more and more the hand of a Creator and make it less and less likely this could all have h ...
Planetary Diversity - MIT Computer Science and Artificial
... This question must be asked, even if only to explain why it is unimportant. Planetary scientists study what is in orbit around stars but not doing what a star does (or used to do in an earlier life), which is fusion. All scientific labeling is secondary to the essenceof science, and labels such as " ...
... This question must be asked, even if only to explain why it is unimportant. Planetary scientists study what is in orbit around stars but not doing what a star does (or used to do in an earlier life), which is fusion. All scientific labeling is secondary to the essenceof science, and labels such as " ...
Powers of ten notation
... If the Sun formed from a single spherical rotating cloud, wouldn’t you expect that all the pieces would have the same angular momentum as the original cloud? How must the solar system have changed since the time of its formation that this is no longer the case? ...
... If the Sun formed from a single spherical rotating cloud, wouldn’t you expect that all the pieces would have the same angular momentum as the original cloud? How must the solar system have changed since the time of its formation that this is no longer the case? ...
Here
... 1) The length of the daylight hours at a given spot varies throughout the year: the Sun is out a longer time when it is warmer (i.e. summer), and out a shorter time when it is colder. 2) On a given day, the length of the daylight hours depends on where you are on Earth, in particular it depends on y ...
... 1) The length of the daylight hours at a given spot varies throughout the year: the Sun is out a longer time when it is warmer (i.e. summer), and out a shorter time when it is colder. 2) On a given day, the length of the daylight hours depends on where you are on Earth, in particular it depends on y ...
Reasons for the Seasons Webquest
... TRUTH: Most people believe this statement to be true. The seasons are caused in reality by the 23.5o tilt of the Earth’s axis and the axis always pointing in the same direction. During the course of a year, this one phenomenon changes the duration of time in which the sun is visible in the sky, the ...
... TRUTH: Most people believe this statement to be true. The seasons are caused in reality by the 23.5o tilt of the Earth’s axis and the axis always pointing in the same direction. During the course of a year, this one phenomenon changes the duration of time in which the sun is visible in the sky, the ...
Earth Science Chap.2 Sect. 2
... Precession: a circular motion of the earth’s axis which causes the change relative to distant stars. Caused by forces acting on a spinning body. In the earth’s case, it is the gravitational pull exerted by the moon, sun, and other planets. Causes the earth’s axis to move slowly in a circle. This cir ...
... Precession: a circular motion of the earth’s axis which causes the change relative to distant stars. Caused by forces acting on a spinning body. In the earth’s case, it is the gravitational pull exerted by the moon, sun, and other planets. Causes the earth’s axis to move slowly in a circle. This cir ...
Planetary Cycles
... cycle in the sky with reference to the Sun is called its synodical period, a motion which takes a little over 29 days to complete. With reference to the Earth or a fixed star, the Moon finishes the cycle in about 28 days. This is its sidereal period. An interesting cycle to study is the Lunar or Met ...
... cycle in the sky with reference to the Sun is called its synodical period, a motion which takes a little over 29 days to complete. With reference to the Earth or a fixed star, the Moon finishes the cycle in about 28 days. This is its sidereal period. An interesting cycle to study is the Lunar or Met ...
3D depictions of effect of earth rotation on apparent
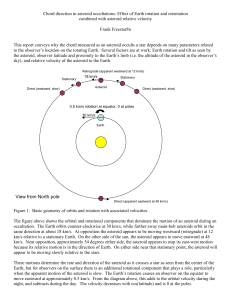
... The figure above shows the orbital and rotational components that dominate the motion of an asteroid during an occultation. The Earth orbits counter-clockwise at 30 km/s, while farther away main-belt asteroids orbit in the same direction at about 18 km/s. At opposition the asteroid appears to be mov ...
... The figure above shows the orbital and rotational components that dominate the motion of an asteroid during an occultation. The Earth orbits counter-clockwise at 30 km/s, while farther away main-belt asteroids orbit in the same direction at about 18 km/s. At opposition the asteroid appears to be mov ...
Theme 5: The Rise of the Telescope:
... turbulence inherent in making observations towards the Sun. Meanwhile, the discovery of aberration by Bradley in 1728 (see below) offered an entirely independent method of measuring distances. The amount of aberration is given by v/c, where v is the Earth’s orbital velocity. Initially this was seen ...
... turbulence inherent in making observations towards the Sun. Meanwhile, the discovery of aberration by Bradley in 1728 (see below) offered an entirely independent method of measuring distances. The amount of aberration is given by v/c, where v is the Earth’s orbital velocity. Initially this was seen ...
Chapter 2
... keeping the planets in orbit around the Sun is the gravitational force due to the masses of the planet and Sun. This allows us to calculate the mass of the Sun, knowing the orbit of the Earth: ...
... keeping the planets in orbit around the Sun is the gravitational force due to the masses of the planet and Sun. This allows us to calculate the mass of the Sun, knowing the orbit of the Earth: ...
Galileo and the physics of motion
... • Study orbital periods ! get masses - planets around Sun ! Sun’s mass - Jupiter’s moons around Jupiter ! Jupiter’s mass • Also used for stars (more on this later) - two nearby stars orbiting each other ! their masses - an exoplanet orbiting a star will cause the star to wobble a bit ! can give ma ...
... • Study orbital periods ! get masses - planets around Sun ! Sun’s mass - Jupiter’s moons around Jupiter ! Jupiter’s mass • Also used for stars (more on this later) - two nearby stars orbiting each other ! their masses - an exoplanet orbiting a star will cause the star to wobble a bit ! can give ma ...
here.
... 21) Which of the following best describes why we have seasons on Earth? A) Earth's elliptical orbit means we are closer to the Sun and therefore receive more intense sunlight at some times of year than at others. B) The varying speed of Earth in its orbit around the Sun gives us summer when we are m ...
... 21) Which of the following best describes why we have seasons on Earth? A) Earth's elliptical orbit means we are closer to the Sun and therefore receive more intense sunlight at some times of year than at others. B) The varying speed of Earth in its orbit around the Sun gives us summer when we are m ...
Seasons
... C. The actual backwards motion of some planets orbiting the Sun D. The moon’s motion relative to the stars, not the Sun E. A secret play the 49ers will use in the Superbowl ...
... C. The actual backwards motion of some planets orbiting the Sun D. The moon’s motion relative to the stars, not the Sun E. A secret play the 49ers will use in the Superbowl ...
More on Stars and the Sky
... objects appear stationary. Why? What is the typical parallax of a nearby star? Why is it not possible to measure the parallax better than 0.01” from ground based instruments, but can be done from space? What is the precession of the Earth. Which of the following would change due to precession celest ...
... objects appear stationary. Why? What is the typical parallax of a nearby star? Why is it not possible to measure the parallax better than 0.01” from ground based instruments, but can be done from space? What is the precession of the Earth. Which of the following would change due to precession celest ...
ANelsonTalk1
... These were believed to be the most holy of stars In order for the deceased to be reincarnated, they had to reach this destination from their place of burial. Elaborate ceremonies were held called Pedj Shes or the “stretching of the cord” before each pyramid was built ...
... These were believed to be the most holy of stars In order for the deceased to be reincarnated, they had to reach this destination from their place of burial. Elaborate ceremonies were held called Pedj Shes or the “stretching of the cord” before each pyramid was built ...
Copernican heliocentrism

Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. It positioned the Sun near the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets rotating around it in circular paths modified by epicycles and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model departed from the Ptolemaic system that prevailed in Western culture for centuries, placing Earth at the center of the Universe, and is often regarded as the launching point to modern astronomy and the Scientific Revolution.Copernicus was aware that the ancient Greek Aristarchus had already proposed a heliocentric theory, and cited him as a proponent of it in a reference that was deleted before publication, but there is no evidence that Copernicus had knowledge of, or access to, the specific details of Aristarchus' theory. Although he had circulated an outline of his own heliocentric theory to colleagues sometime before 1514, he did not decide to publish it until he was urged to do so late in his life by his pupil Rheticus. Copernicus's challenge was to present a practical alternative to the Ptolemaic model by more elegantly and accurately determining the length of a solar year while preserving the metaphysical implications of a mathematically ordered cosmos. Thus his heliocentric model retained several of the Ptolemaic elements causing the inaccuracies, such as the planets' circular orbits, epicycles, and uniform speeds, while at the same time re-introducing such innovations as,Earth is one of several planets revolving around a stationary Sun in a determined orderEarth has three motions: daily rotation, annual revolution, and annual tilting of its axisRetrograde motion of the planets is explained by Earth's motionDistance from Earth to the Sun is small compared to the distance to the stars.↑ 1.0 1.1 ↑